ORIENTAL AND PALEARCTIC REGIONS
[Europe invasive]
Etymology: Korea
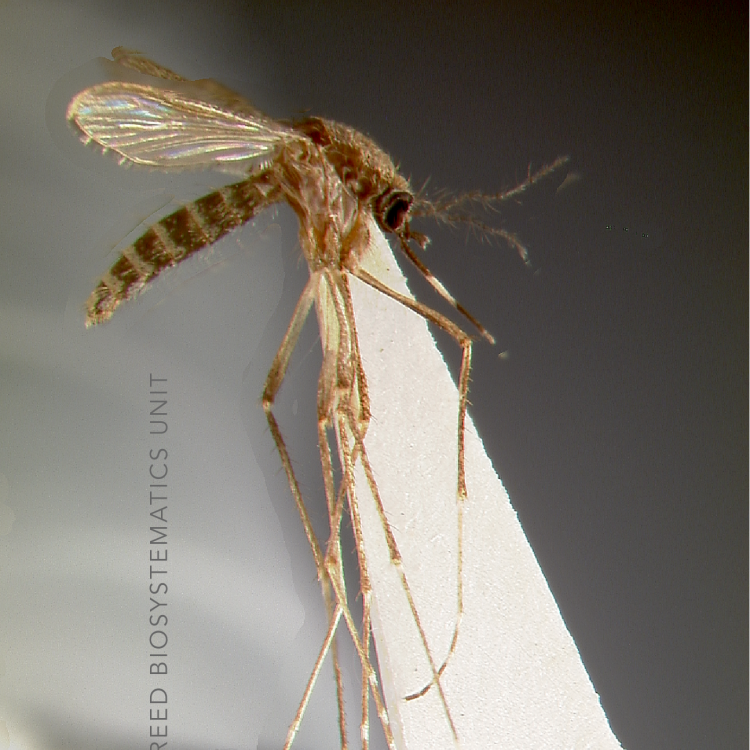
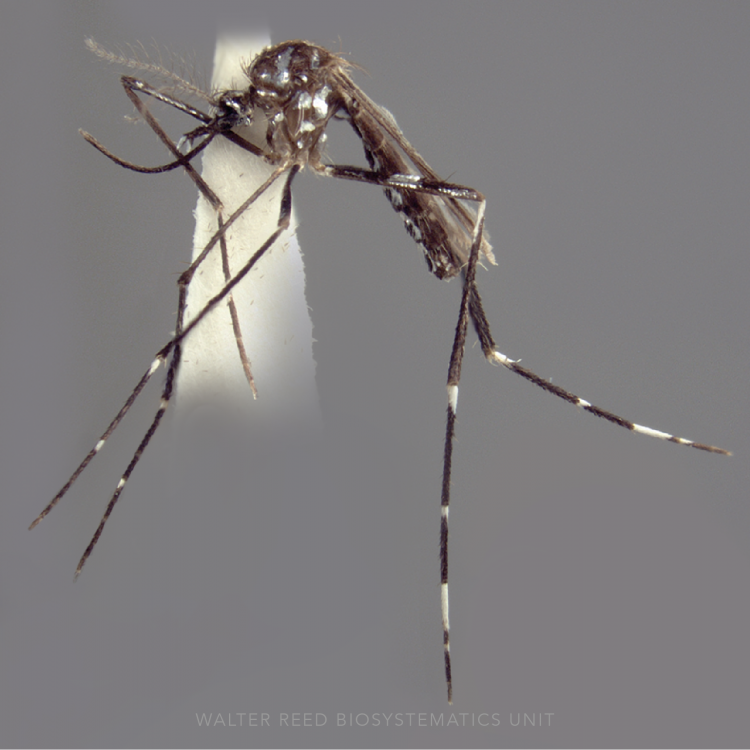
Aedes koreicus belongs to the recently re-established Aedes subgenus Hulecoeteomyia (originally described as a genus and previously recognized as the Chrysolineatus Subgroup of genus Aedes). Species within the genus are best identified on a combination of larval and adult characters, as male genitalia and pupal stages lack species diagnostic characters. Aedes koreicus was described from specimens collected in South Korea and is native to north-east China, Russia, the Korean peninsula, and Japan. In 2008, Ae. koreicus was discovered out of its range as an established population in an industrial area of Belgium, and later detected in Italy in 2011 and then Switzerland. Predictive models show that the climatic and environmental characteristics of most of northern Europe would support the establishment of this species. Aedes koreicus has no synonyms, or subspecies, but a morphological variant is reported from the southern Korean island of Jeju-do which bears a basal hind band on the Ta-III5. It is the Jeju-do morphotype that has invaded Europe.
Type locality: Korea
Type depository: Natural History Museum, London, England, United Kingdom (NHMUK)
DIAGNOSTIC CHARACTERS (Click photos to view; mouse over and click large photo to zoom in.)
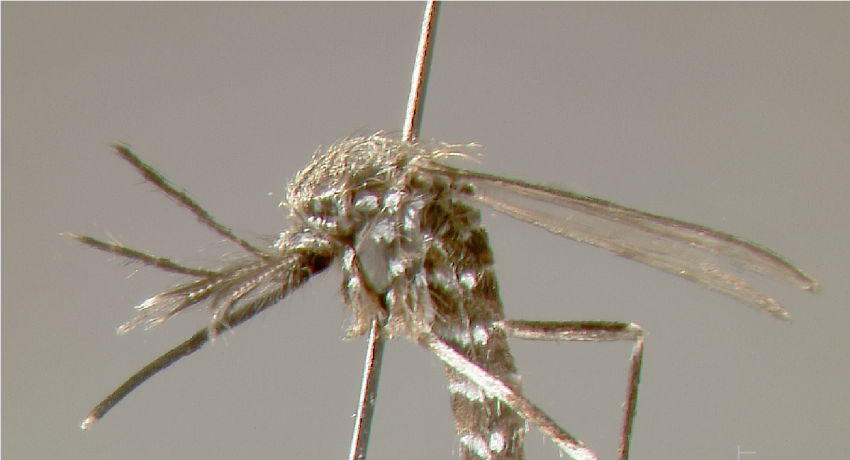
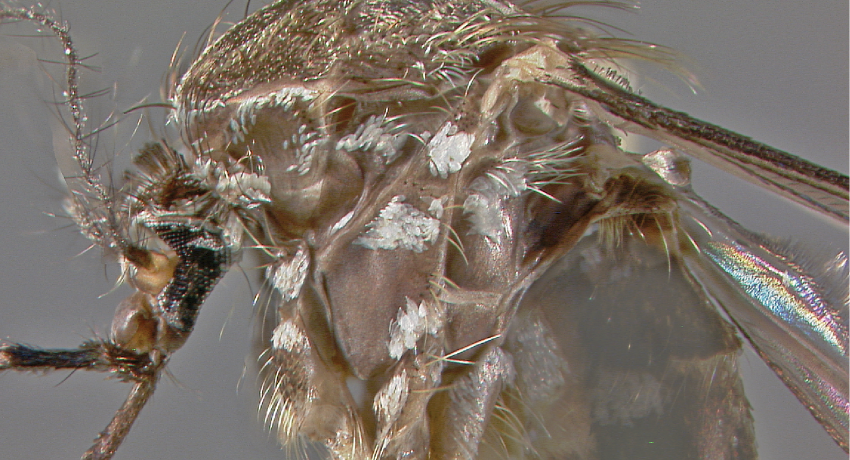
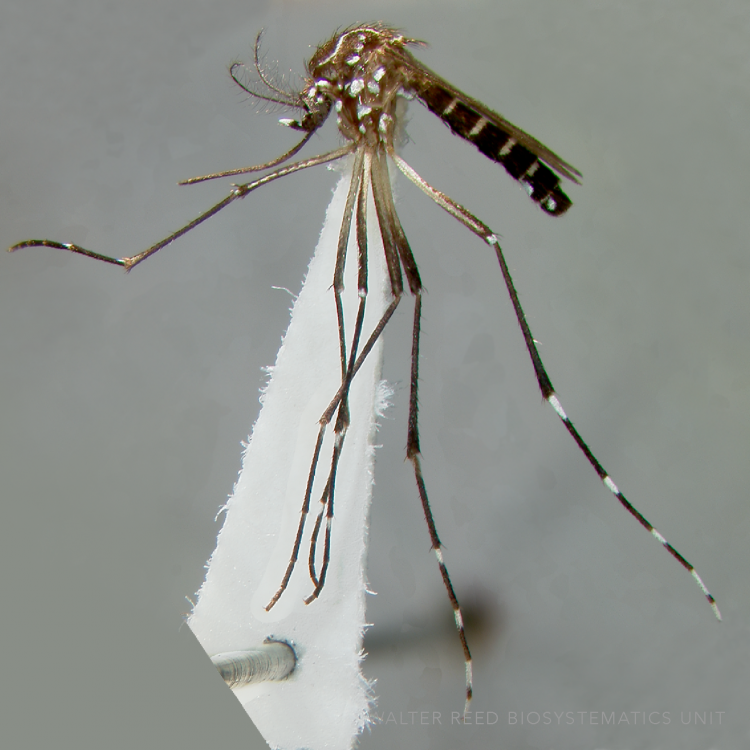
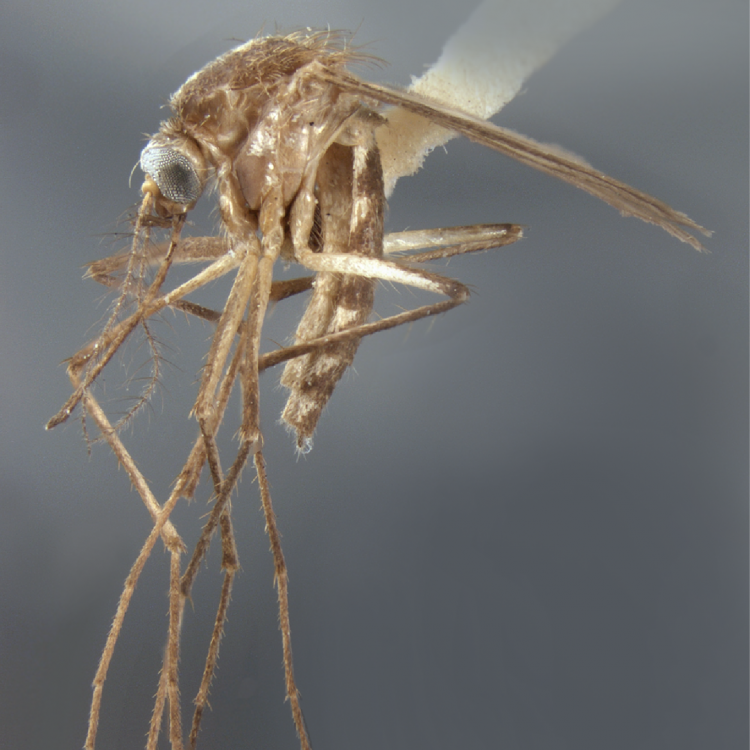
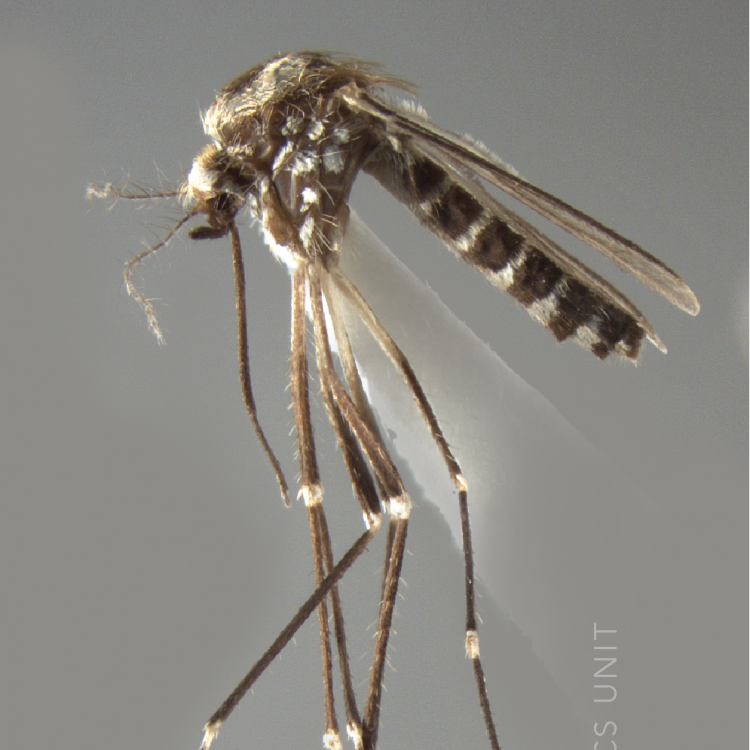
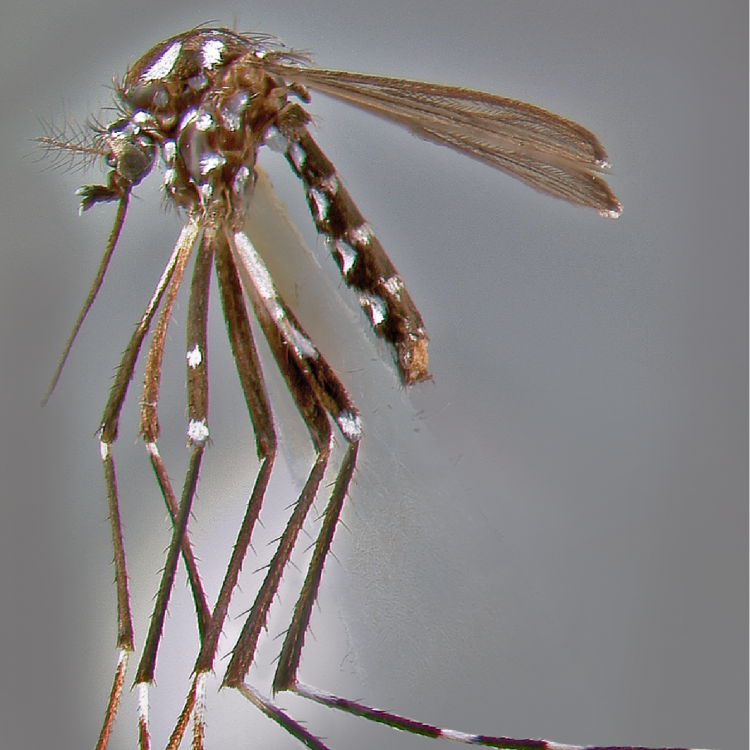
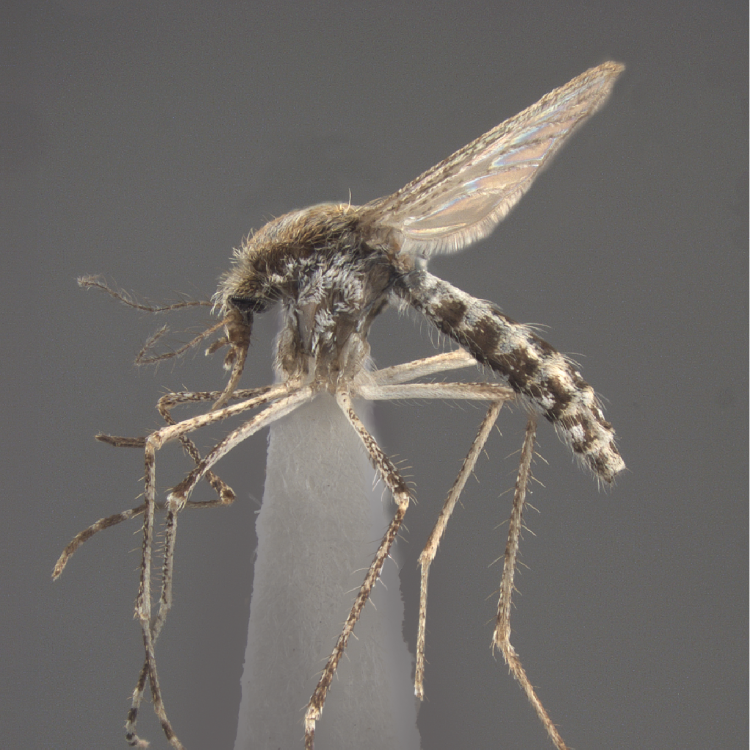
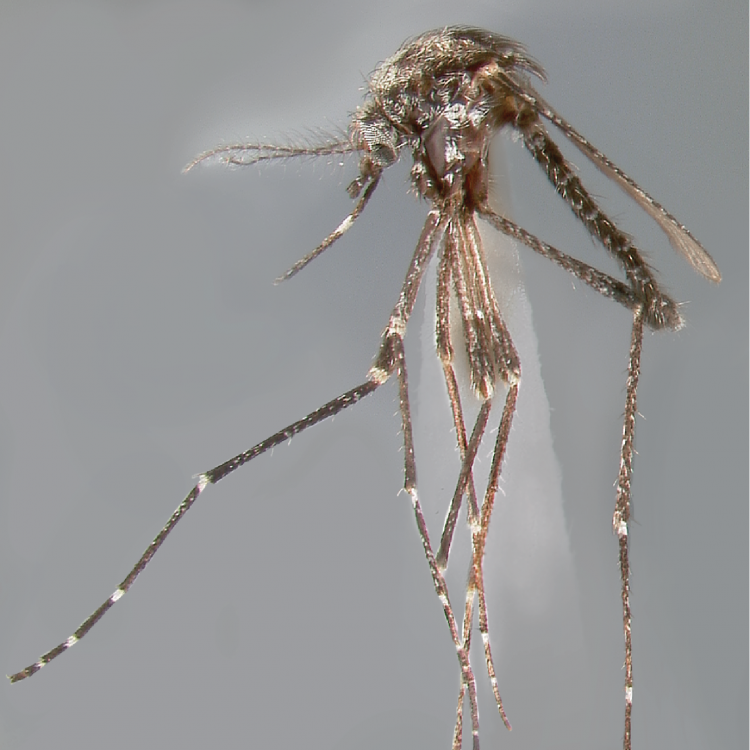
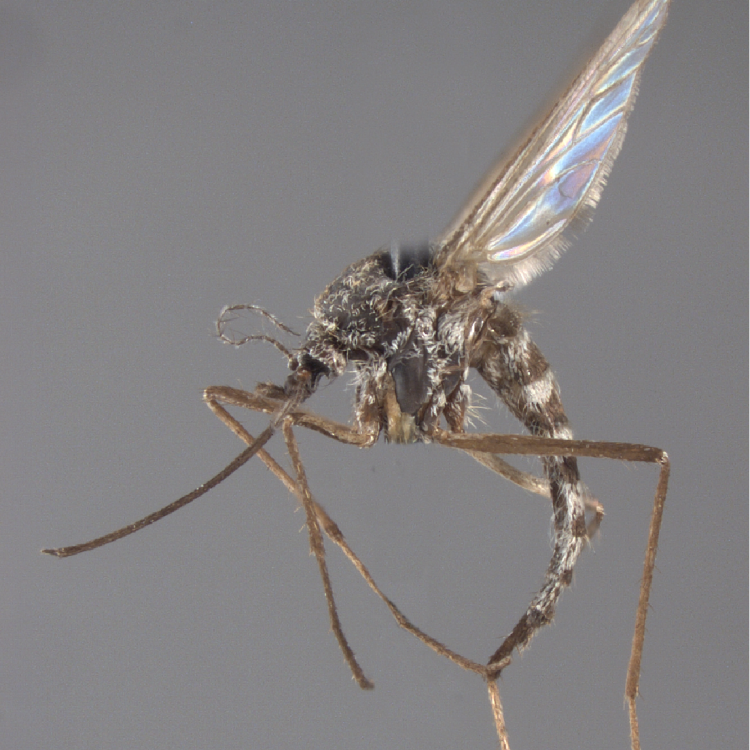
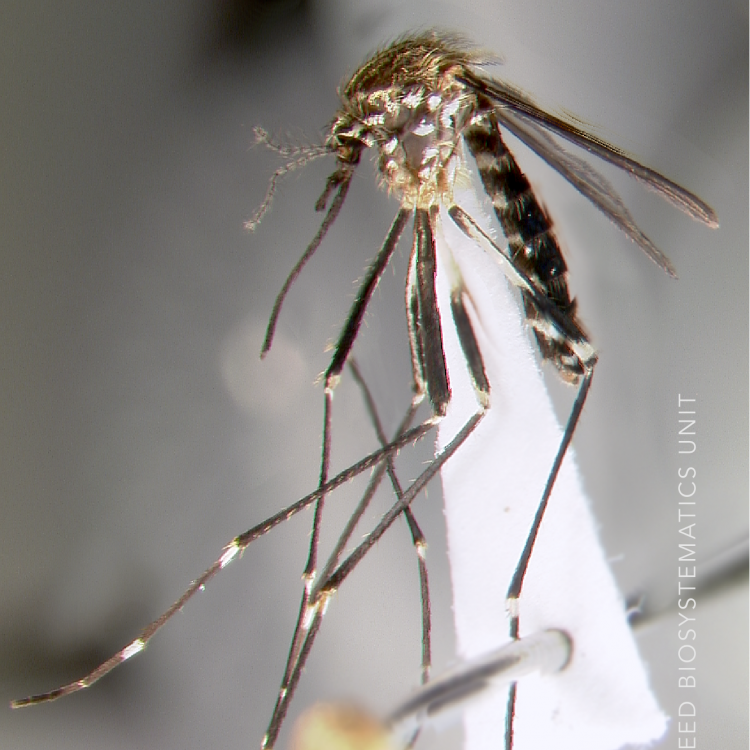
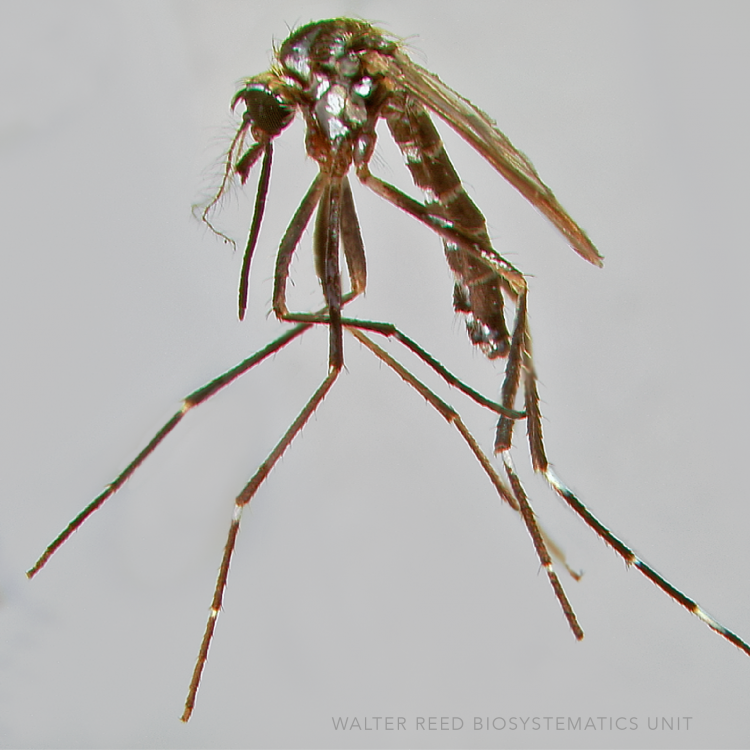
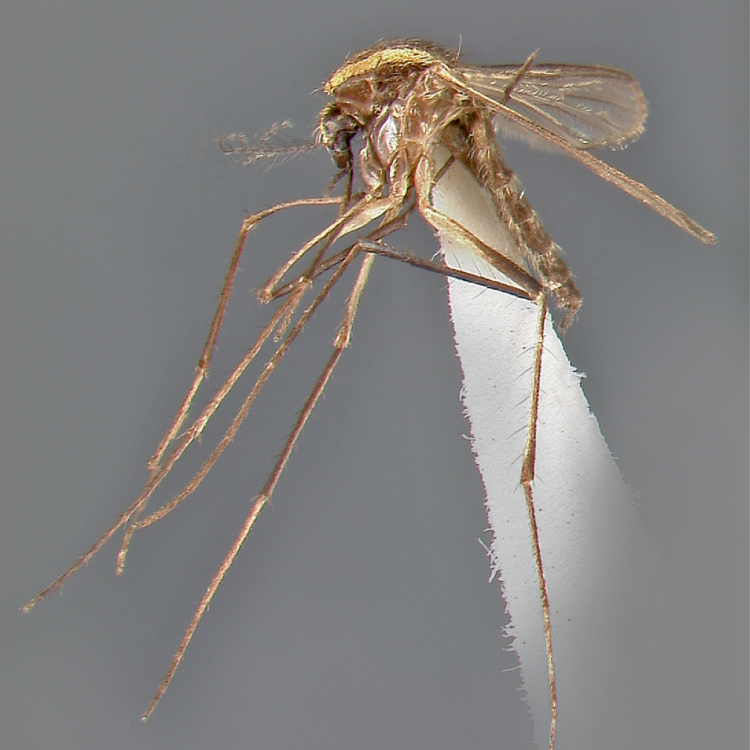
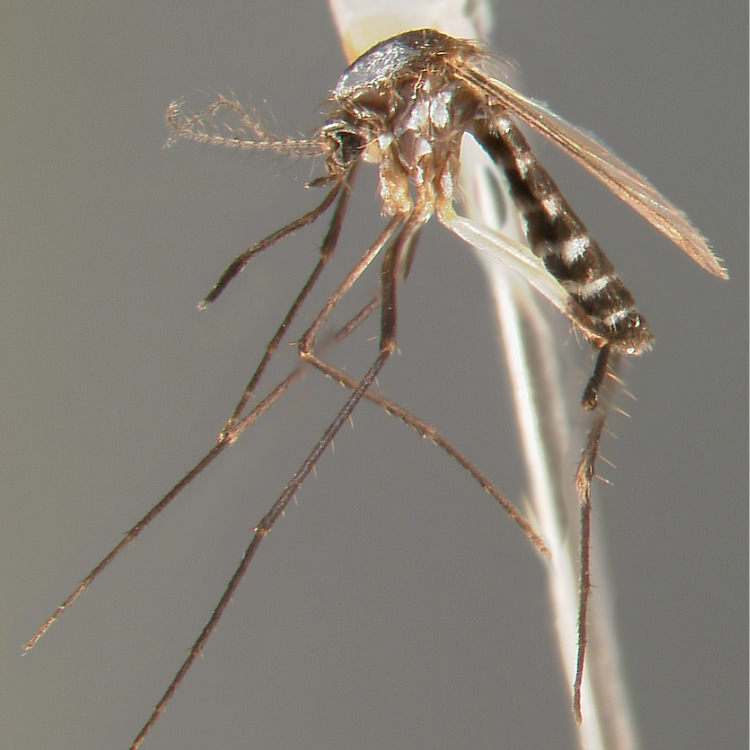
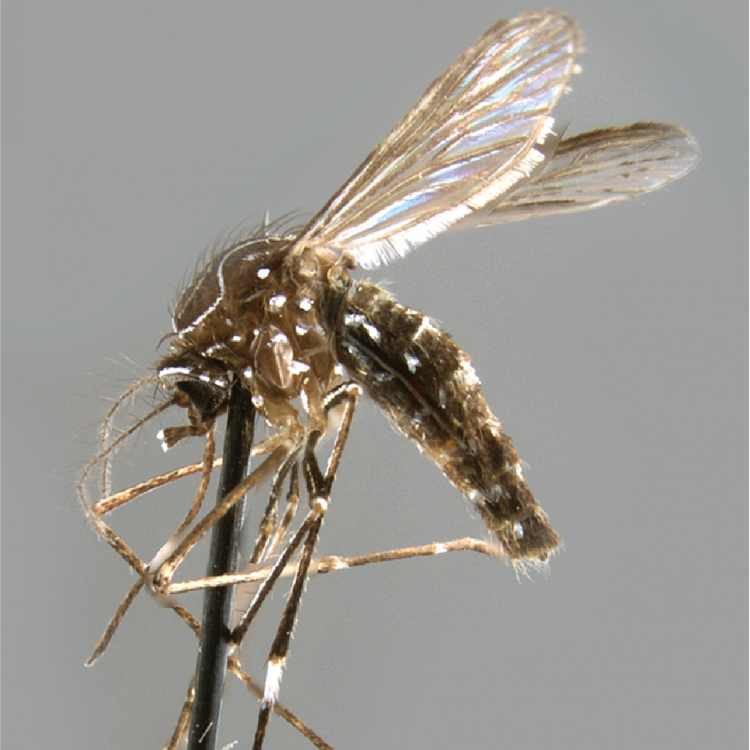
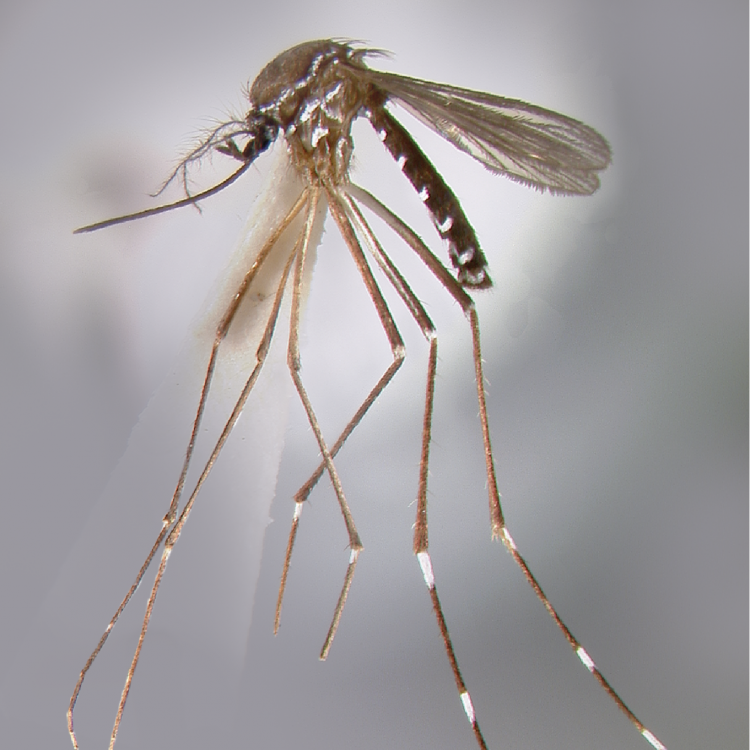
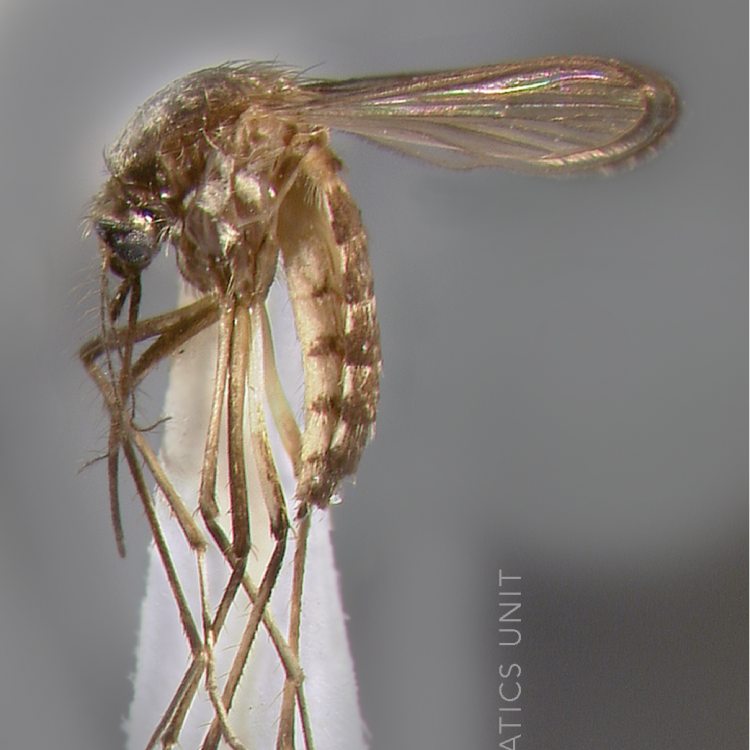
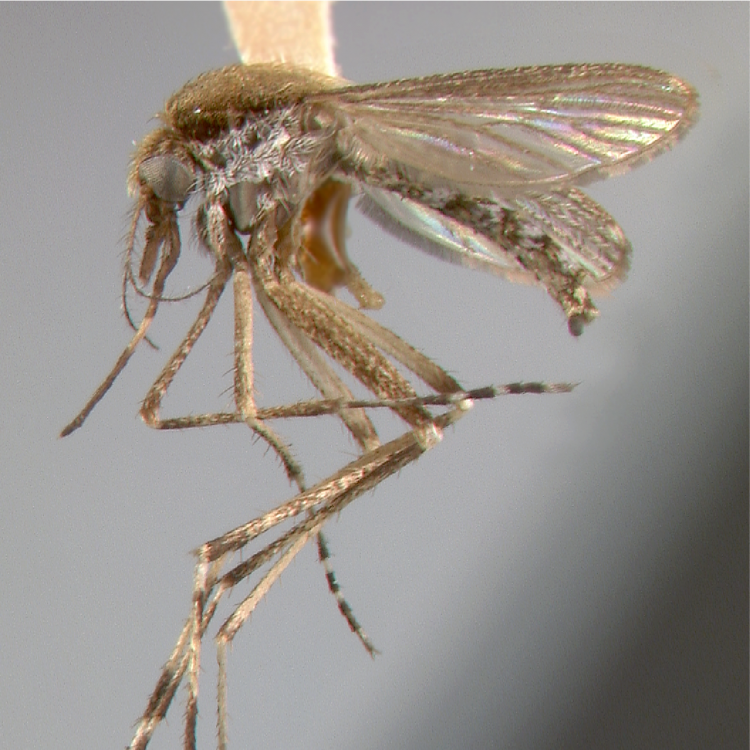
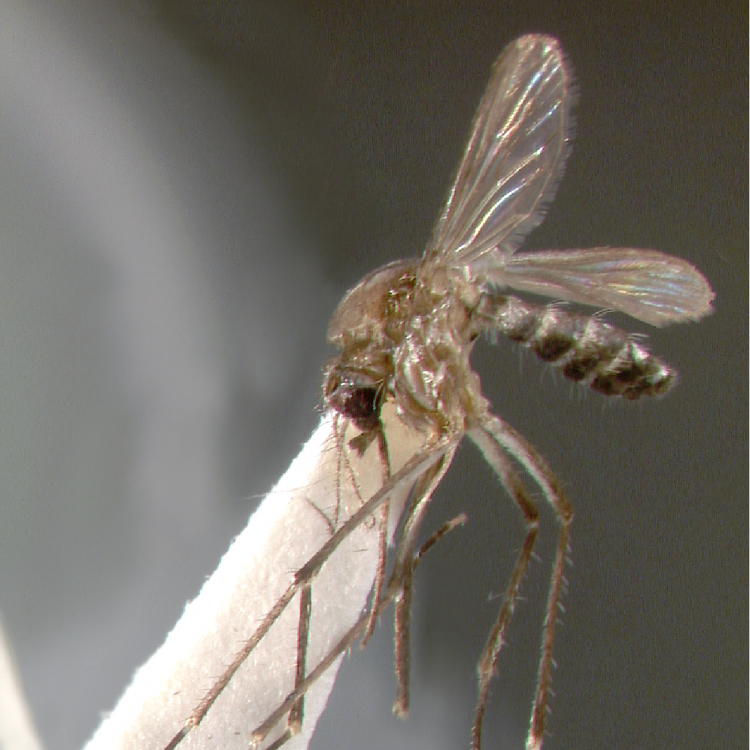
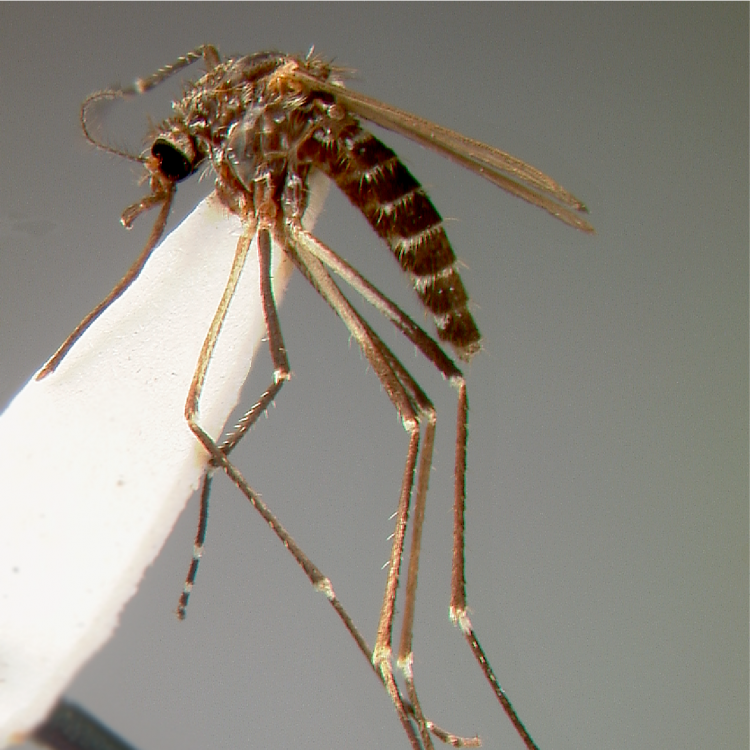
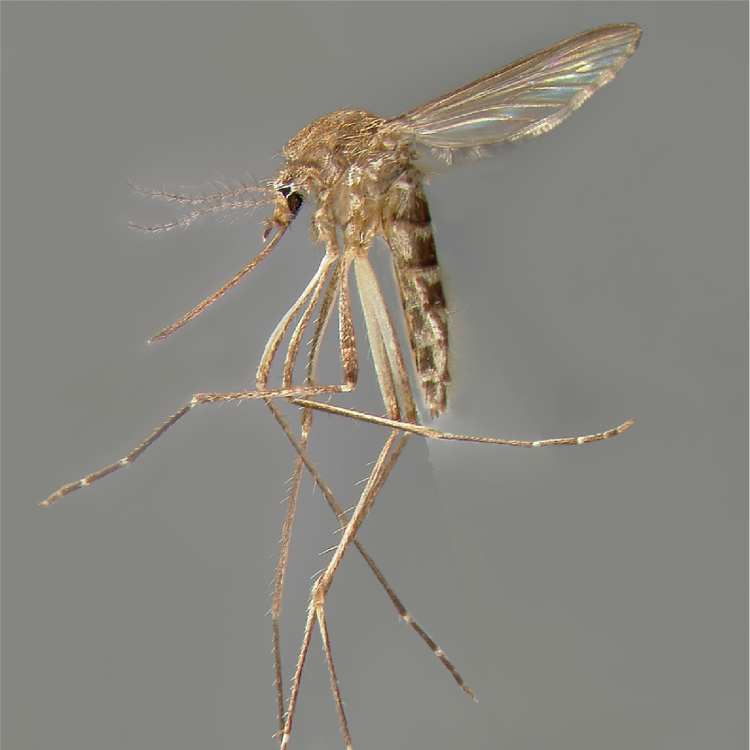
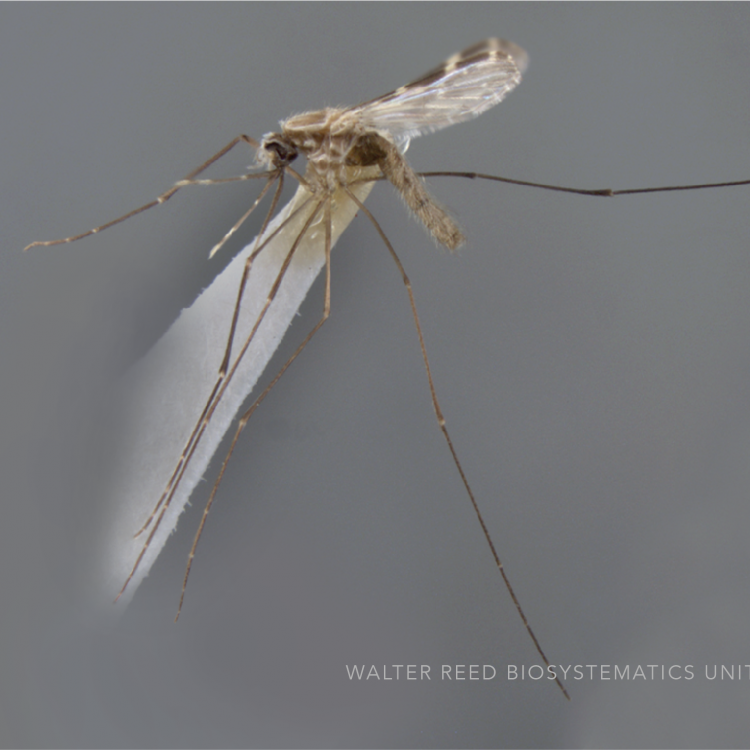
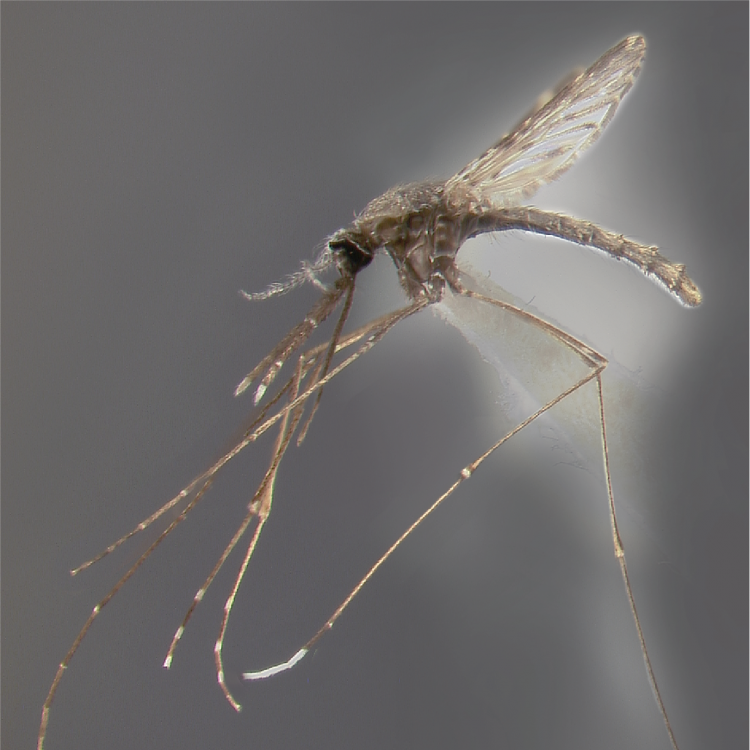
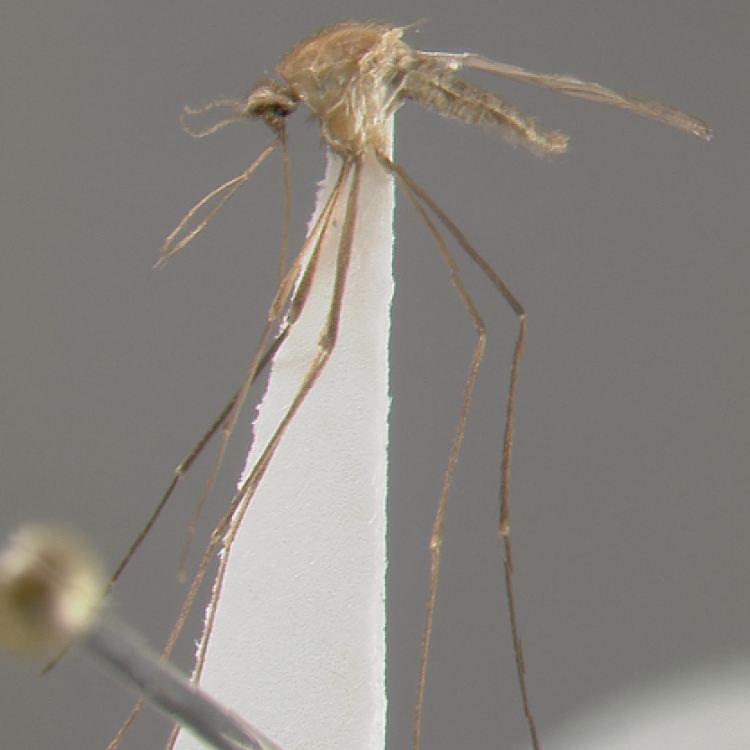
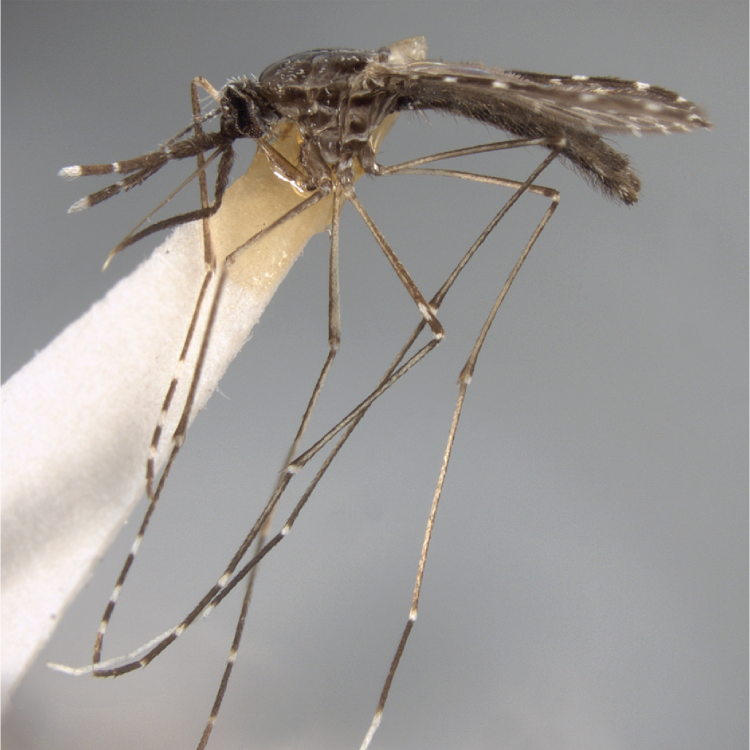
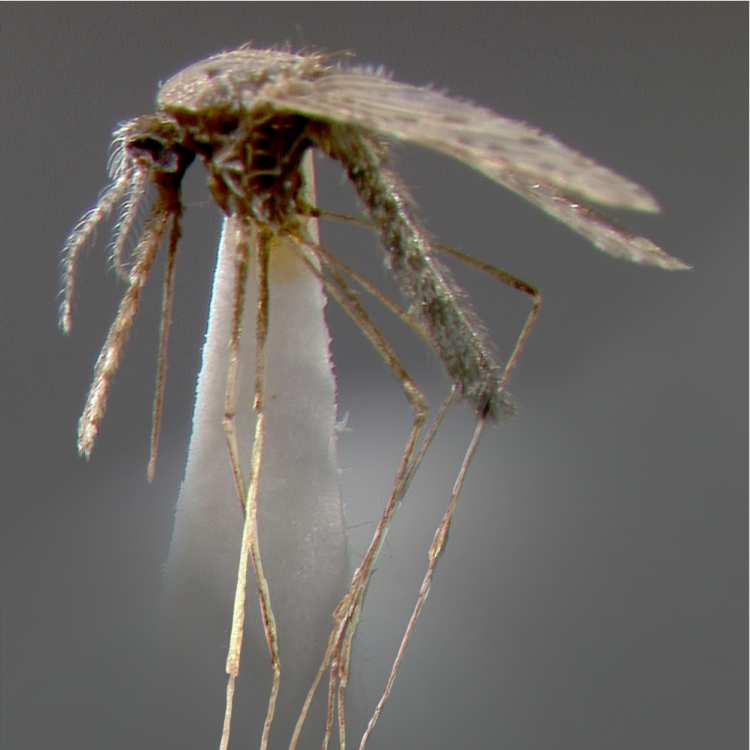
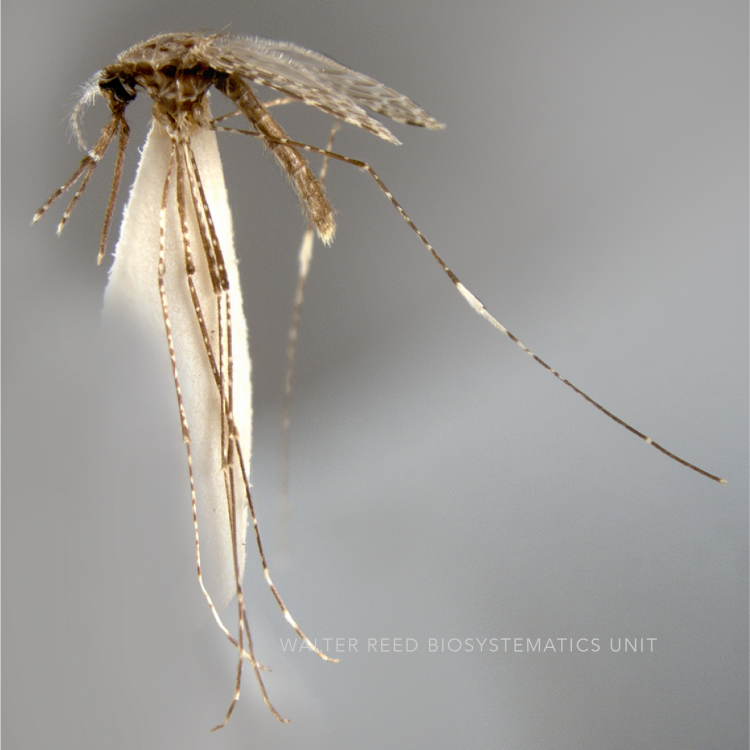
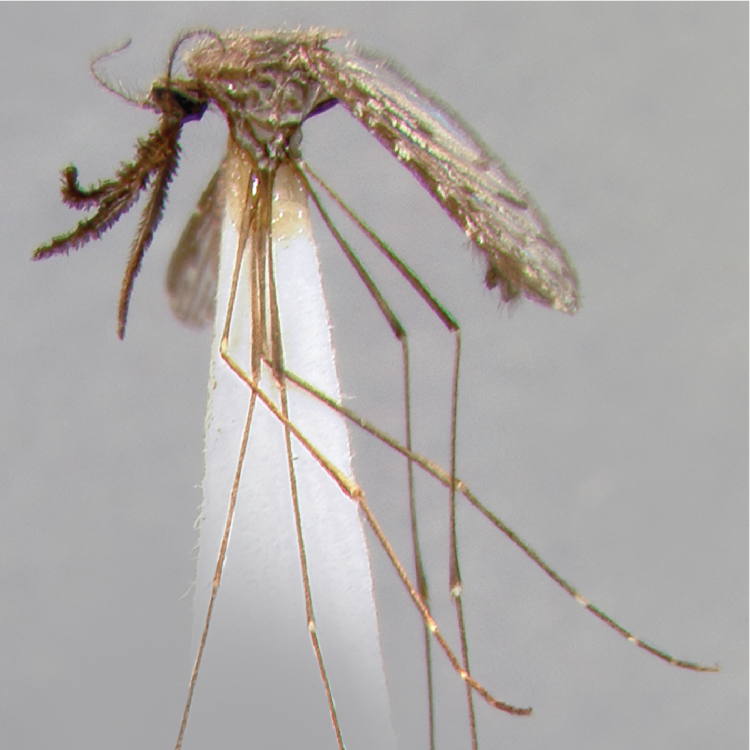
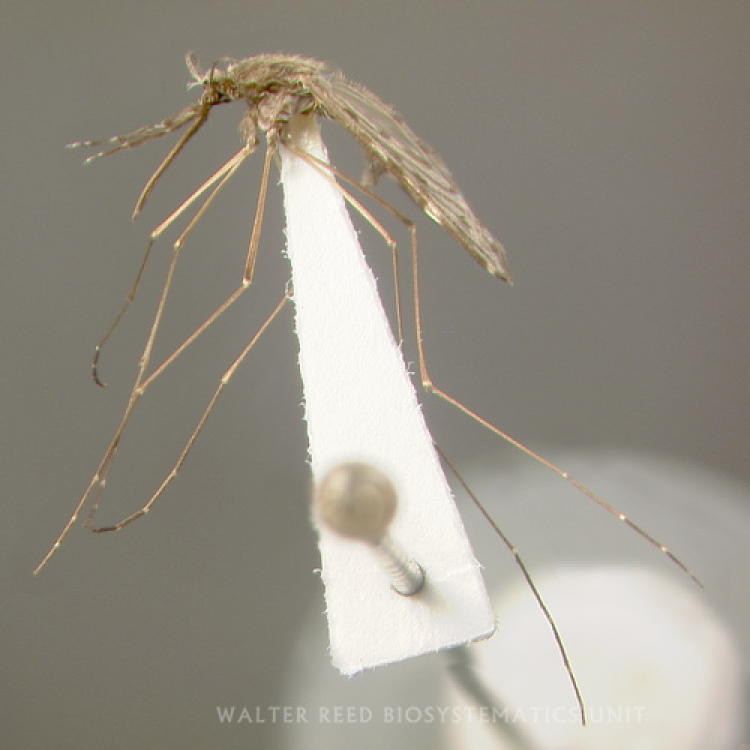
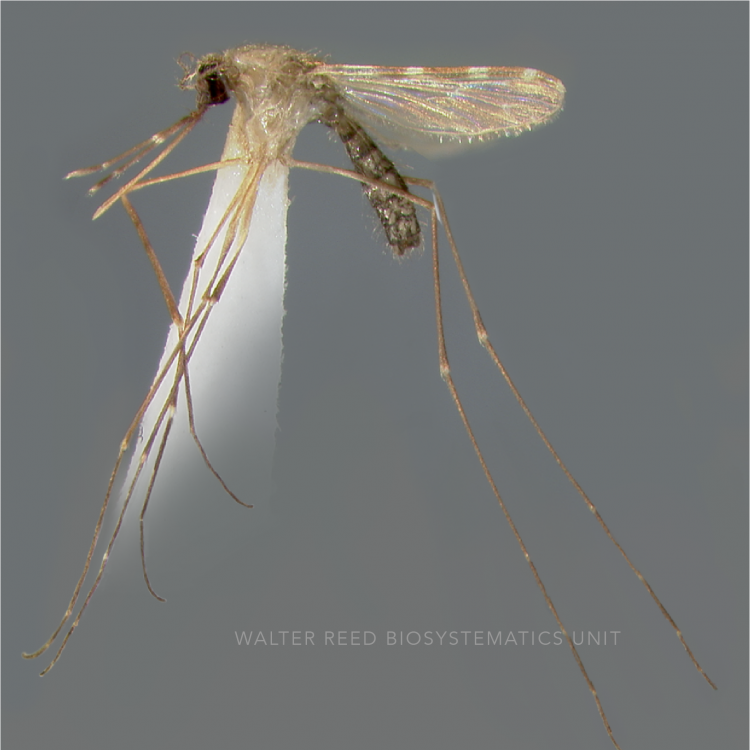
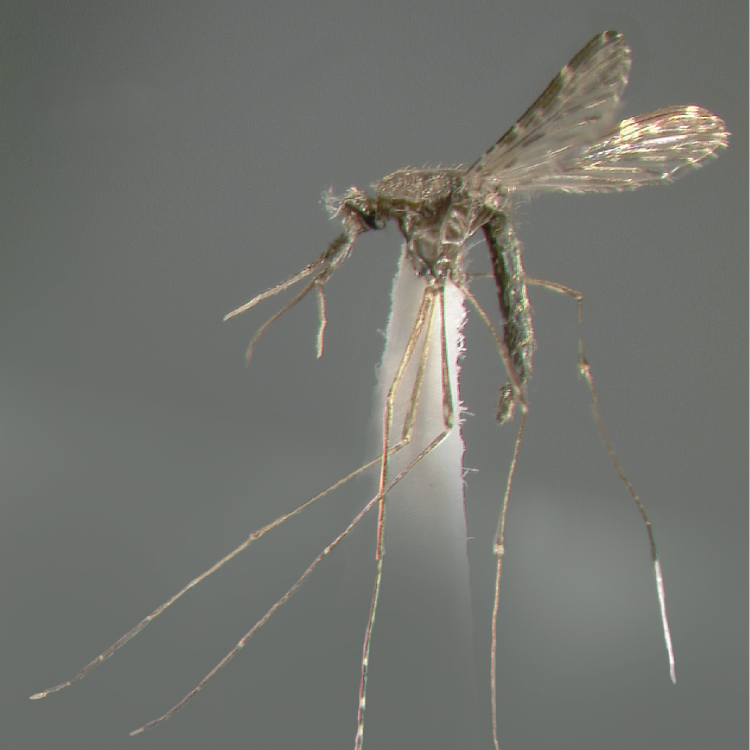
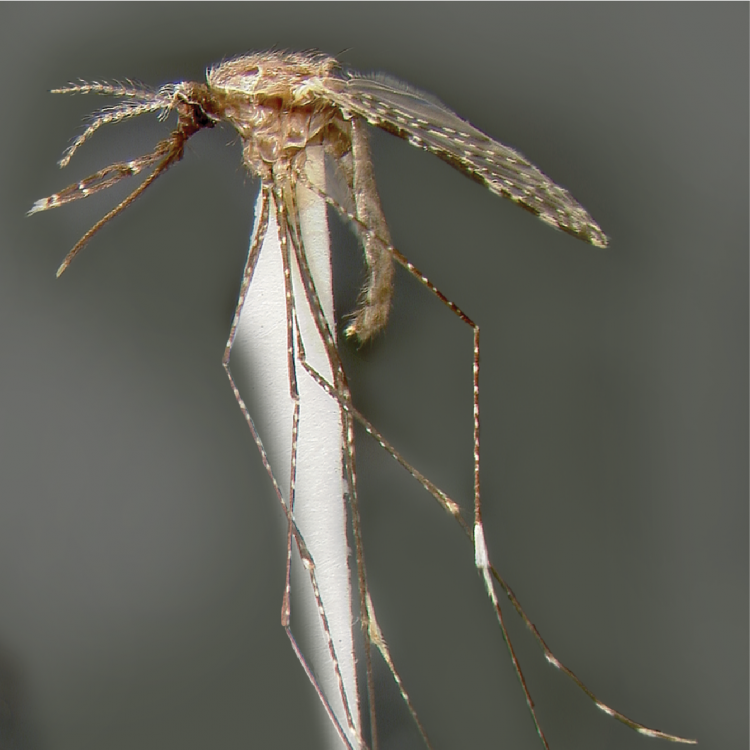
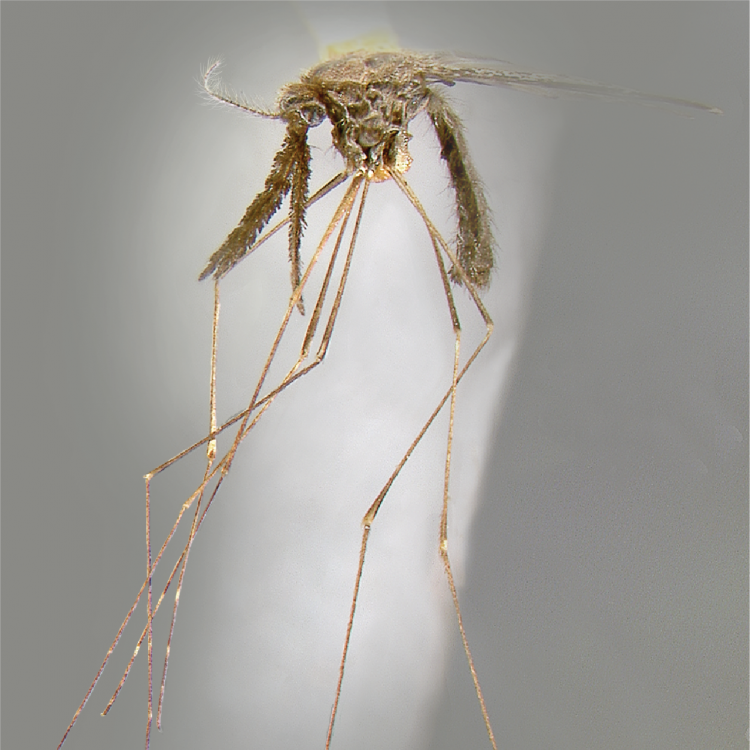
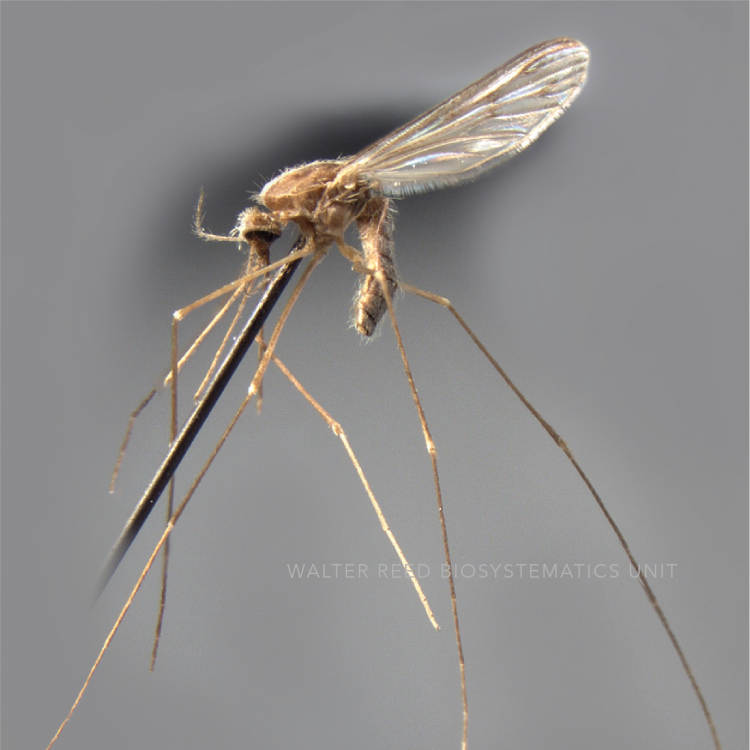
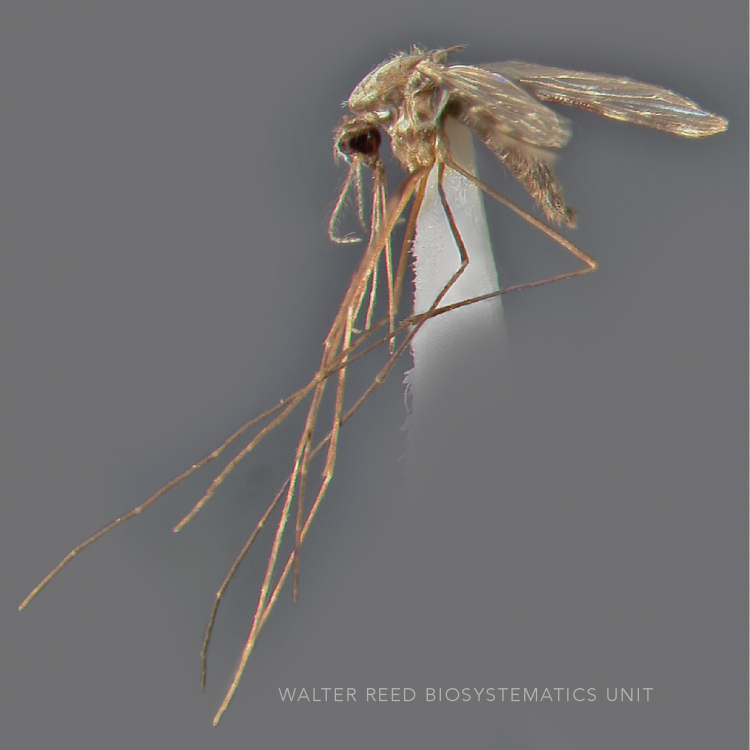
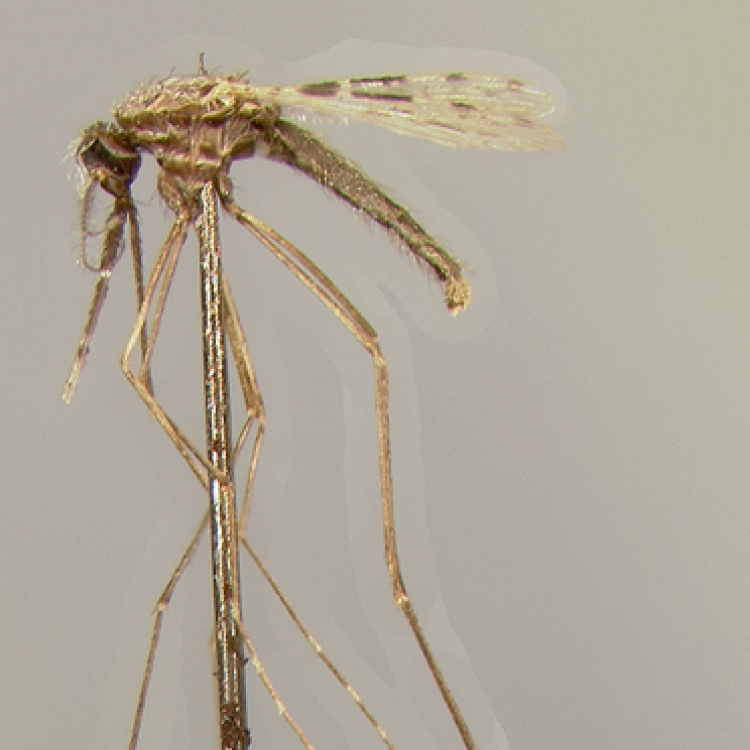
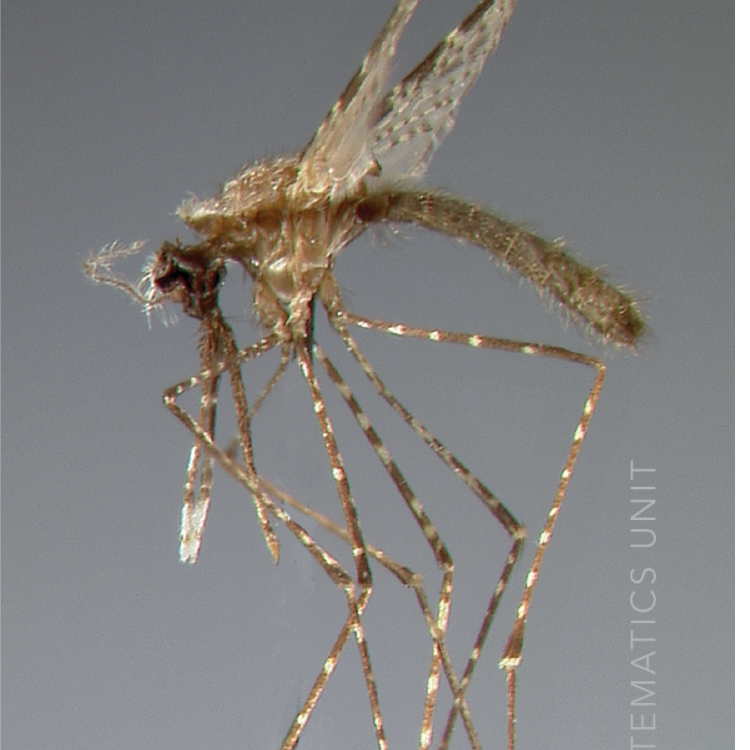
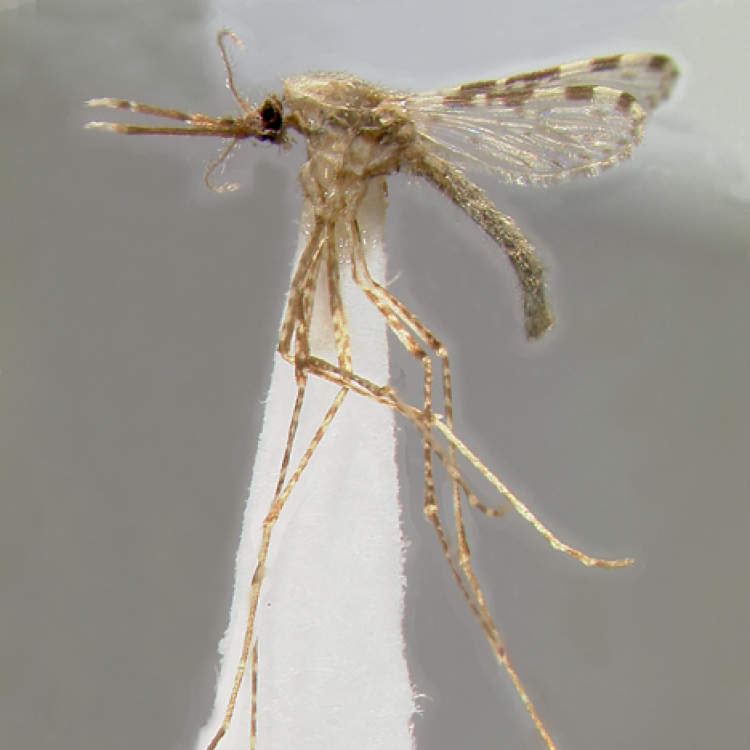
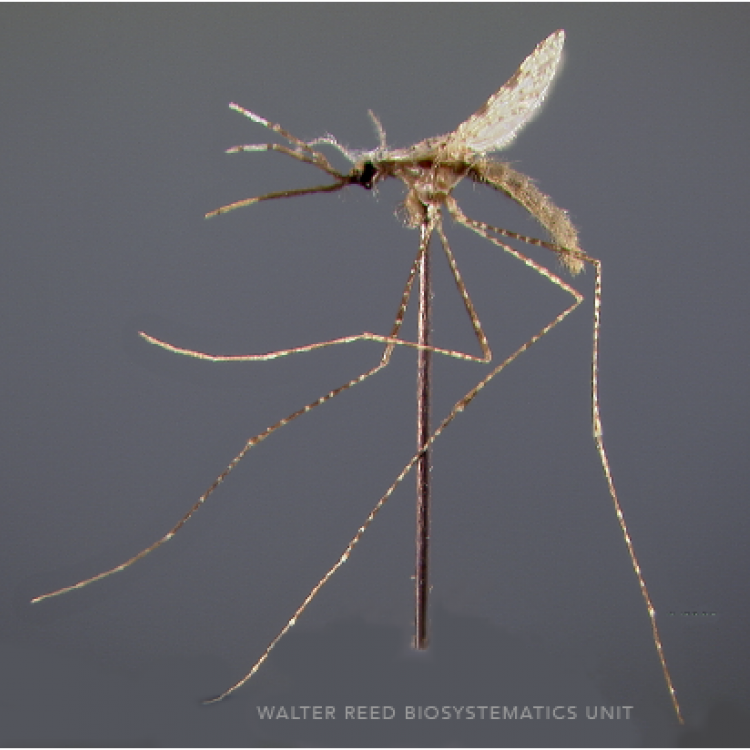
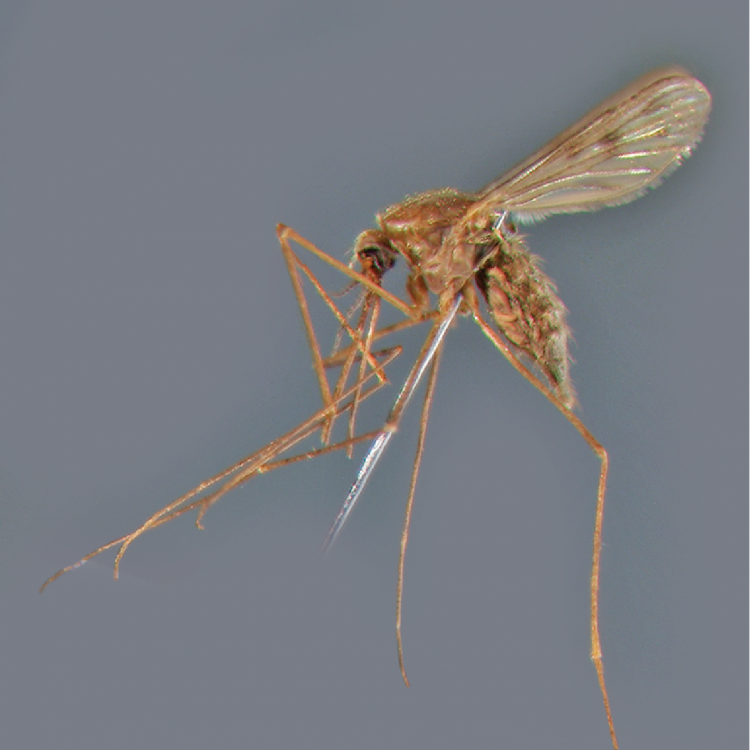
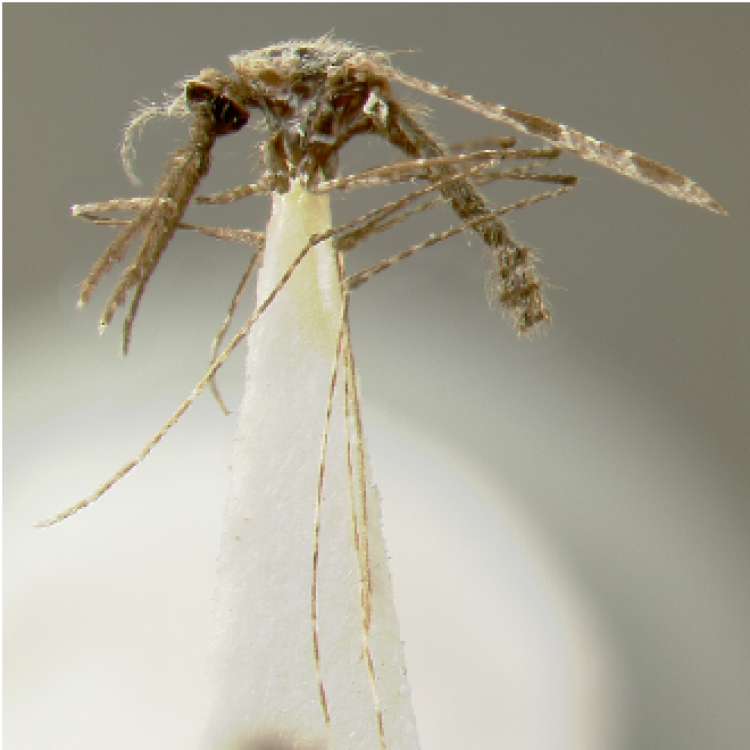
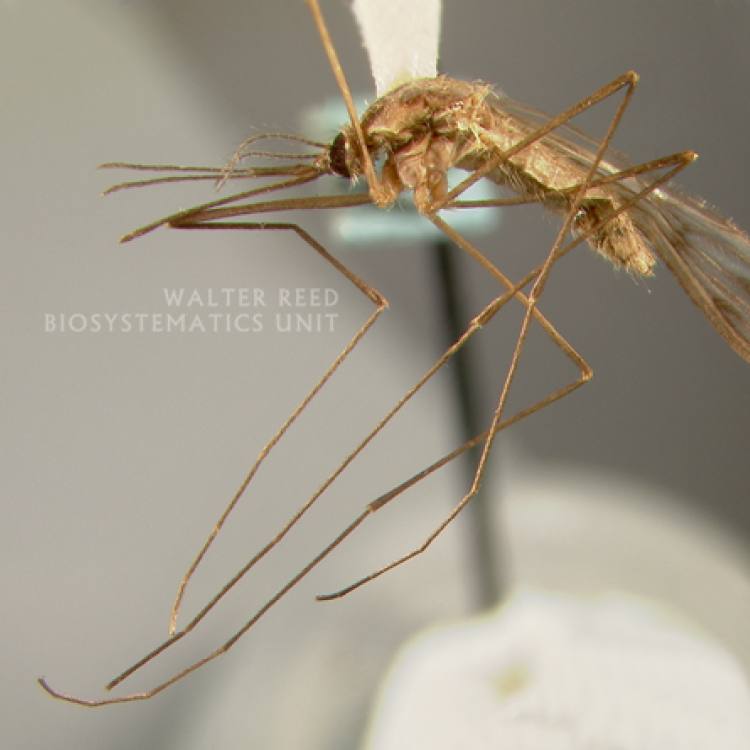
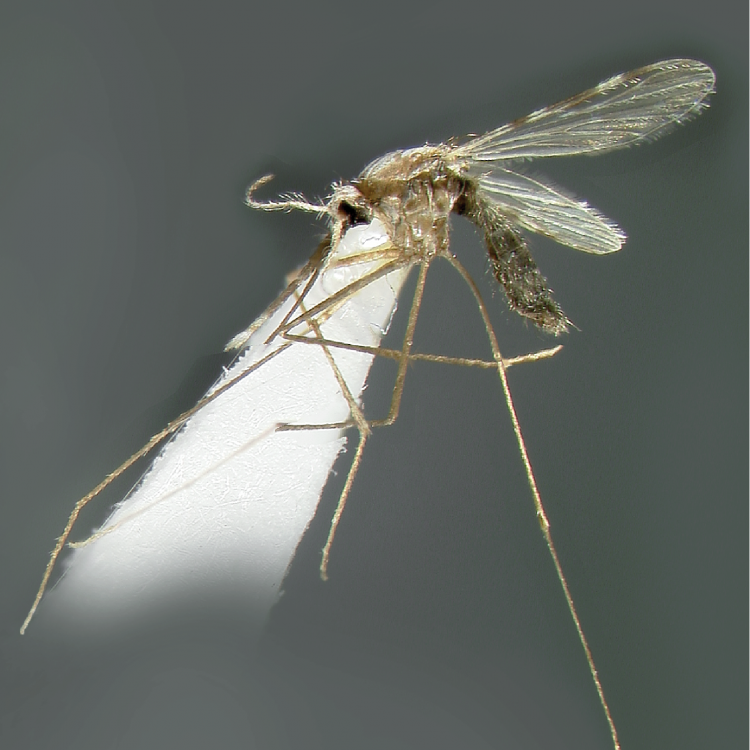
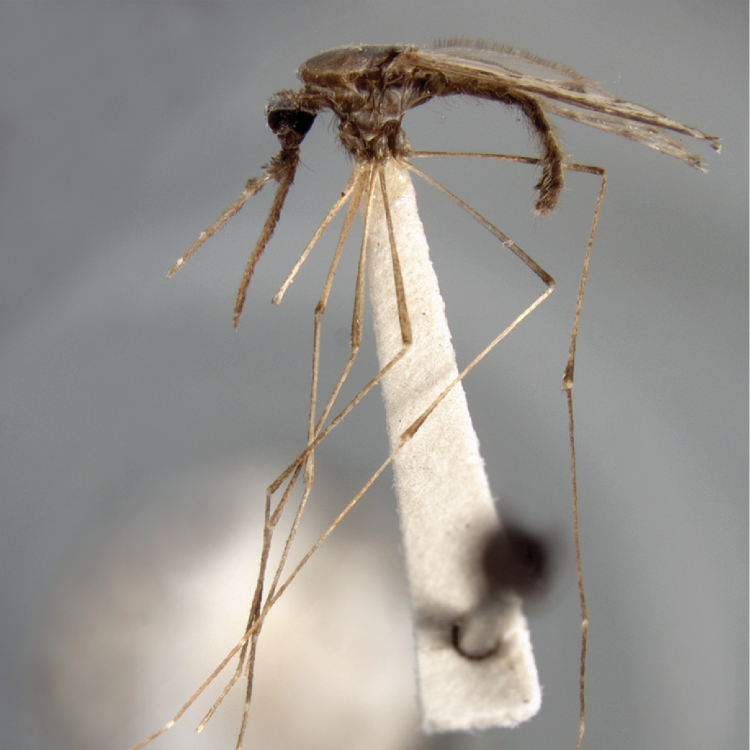
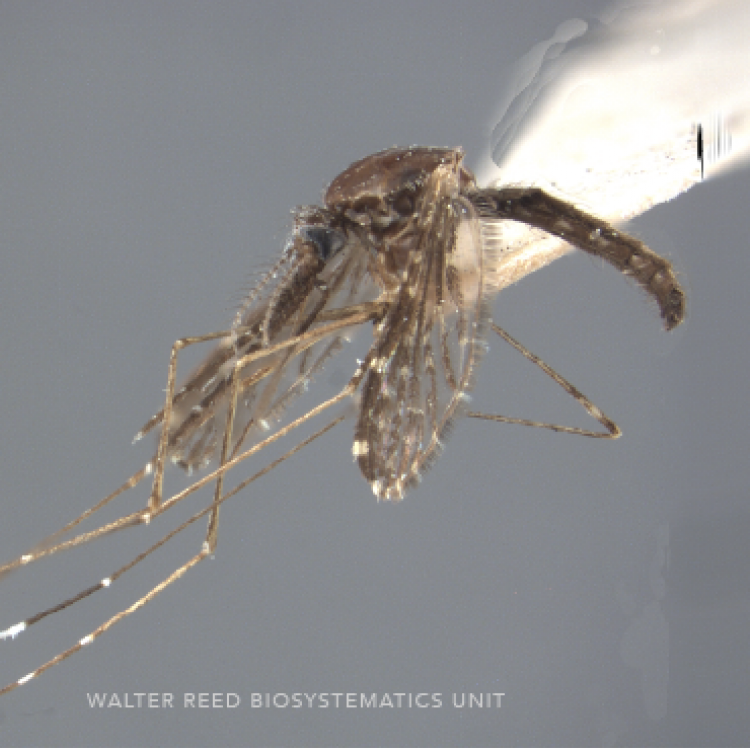
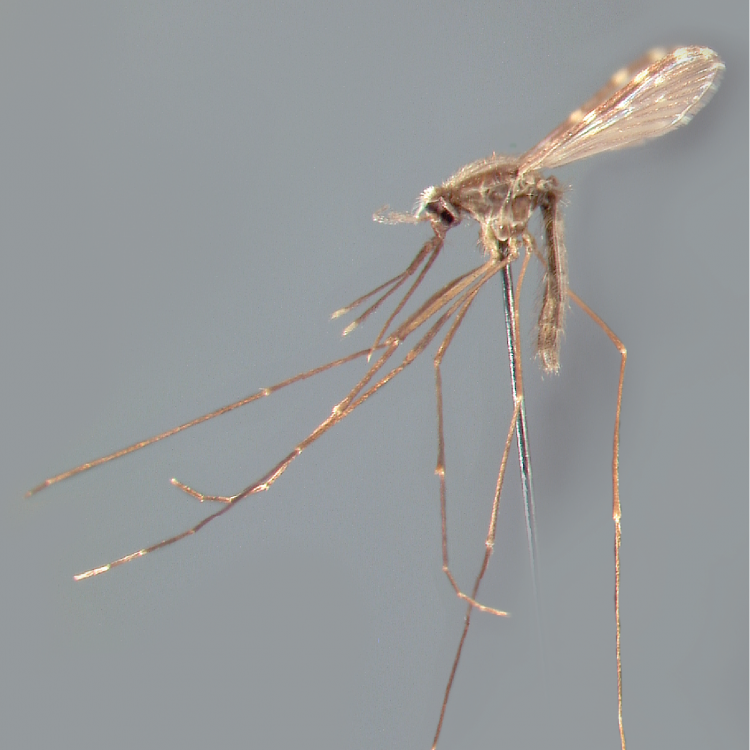
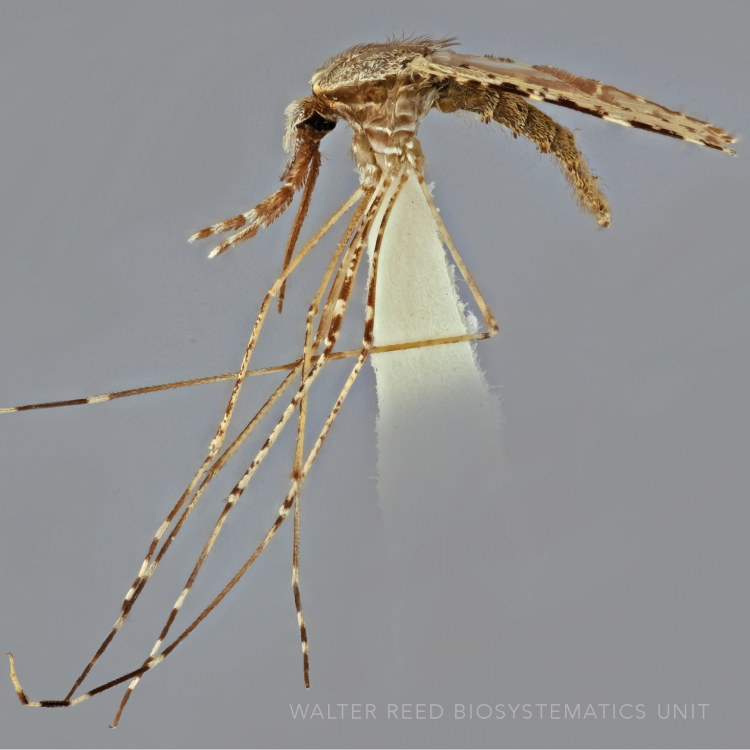
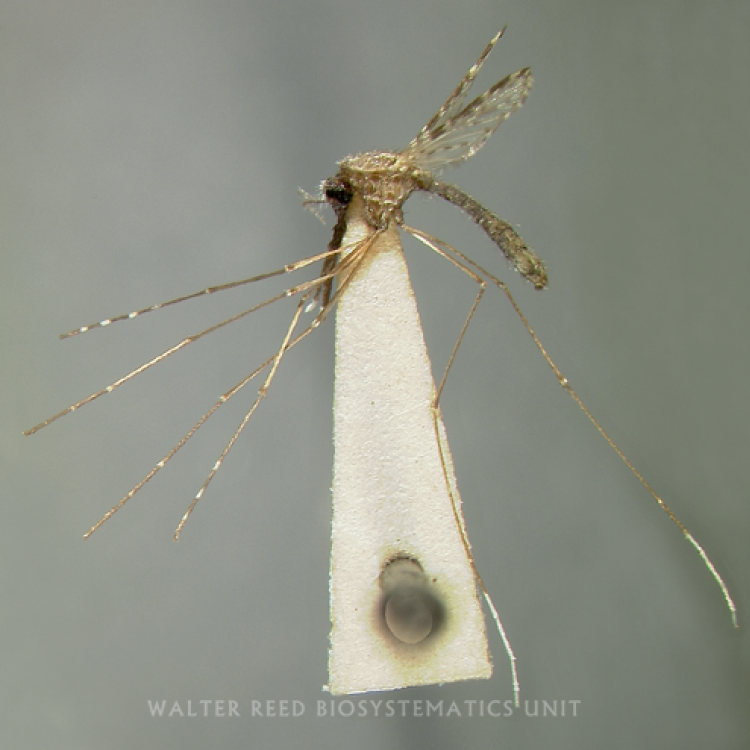
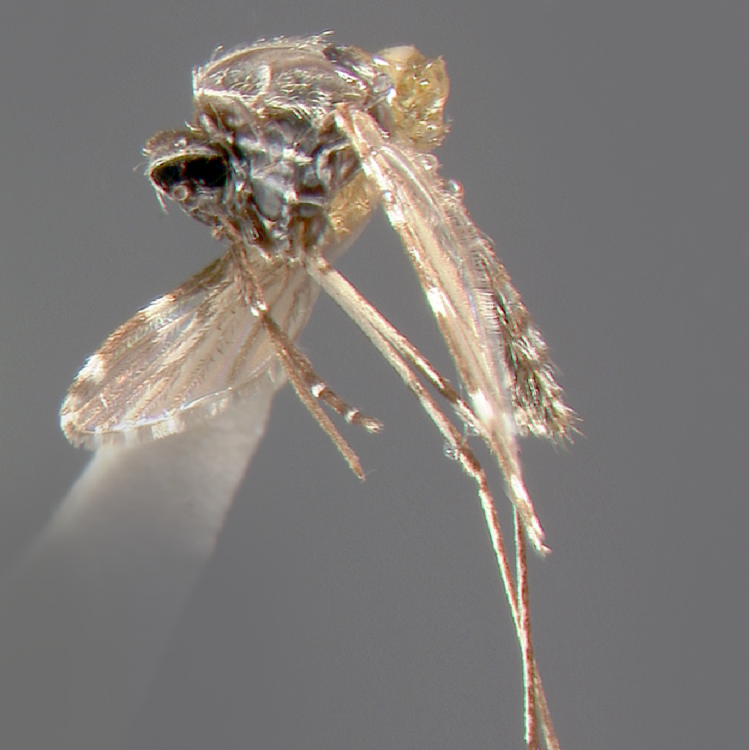
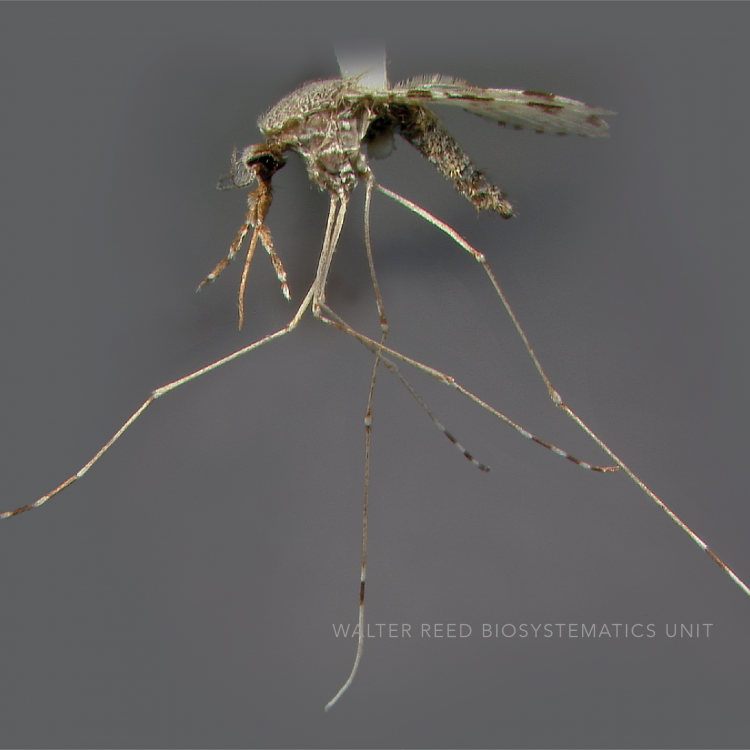
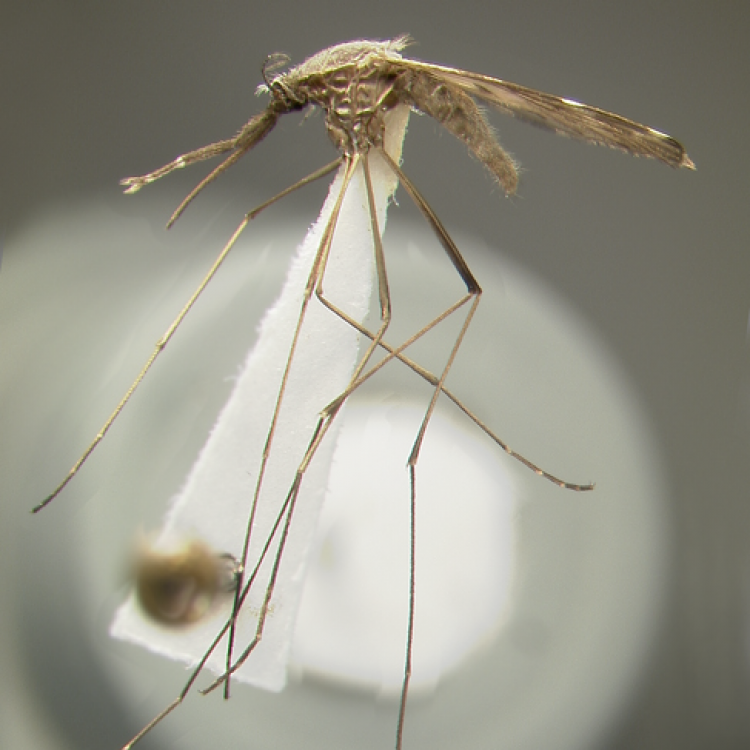
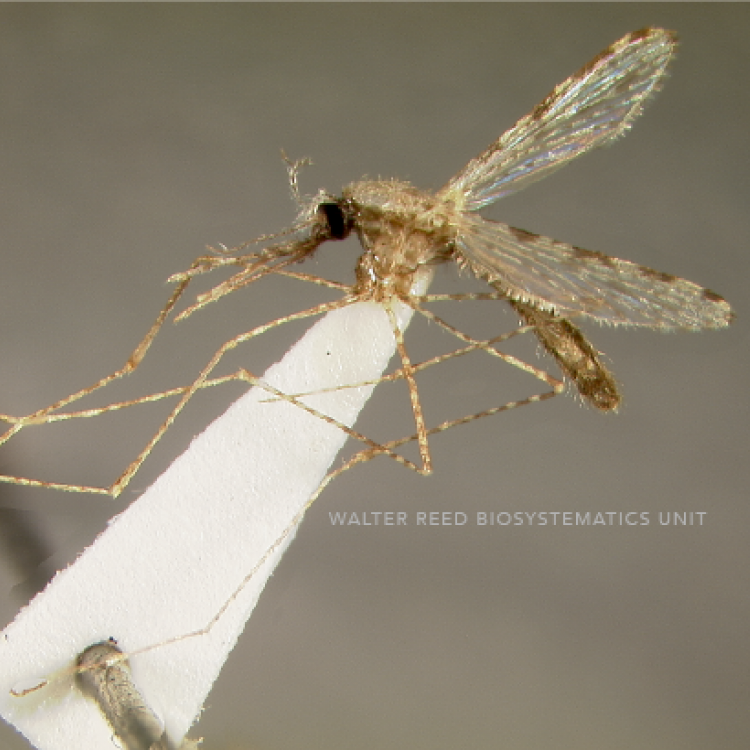
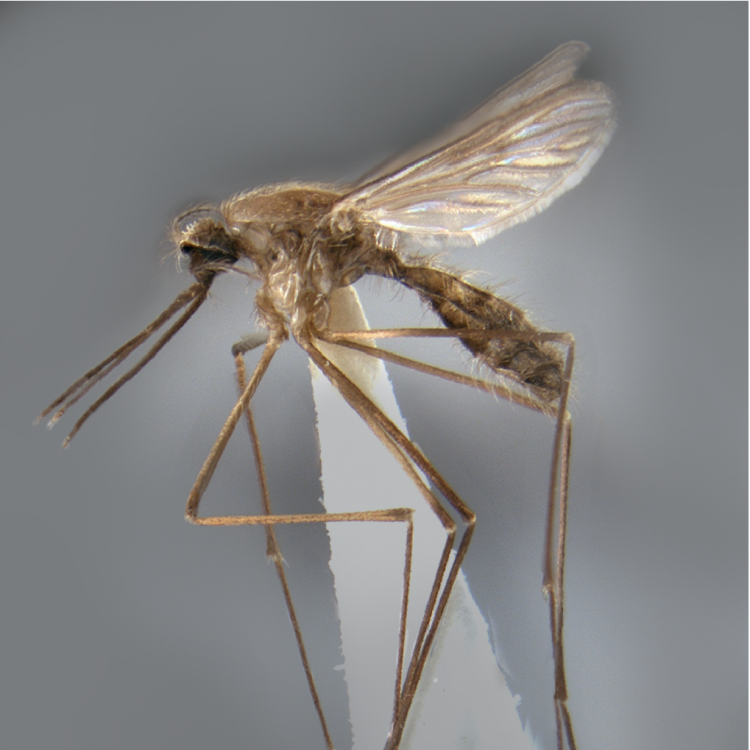
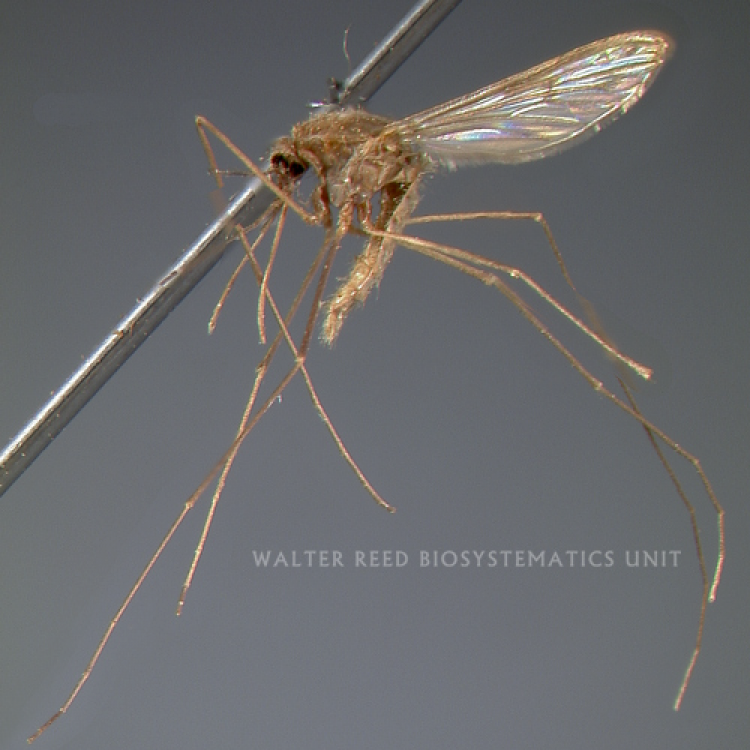
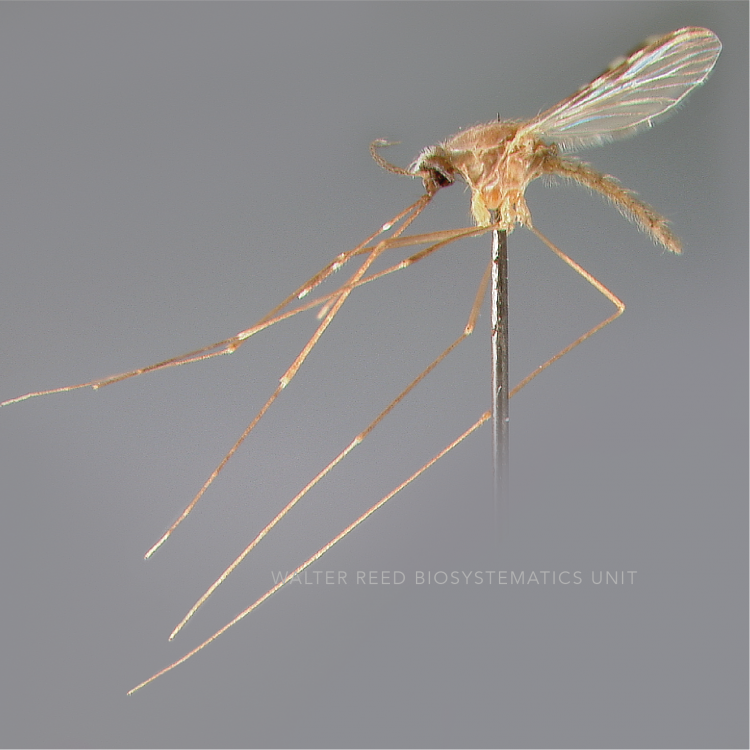
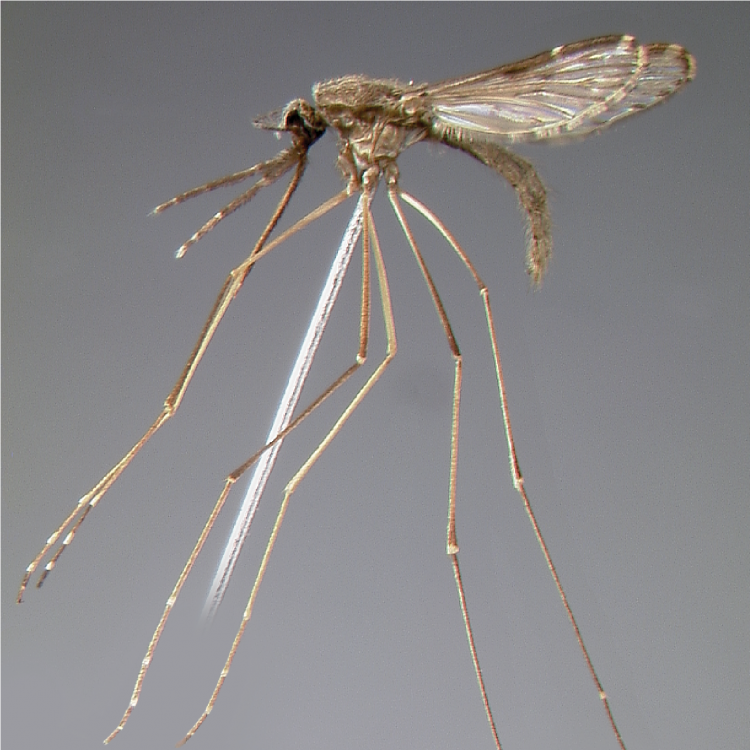
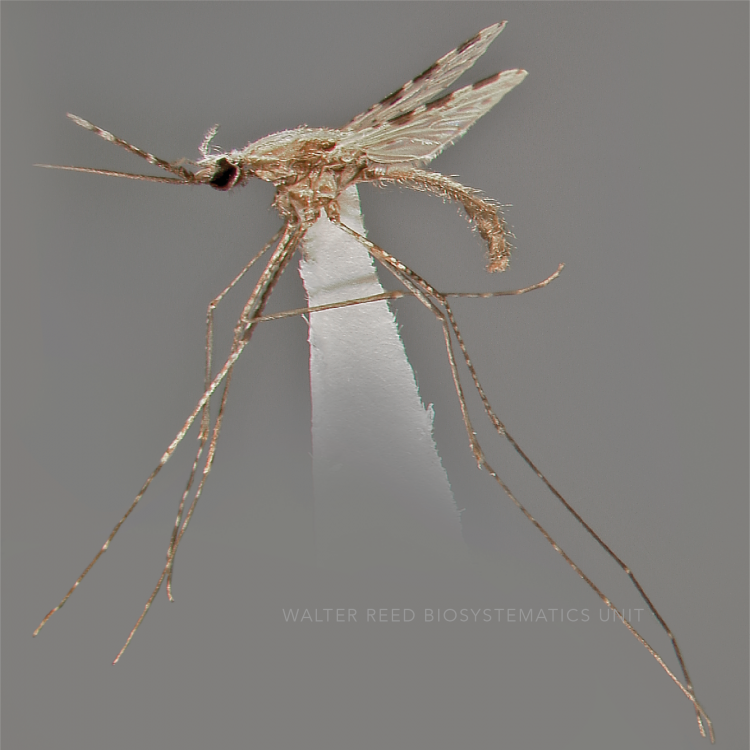
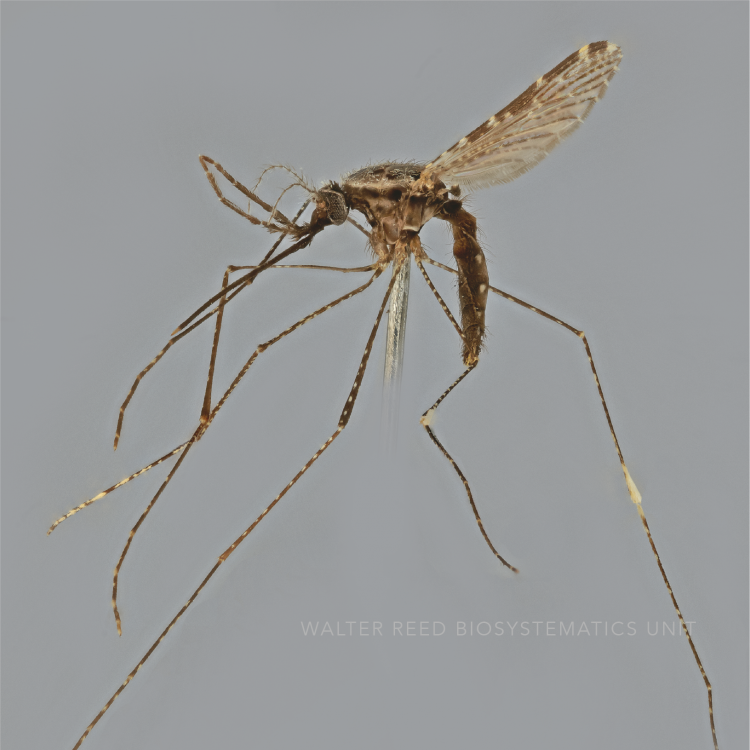
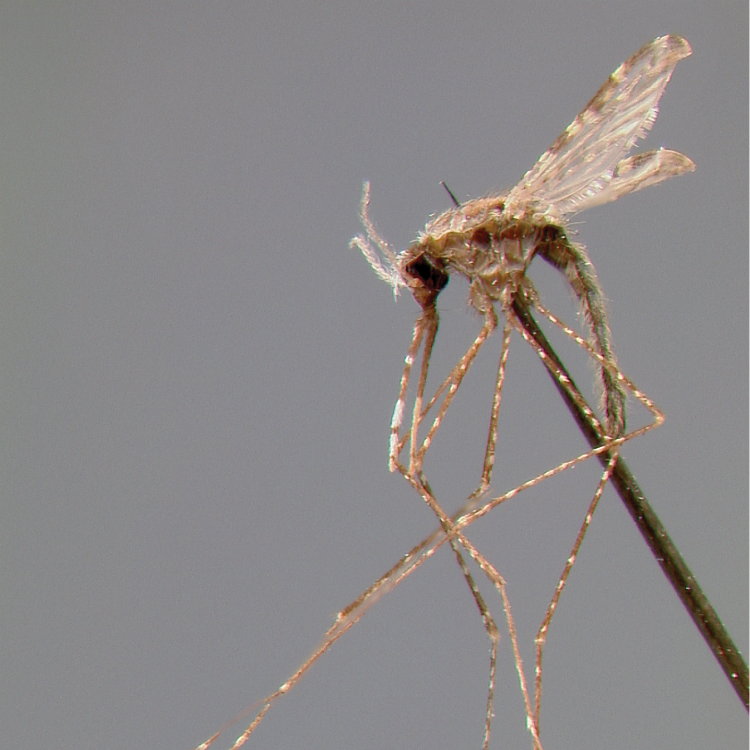
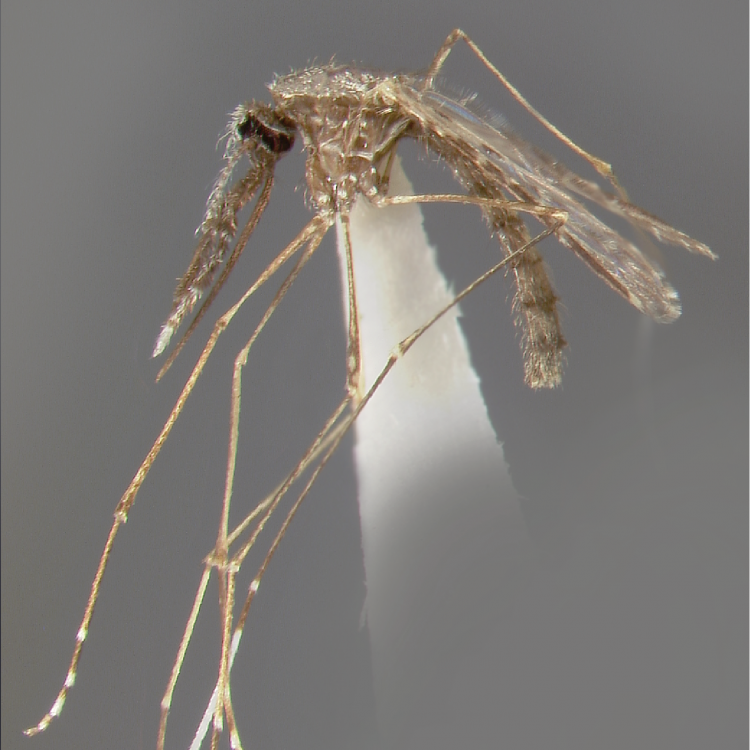
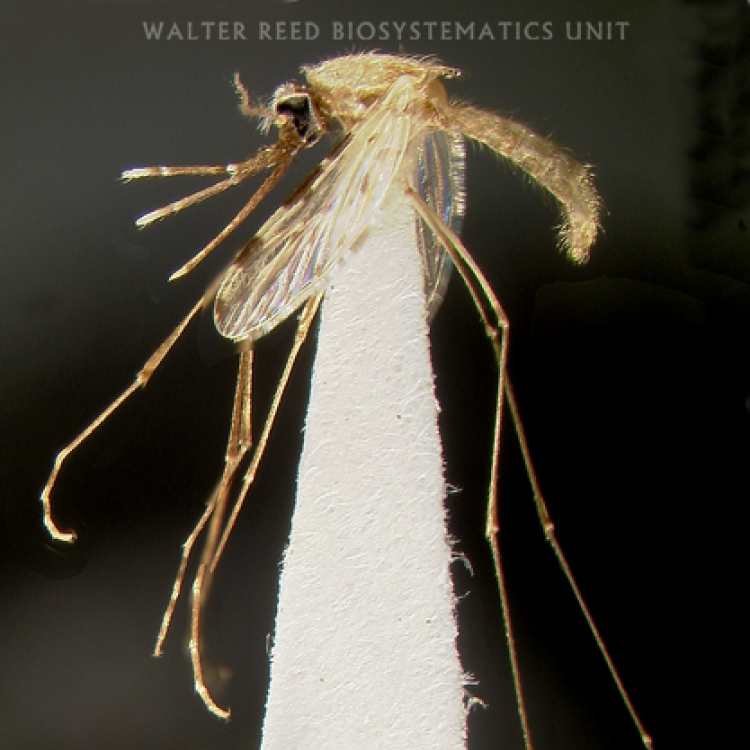
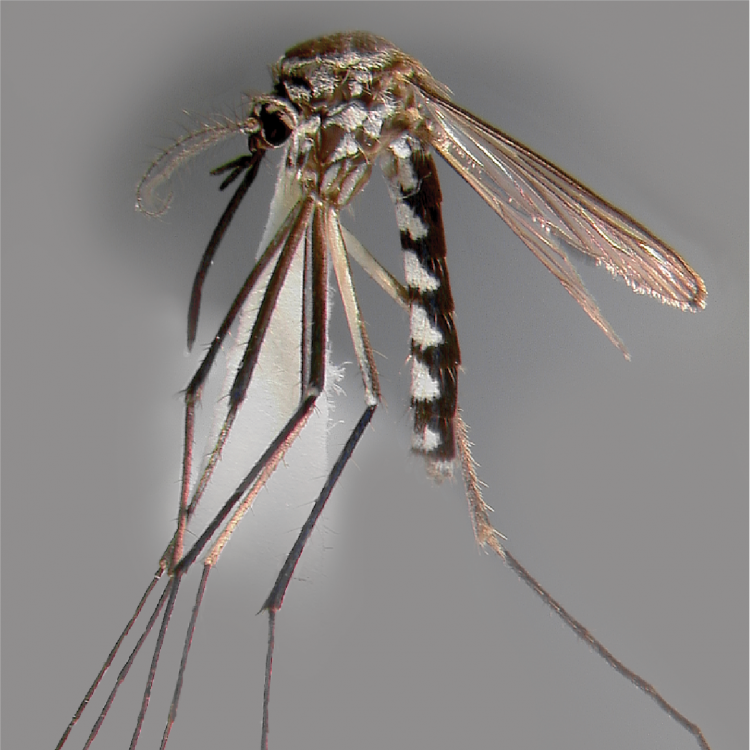
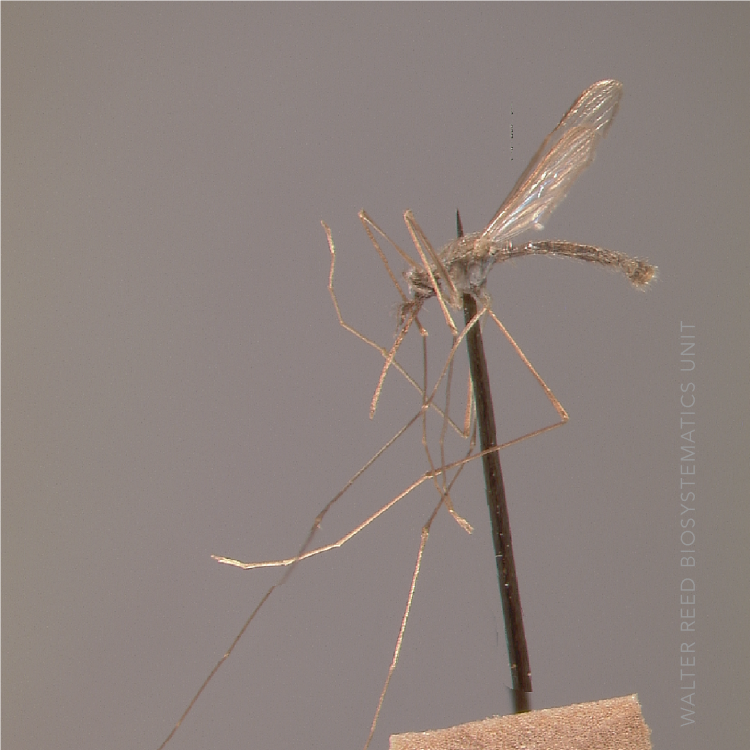
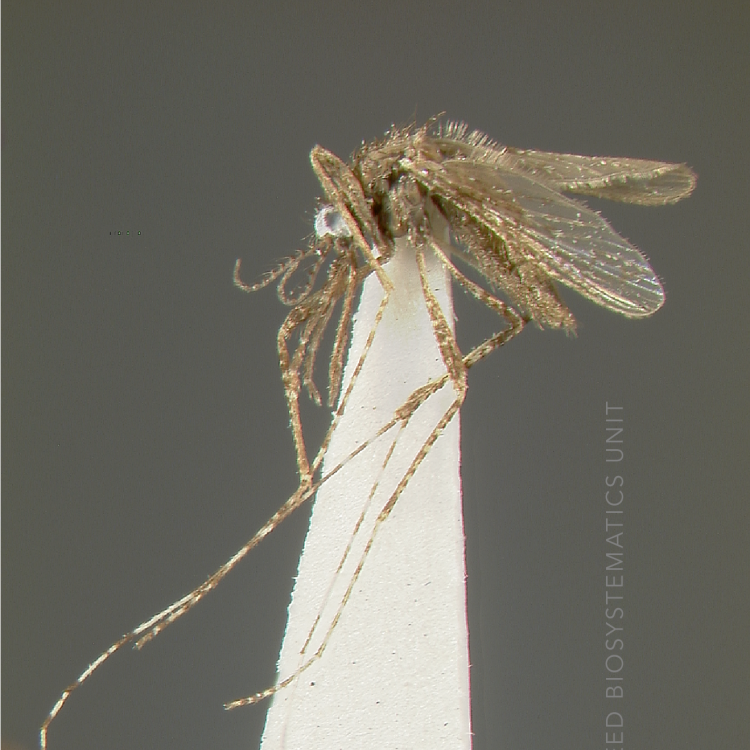
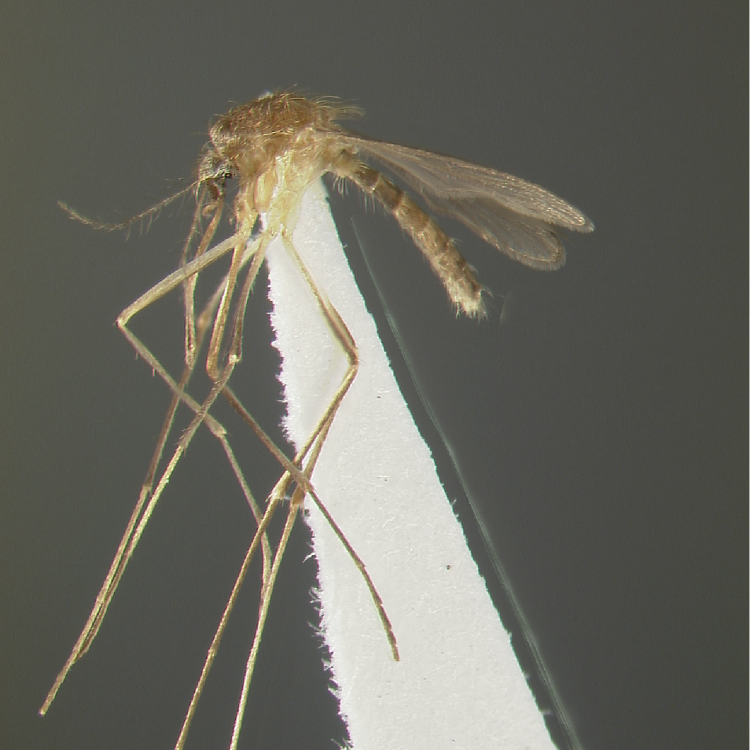
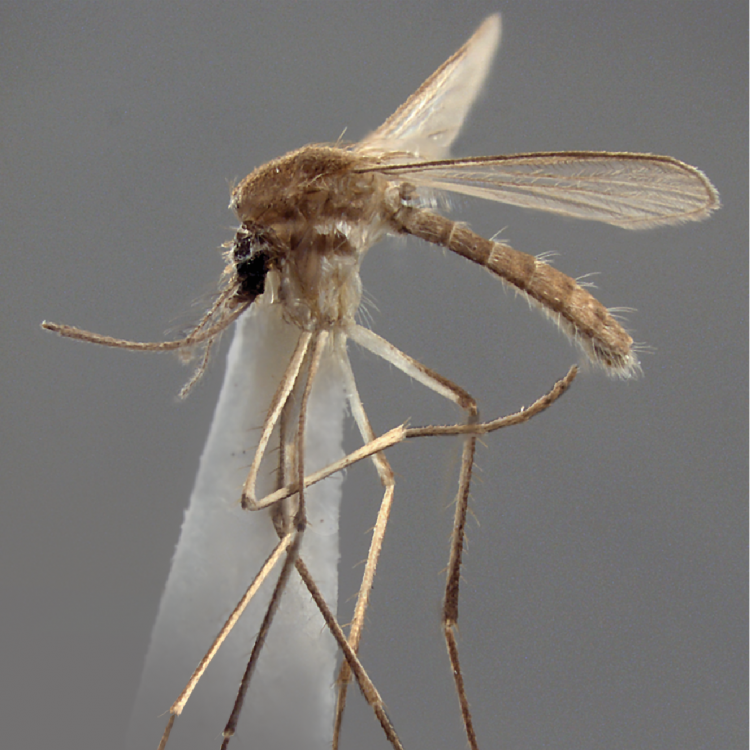
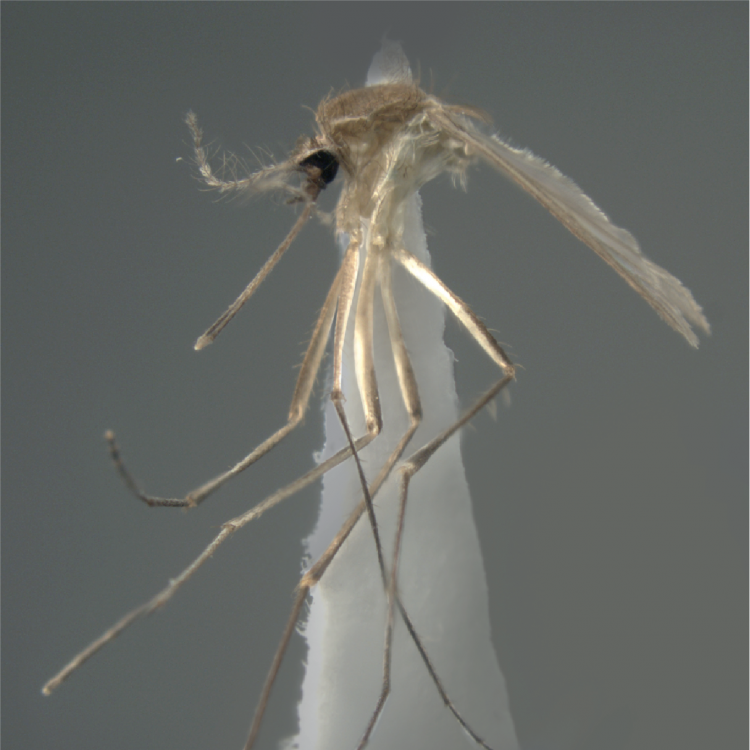
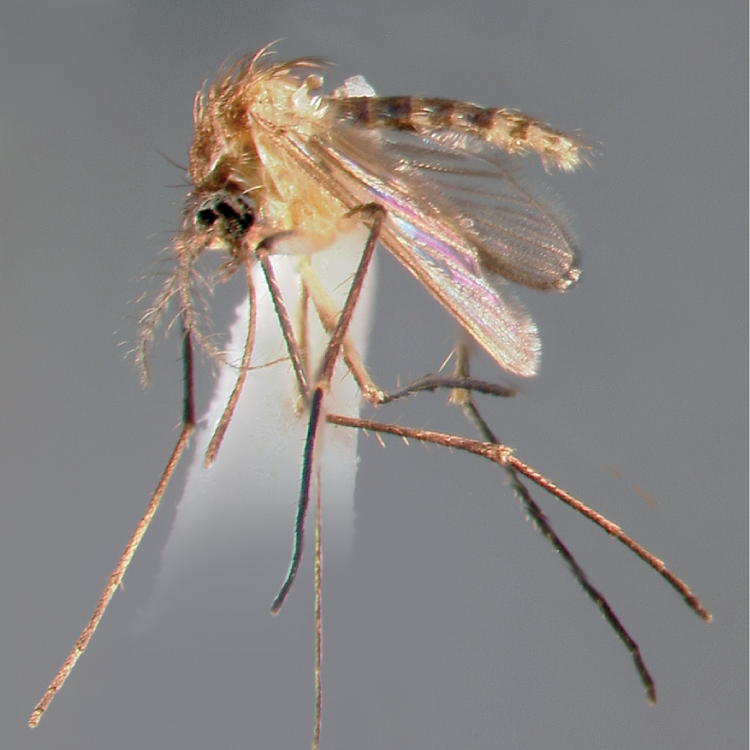
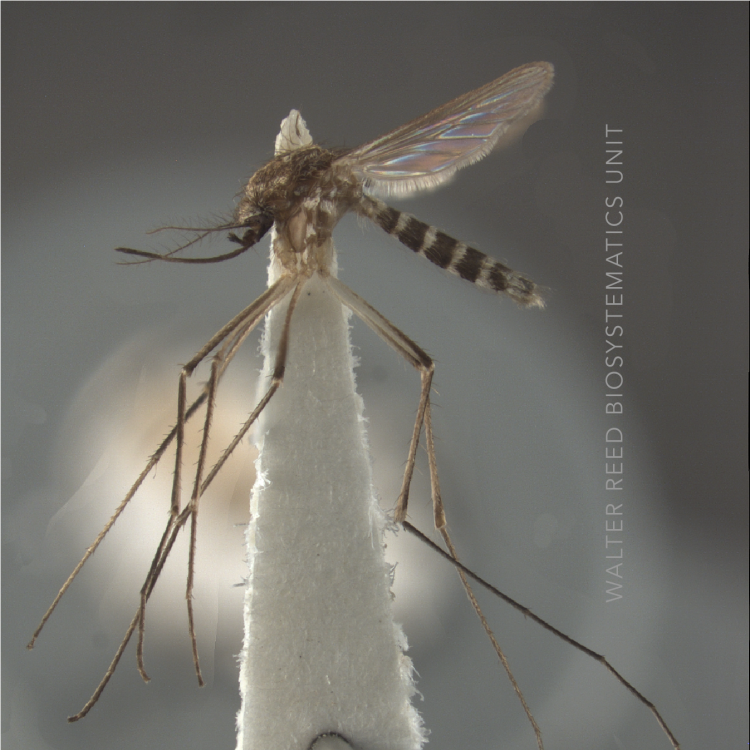
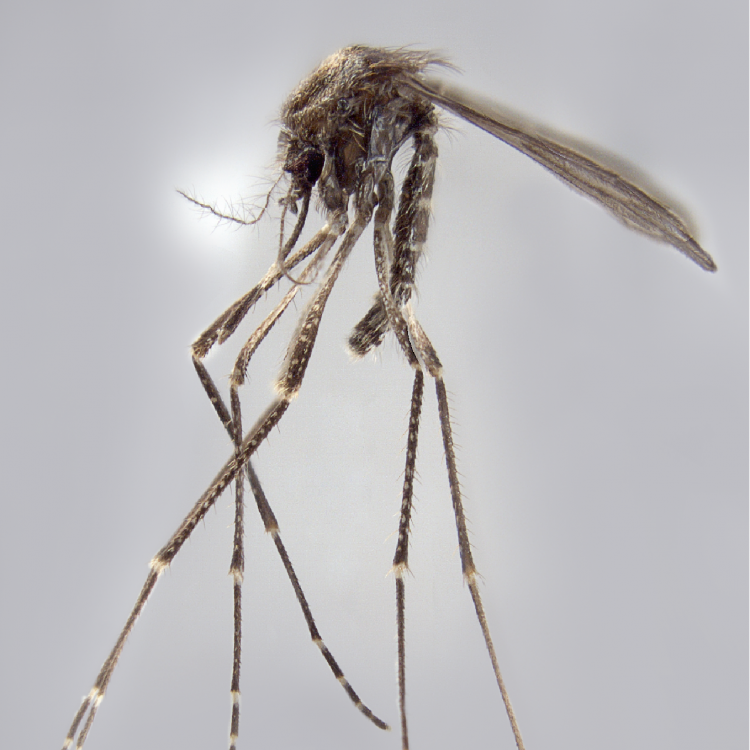
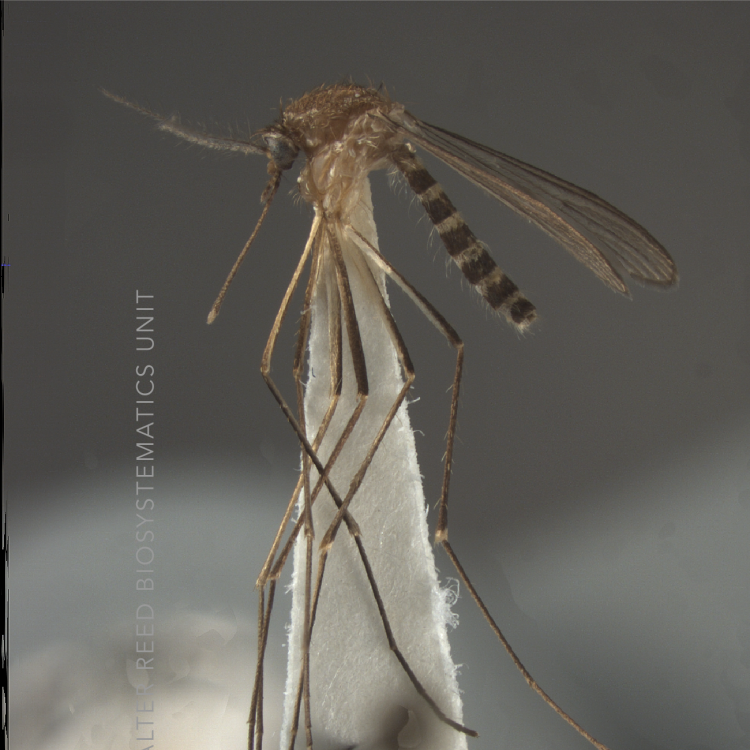
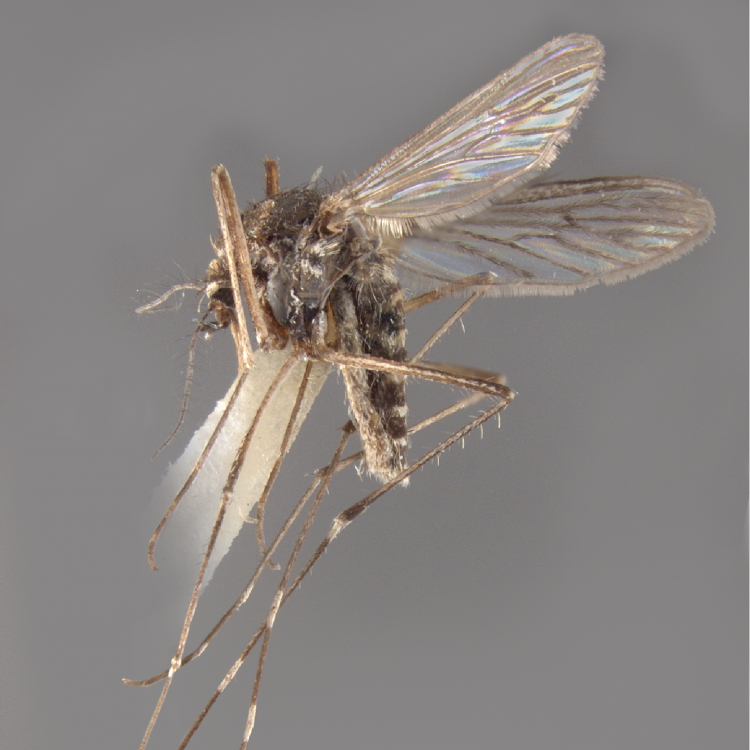
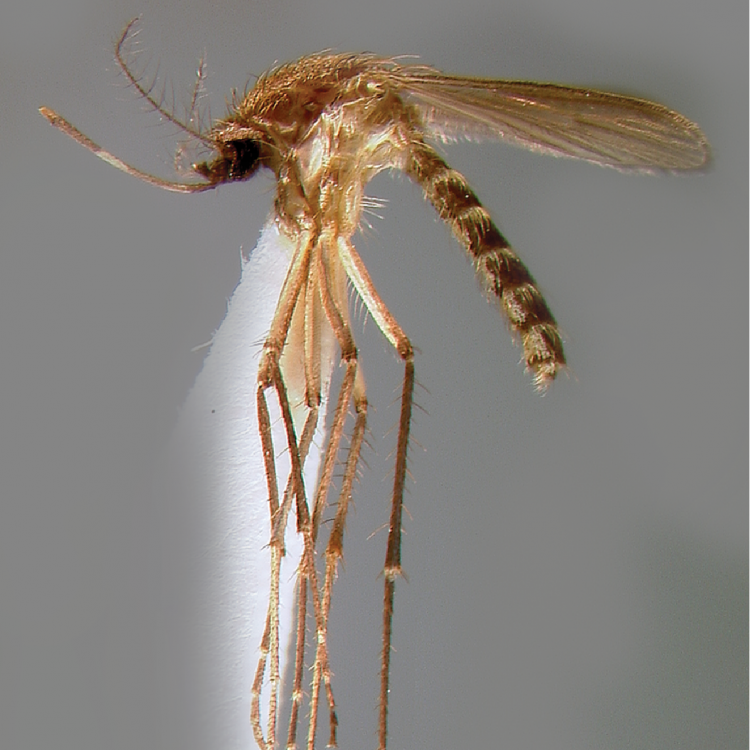
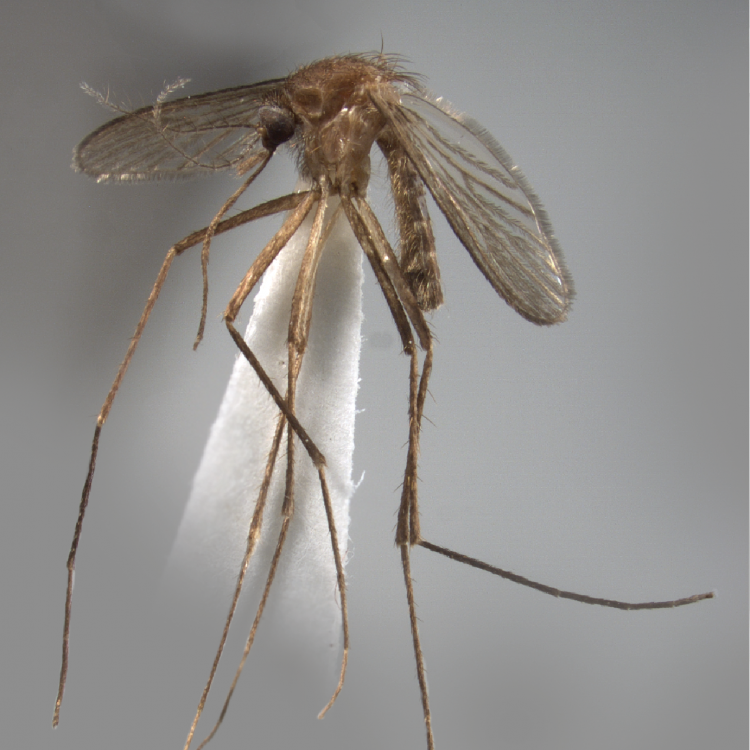
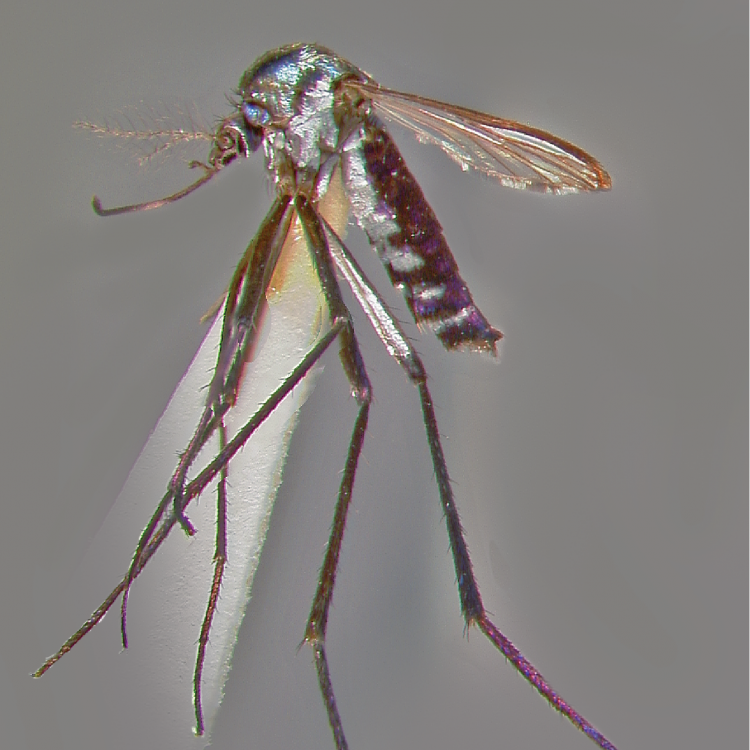
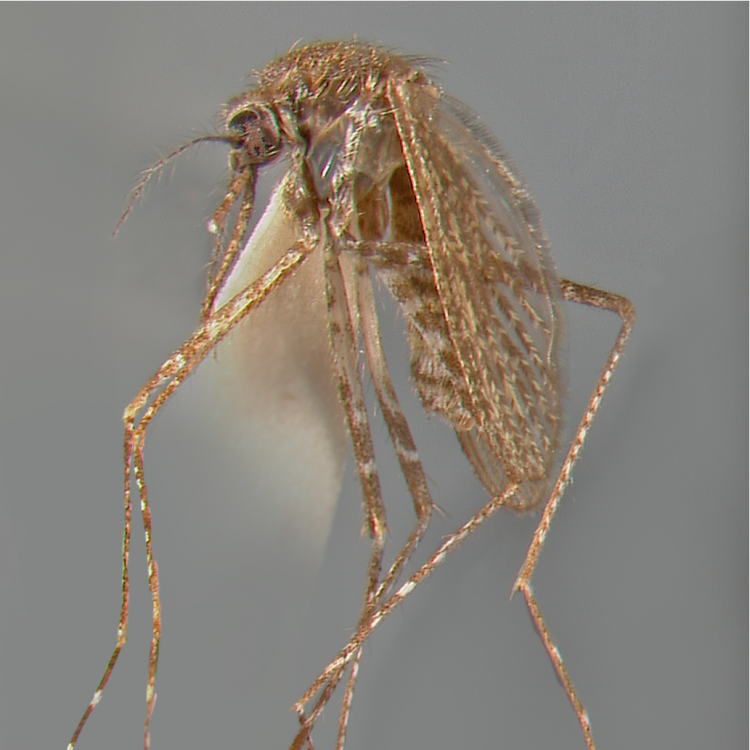
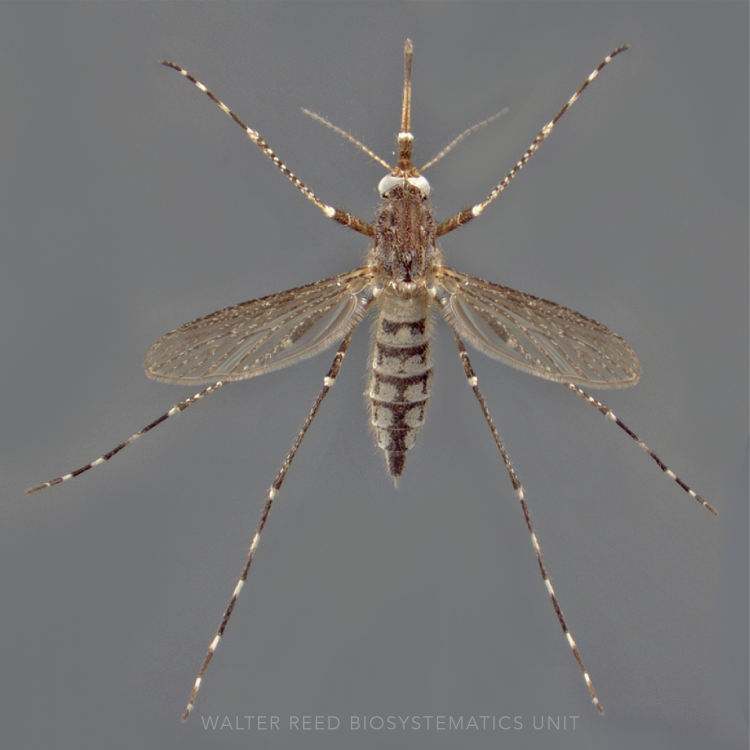
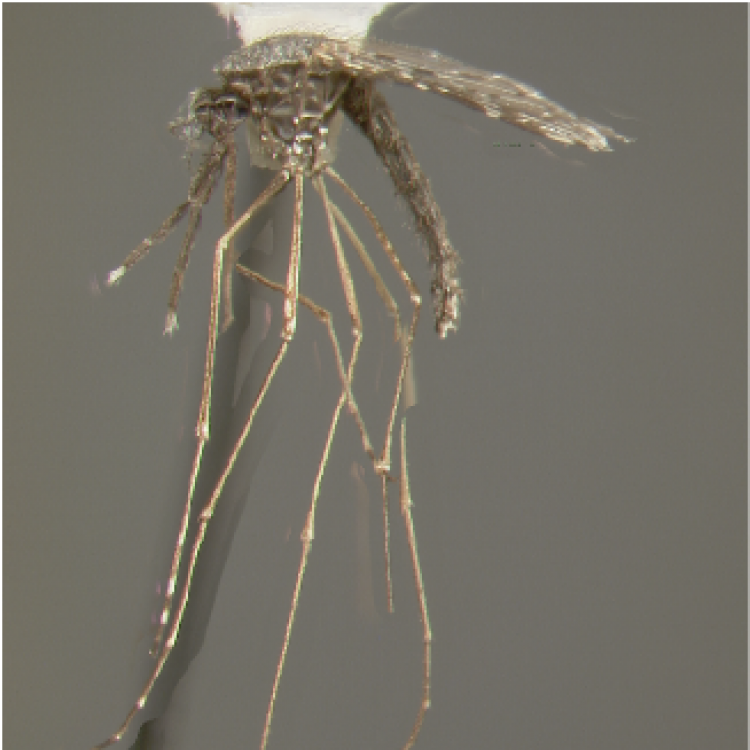
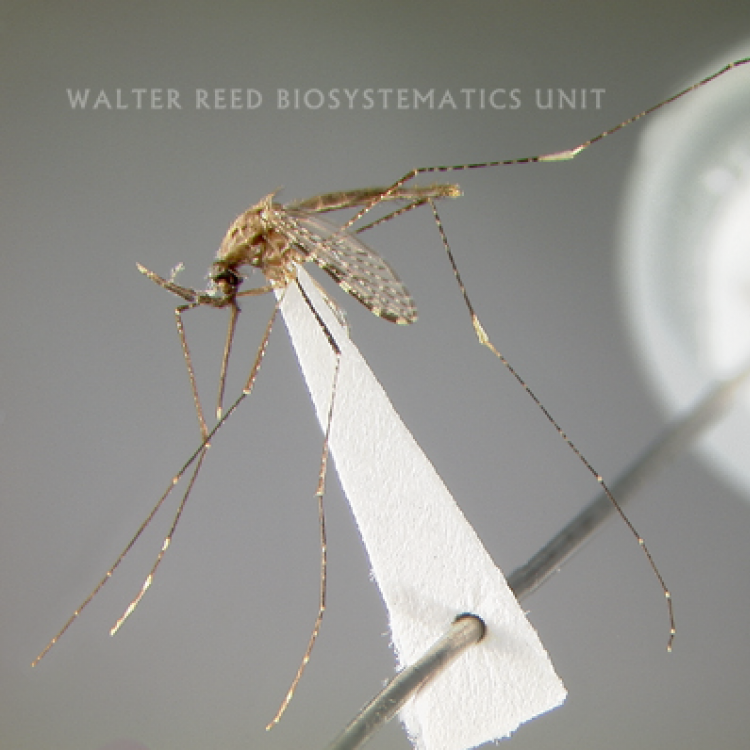
ADULT (illustrated): Head: Proboscis entirely dark-scaled; pedicel usually with more pale scales than dark, often all scales pale. Thorax: Postpronum usually with a few broad dark scales; subspiracular area usually with patch of broad white scales; scutum yellow striped with median longitudinal pale stripe, forked posteriorly at prescutellar area; lateral scutellar lobes with narrow scales. Legs: Fe-II with anterior and dorsal surfaces white preapically; Ta-III1–4 white-banded basally; all legs with basal tarsal bands.
LARVA (not illustrated): Head: Seta 5-C 3–7 branched. Thorax: Seta 7-T with greatly elongate tapered branches, generally similar to seta 6-M. Terminal segments: Seta 1-S relatively short, none of the branches reaching apex of siphon, usually at end or beyond pecten; saddle spiculate on posterior margin; seta 1-X single, on saddle; comb with comb scales in patch, comb scales paddle-shaped and fringed.
TAXONOMIC KEYS
Tanaka et al. 1979
Exemplar DNA sequences
Ae. koreicus COI: JF430393, KM258298–99, KM457599–600, KT358407, KT962063.
BIONOMICS
Immatures
In the Oriental Region, immature Ae. koreicus are typically found in small rock pools, tree holes, plant axils, containing still fresh water with decaying tree leaves. In Europe, the invasive population immatures are primarily associated with artificial containers like abandoned tires and unused construction equipment, as well as sometimes in temporary ground pools.
Adults
Females Ae. koreicus are highly anthropophilic. Unlike its sister taxa Ae. japonicus that is more rurally associated, Ae. koreicus is found in urban areas, in close proximity to humans, heightening concern for its role in arthropod-borne disease transmission. In colder regions, the species overwinters as eggs.
DISTRIBUTION NOTES
Belgium, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Japan, People's Republic of China, Russia (Southern Districts), Slovenia, South Korea, Switzerland, Taiwan.

WRBU VECTOR HAZARD REPORTS
VHR: Medically Important Mosquitoes of EUCOM
View other WRBU Vector Hazard Reports
Available GIS Models:
IMPORTANT REFERENCES (full citations below)
Edwards 1917: 212 (M, F; Ochlerotatus)
Knight 1948 (1947)c: 633 (M*, F, L*; taxonomy)
LaCasse & Yamaguti 1950: 156 (M*, F*, L*; bionomics, distribution, taxonomy)
Knight 1968 (taxonomy; Chrysolineatus Group)
Miyagi 1971: 147 (A, L); Miyagi 1971 (taxonomy)
Gutsevich et al. 1974: 315 (M*, F, L*)
Tanaka et al. 1979: 322 (M*, F*, P*, L*; keys, taxonomy, review, bionomics)
Capelli et al. 2011 (distribution; Italy)
Versteirt et al. 2012a,b (bionomics, distribution; Belgium)
Robert et al. 2019 (distribution, Euro-Mediterranean)
CURRENT SYNONYMS
None
CITED REFERENCES
Capelli, G., Drago, A., Martini, S., Montarsi, F., Soppelsa, M., Delai, N., . . . Russo, F. (2011). First report in Italy of the exotic mosquito species Aedes (Finlaya) koreicus, a potential vector of arboviruses and filariae. Parasites and Vectors, 4, 188.
Edwards, F.W. (1917). Notes on Culicidae, with descriptions of new species. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 7, 201–229.
Gutsevich, A.V., Monchadskii, A.S., & Shtakel’berg, A.A. (1974). Fauna of the USSR. New series No. 100 Diptera. Vol. III, No. 4. Mosquitoes. Family Culicidae. Jerusalem, Israel: Keter Publishing House Jerusalem Ltd. (Original work published 1971).
Knight, K.L. (1968). Contributions to the mosquito fauna of Southeast Asia. IV. Species of the subgroup chrysolineatus of group D, genus Aedes, subgenus Finlaya Theobald. Contributions of the American Entomological Institute, 2(5), 1–45.
Knight, K.L., & Chamberlain, R.W. (1948). A new nomenclature for the chaetotaxy of the mosquito pupa, based on a comparative study of the genera (Diptera: Culicidae). Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 15, 1–18.
Miyagi, I. (1971). Notes on the Aedes (Finlaya) chrysolineatus subgroup in Japan and Korea (Diptera: Culicidae). Tropical Medicine, 13, 141–151.
Robert, V., Günay, F., Le Goff, G., Boussès, P., Sulesco, T., Khalin, A., Medlock, J.M., Kampen, H., Petrić, D. & F. Schaffner. (2019). Distribution chart for Euro-Mediterranean mosquitoes (western Palaearctic region). Journal of the European Mosquito Control Association, 37, 1–28.
Tanaka, K., Mizusawa, K., & Saugstad, E.S. (1979). A revision of the adult and larval mosquitoes of Japan (including the Ryukyu Archipelago and Ogasawara Islands) and Korea (Diptera: Culicidae). Contributions of the American Entomological Institute, 16, 1–987.
Versteirt, V., DeClerq, E.M., Fonseca, D.M., Pecor, J., Schaffner, F., Coosemans, M., & Van Bortel, W. (2012). Bionomics of the established exotic mosquito species Aedes koreicus in Belgium, Europe. Journal of Medical Entomology, 49(6), 1226–1232.
Versteirt, V., Pecor, J.E., Fonseca, D.M., Coosemans, M., & Van Bortel, W. (2012). Confirmation of Aedes koreicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Belgium and description of morphological differences between Korean and Belgian specimens validated by molecular identification. Zootaxa, 13, 21–32.
CITE THIS PAGE
Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit (Year). Aedes koreicus species page. Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit Website, http://wrbu.si.edu/vectorspecies/mosquitoes/koreicus, accessed on [date (e.g. 03 February 2020) when you last viewed the site].