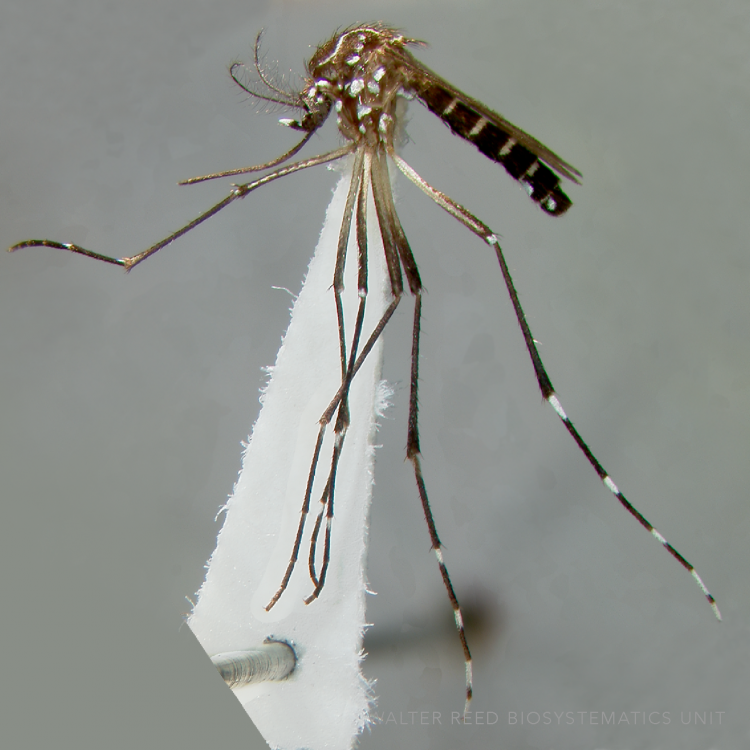
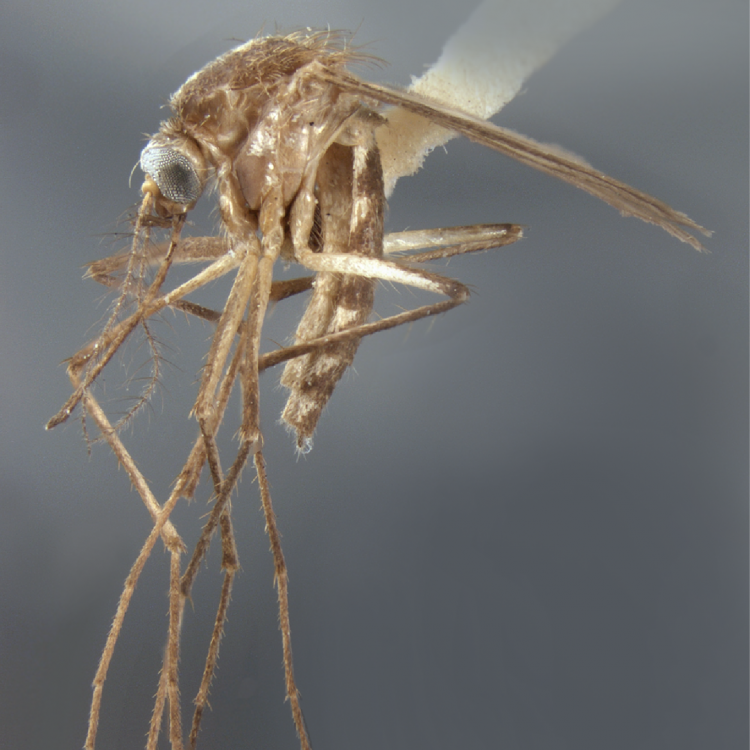
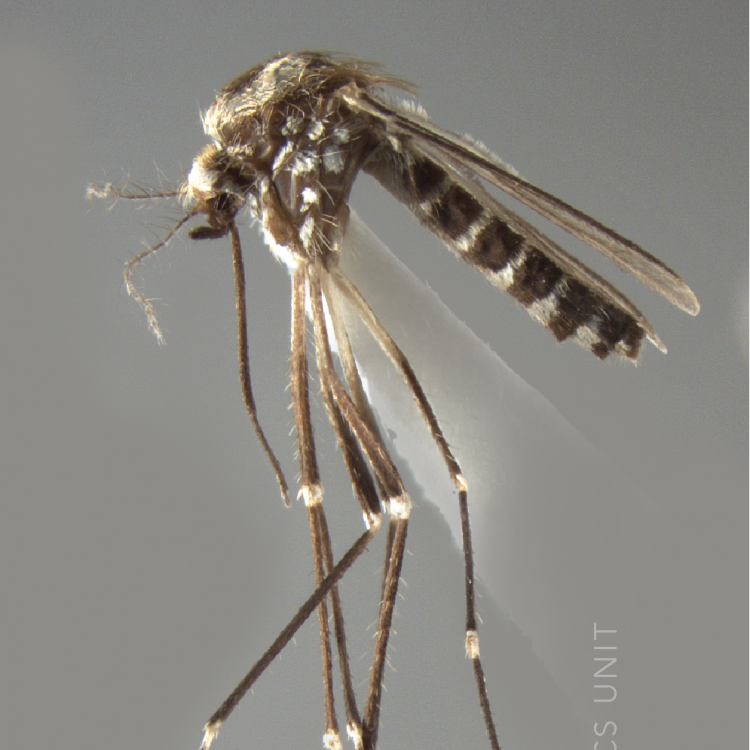
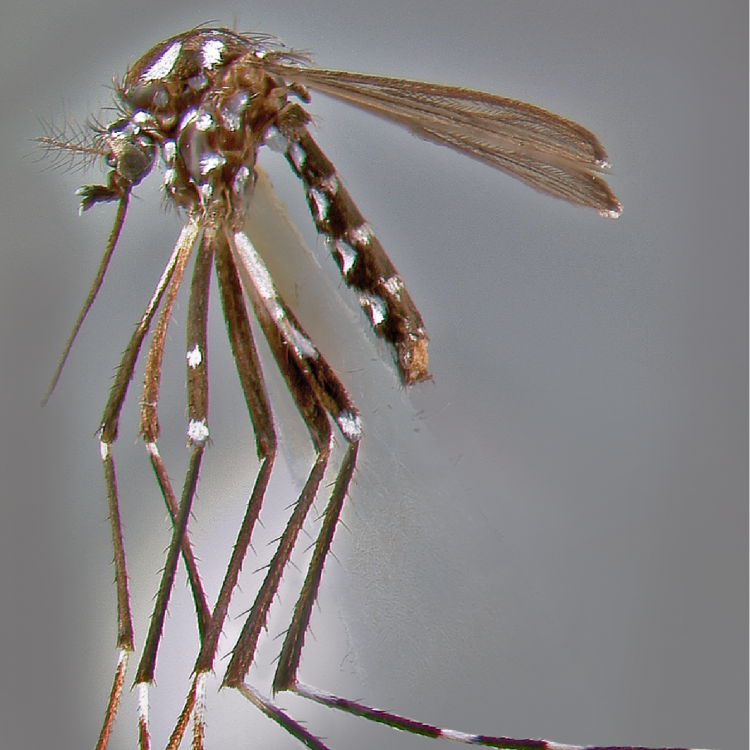
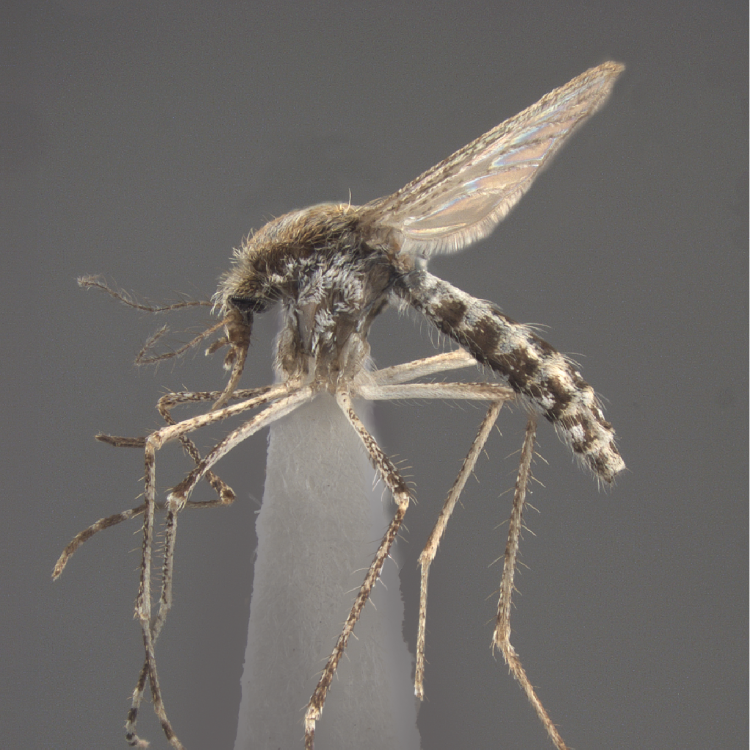
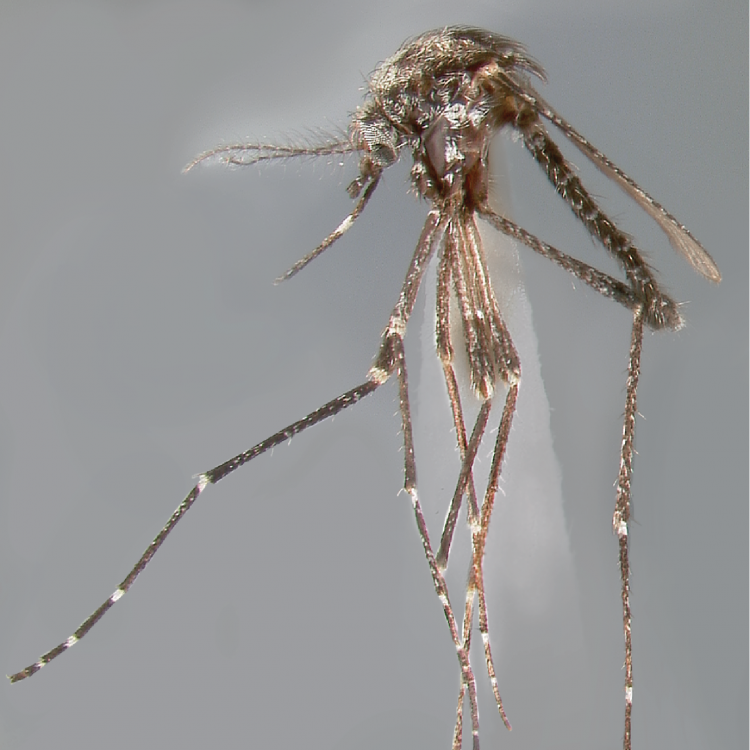
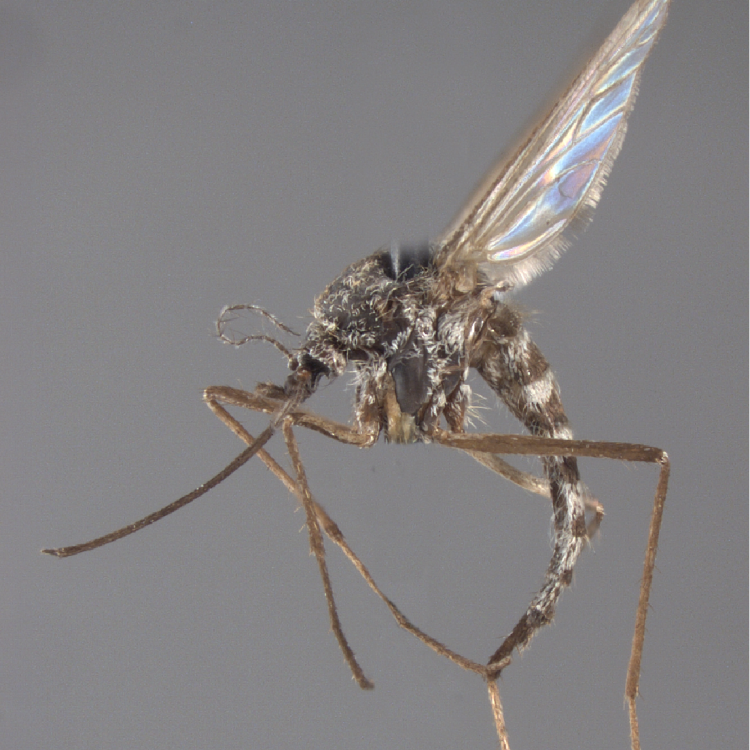
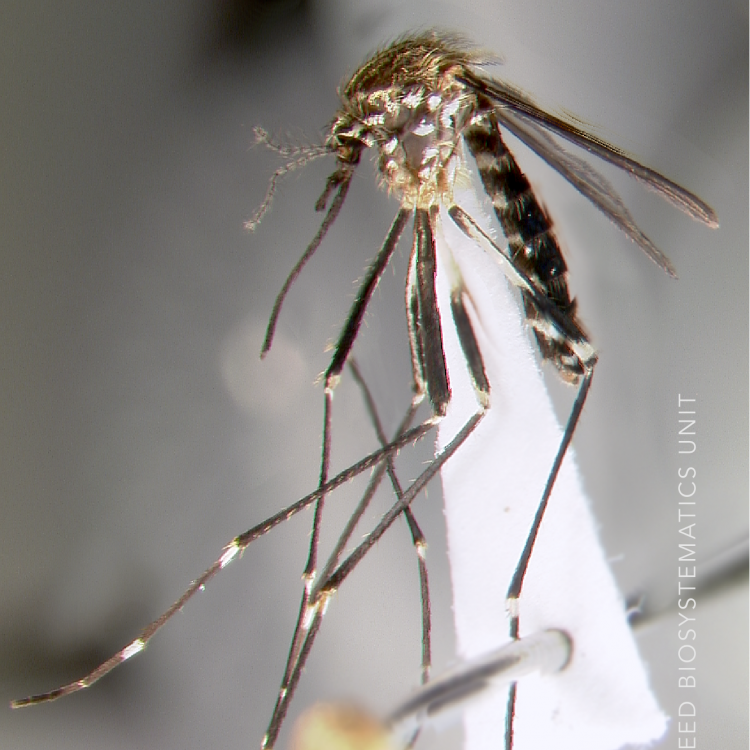
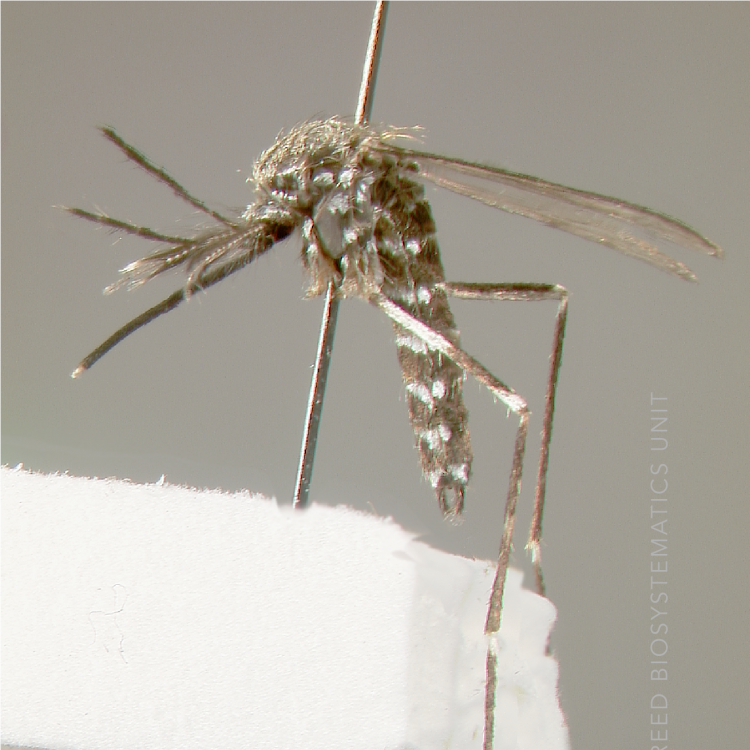
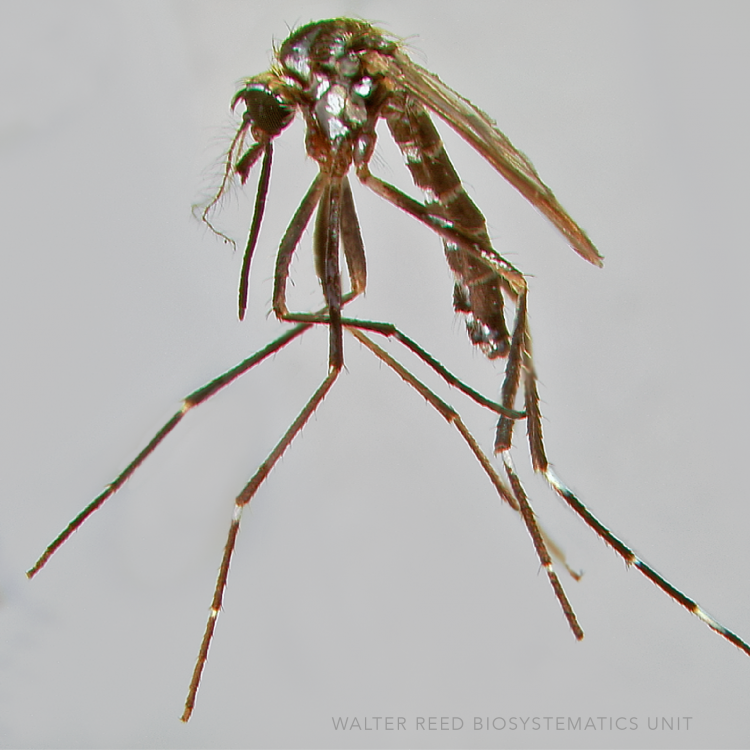
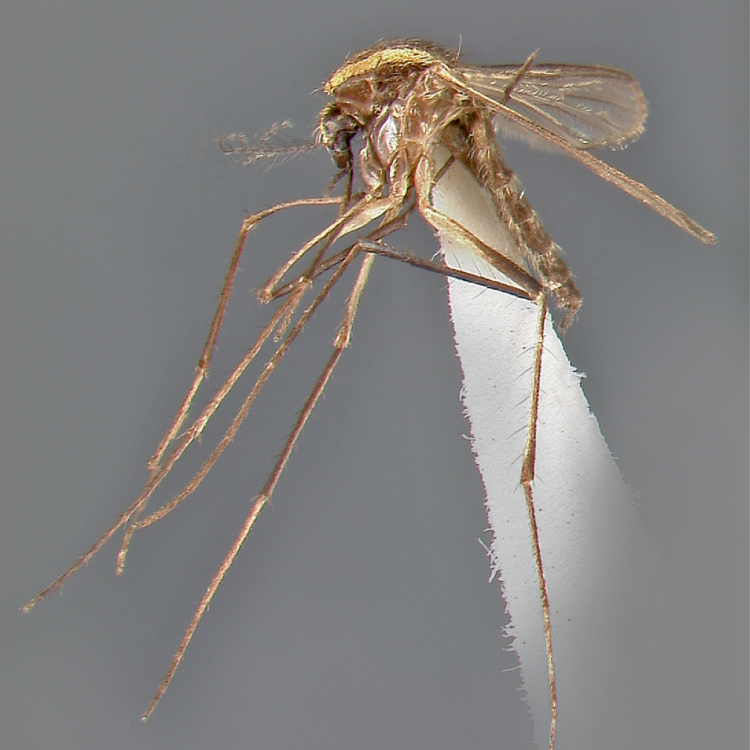
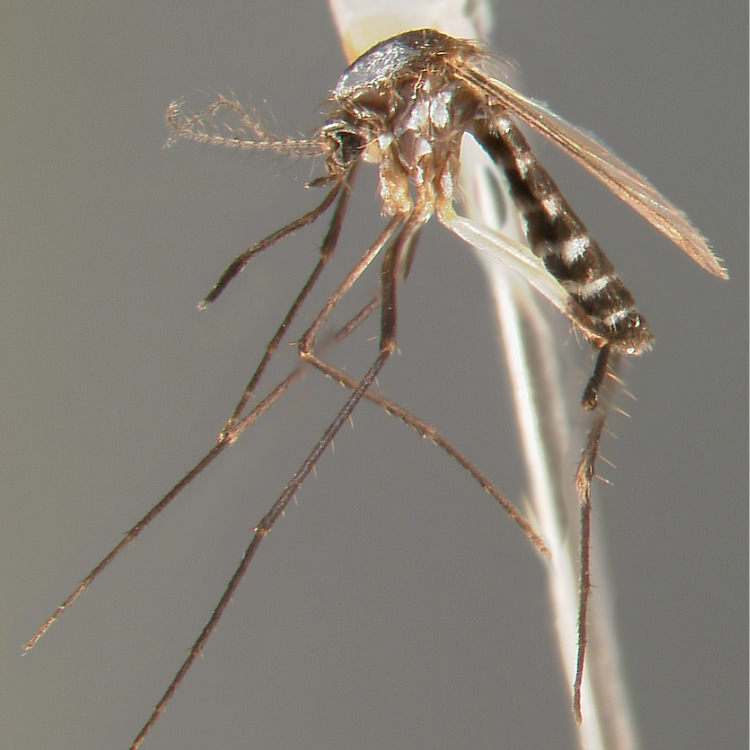
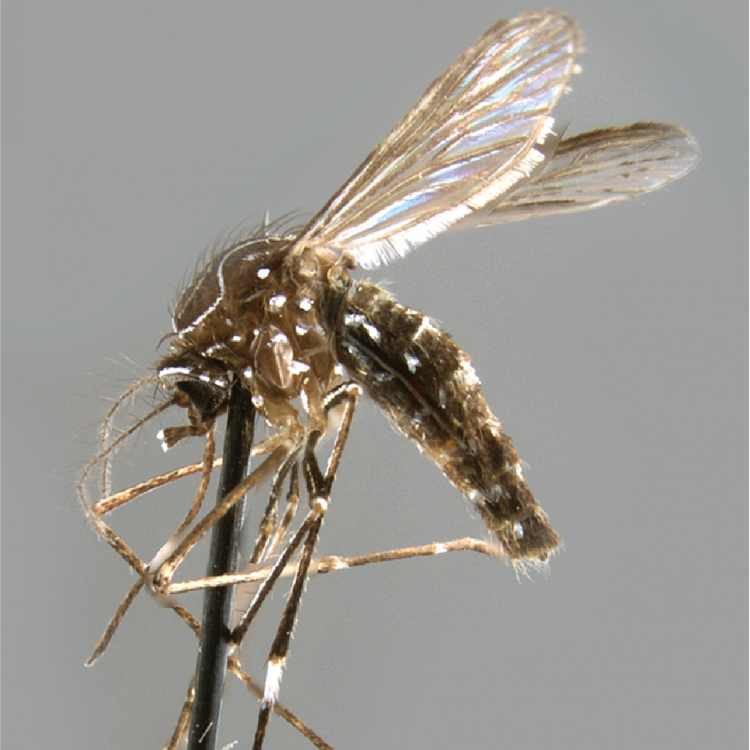
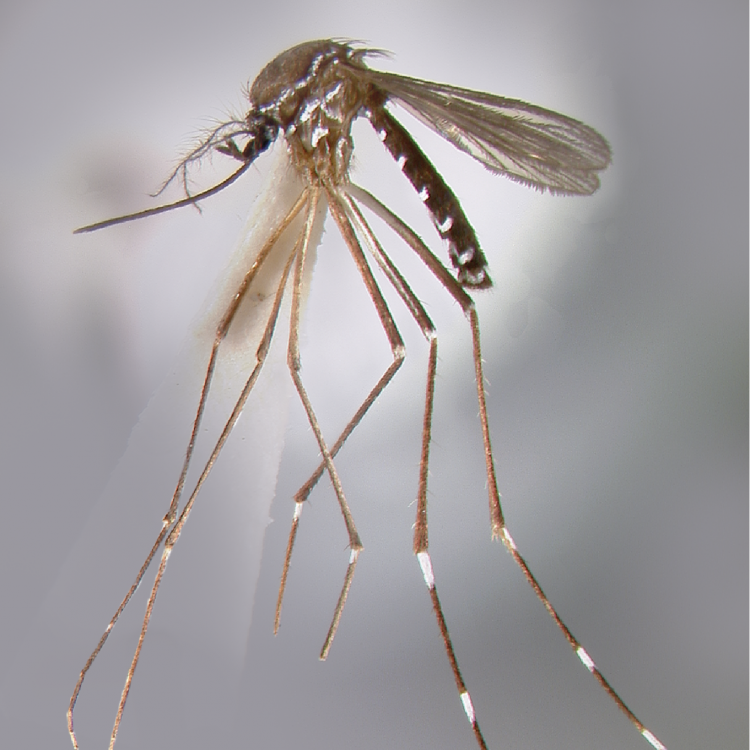
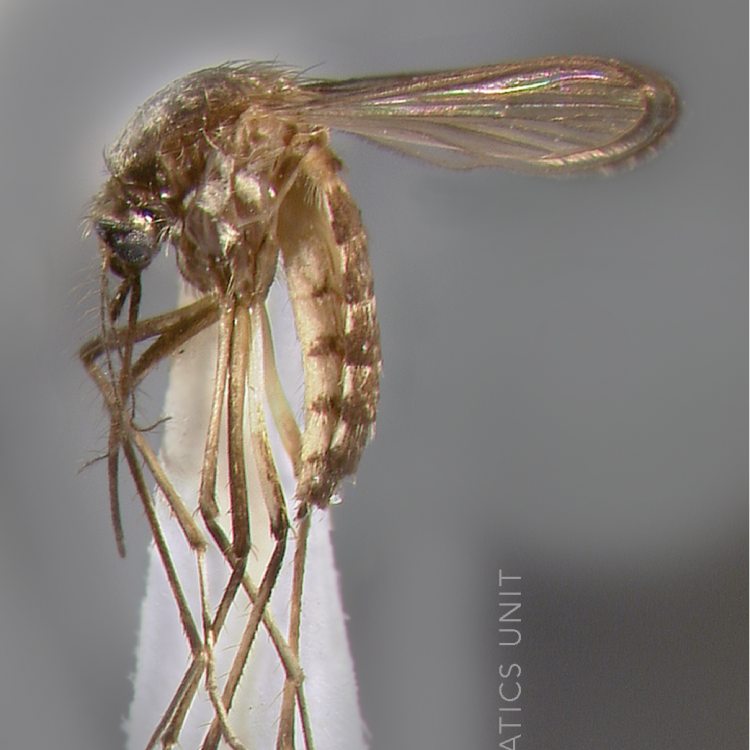
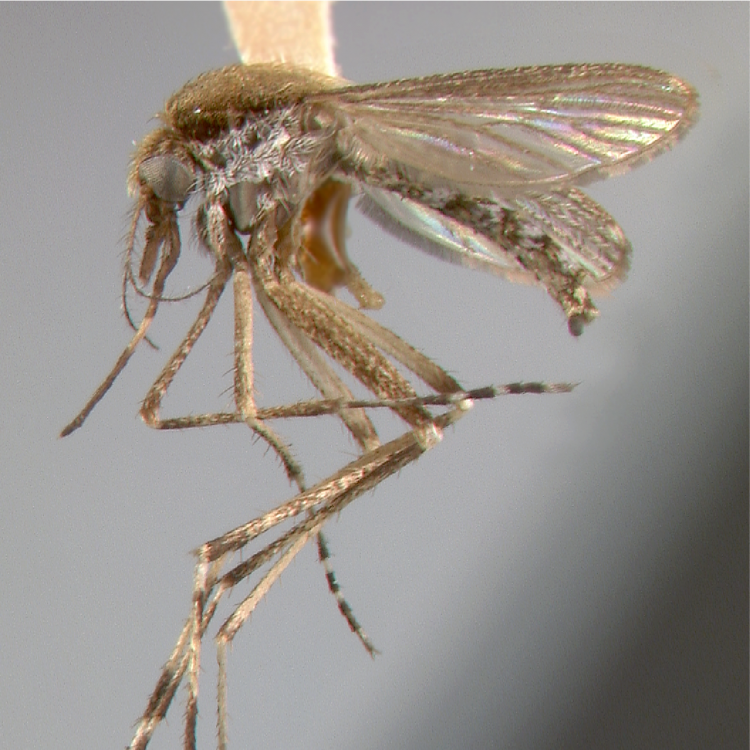
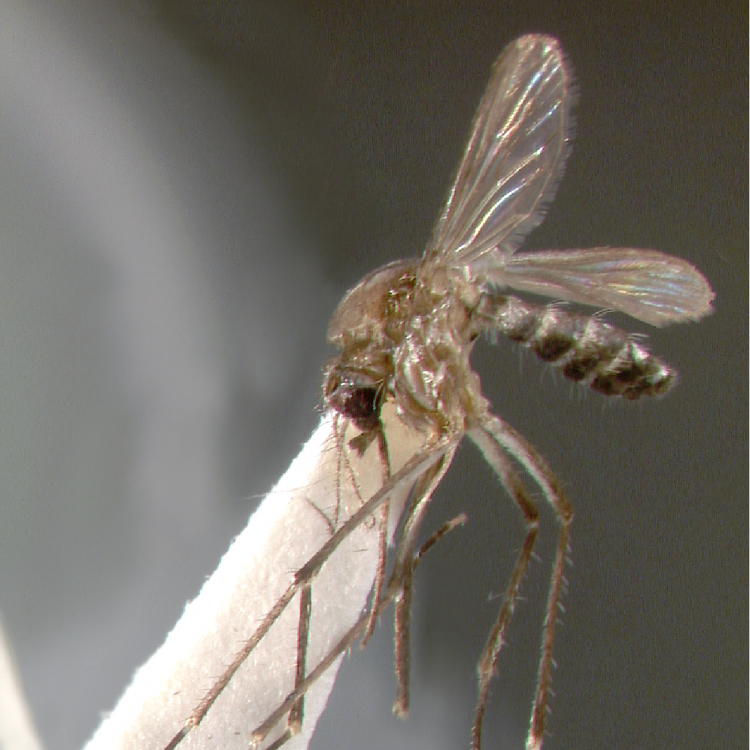
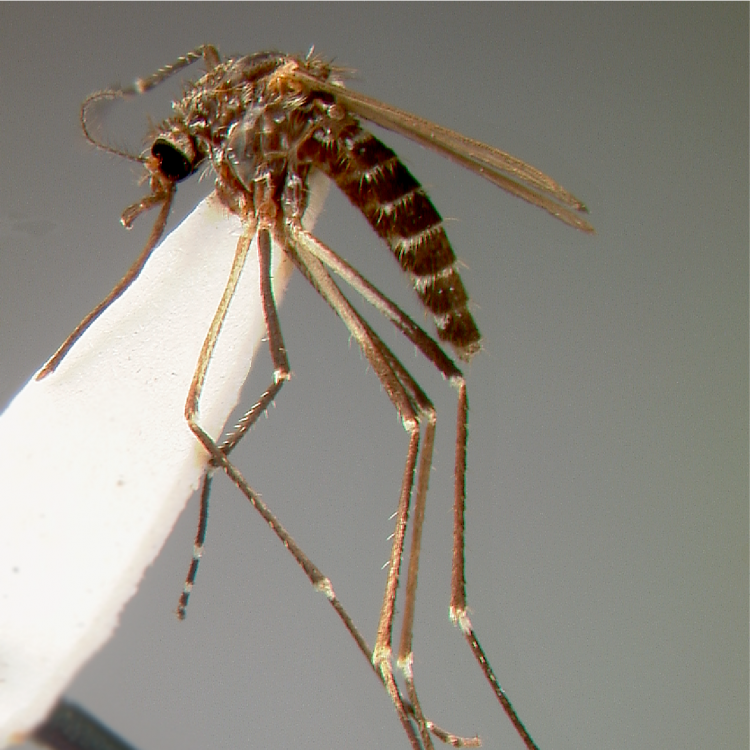
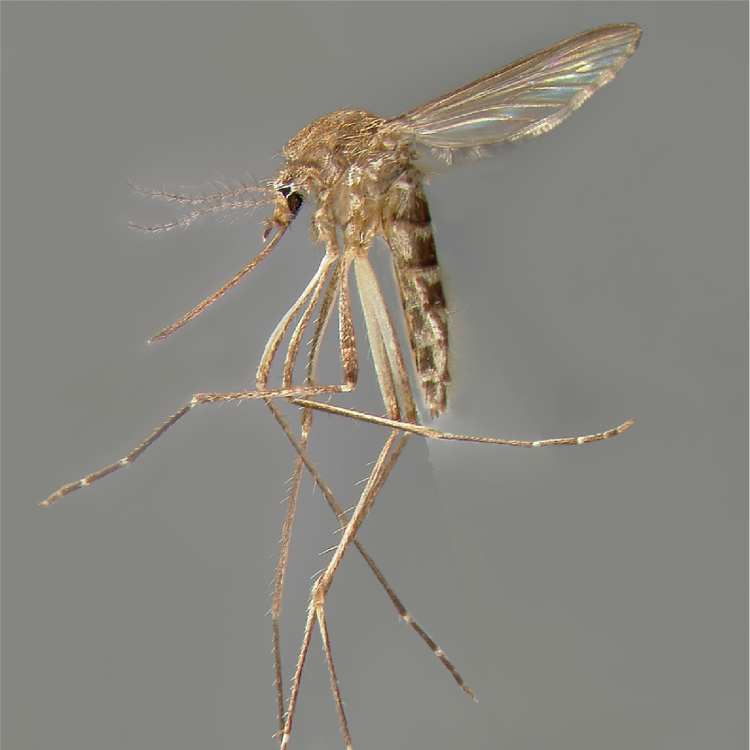
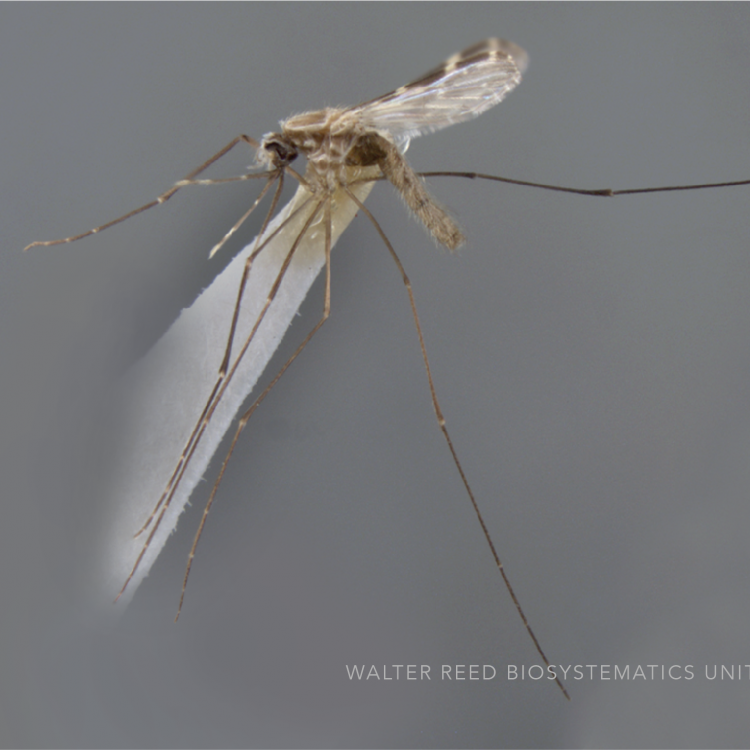
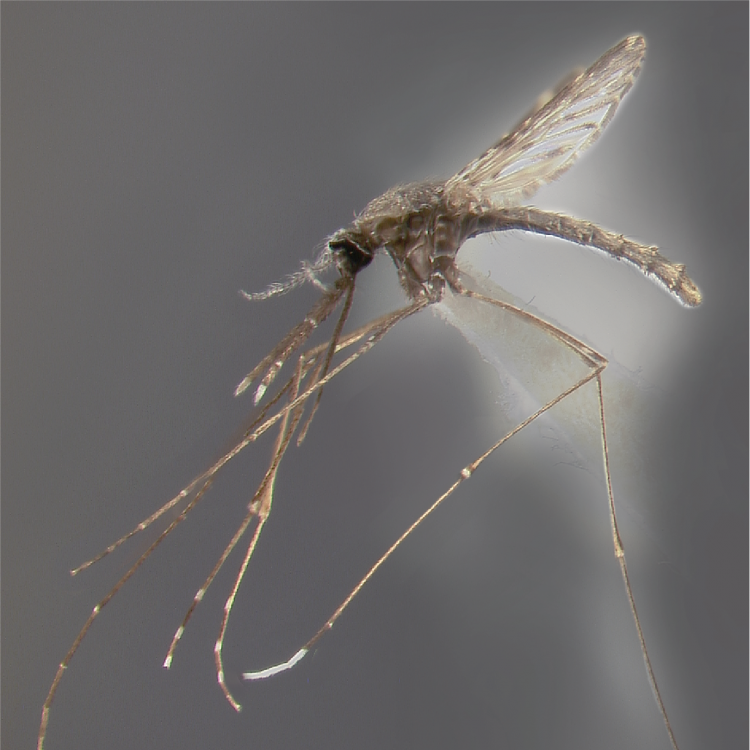
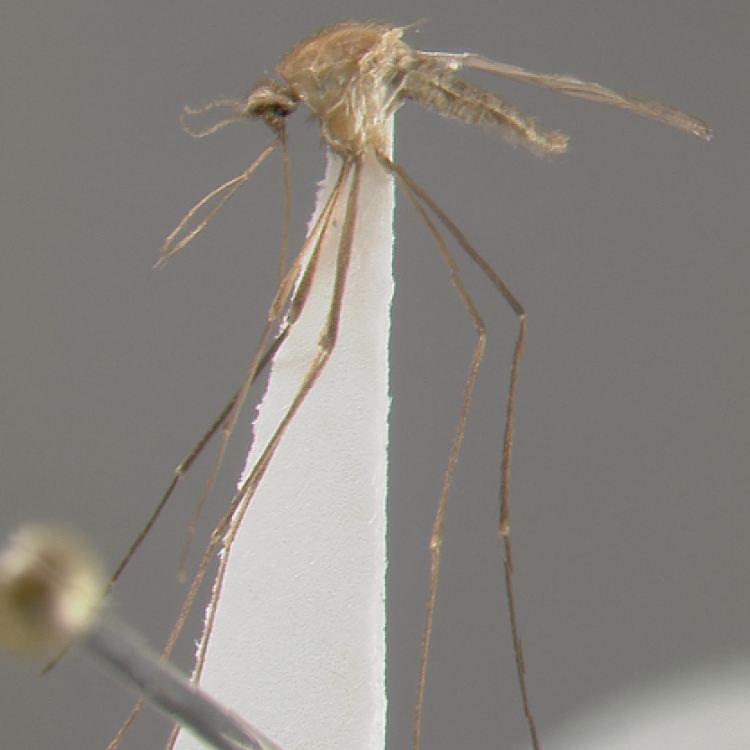
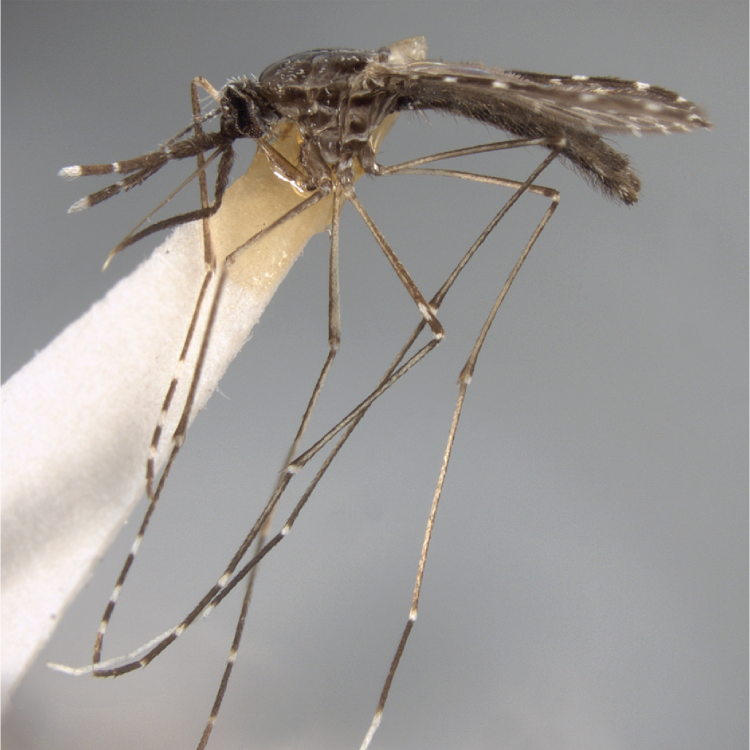
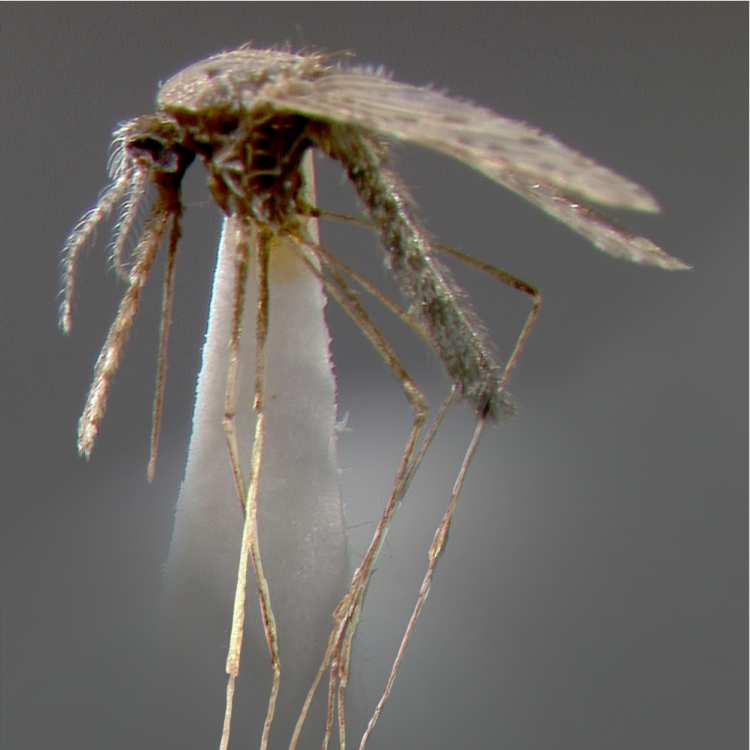
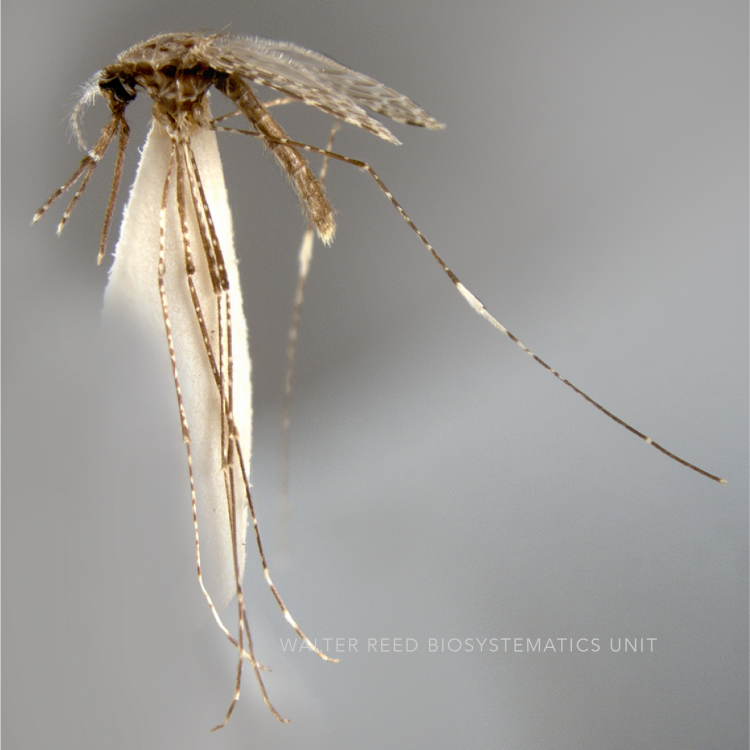
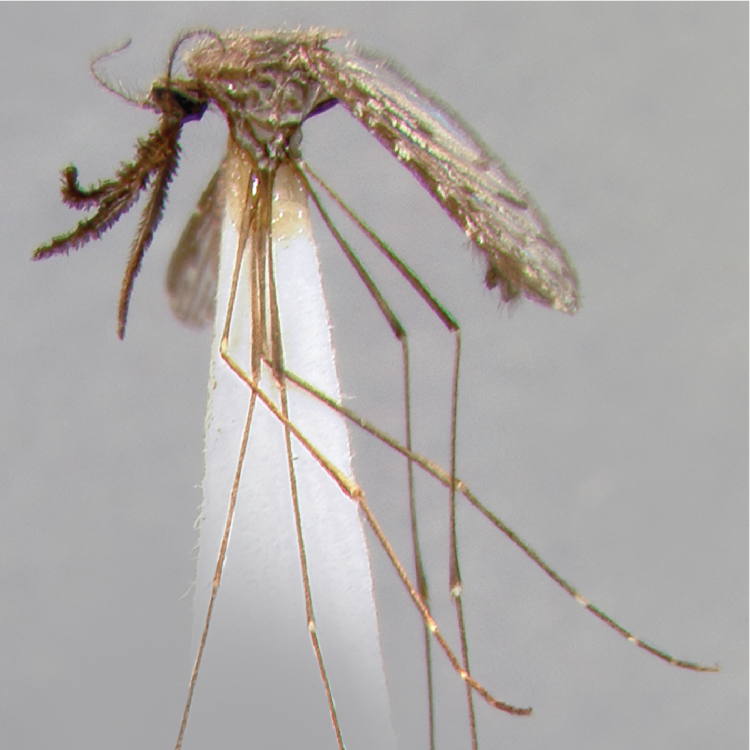
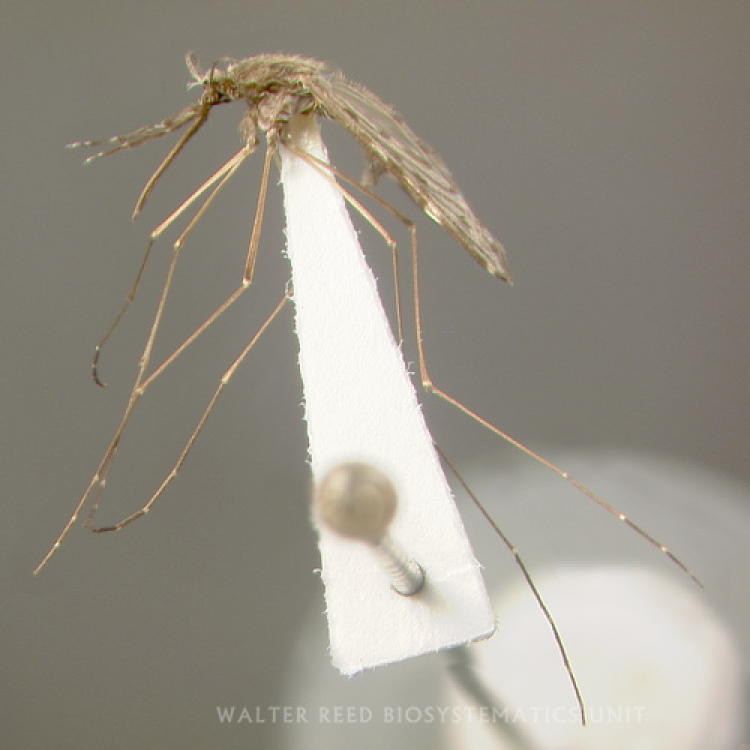
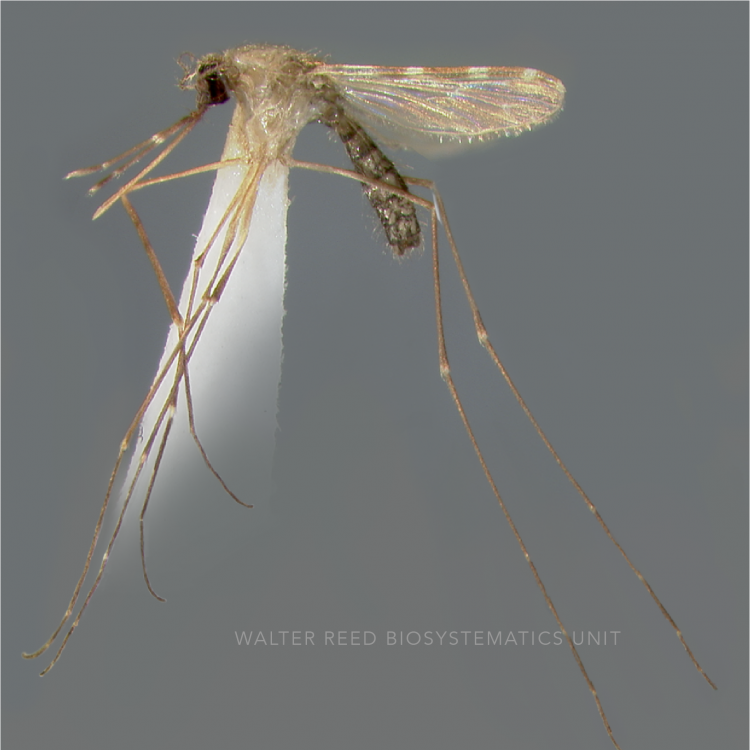
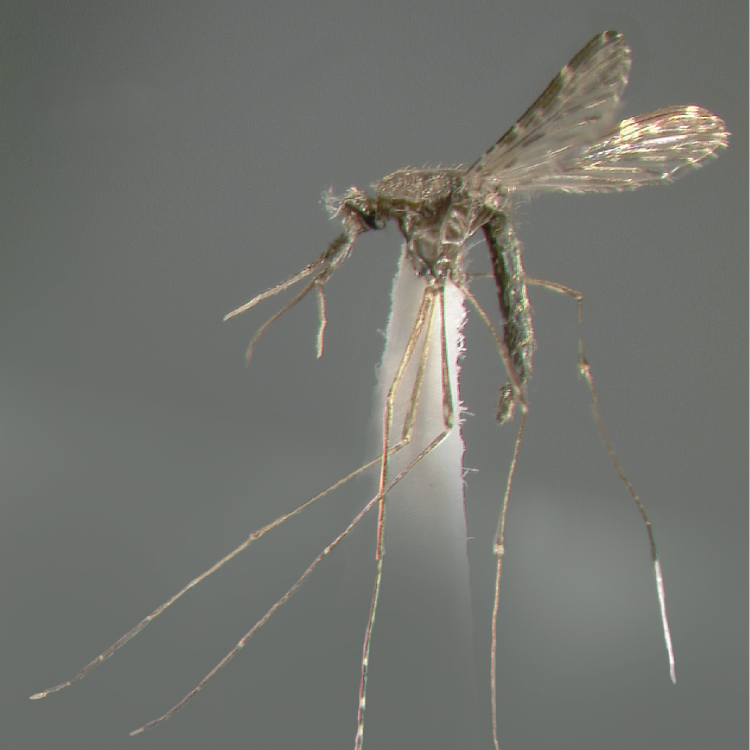
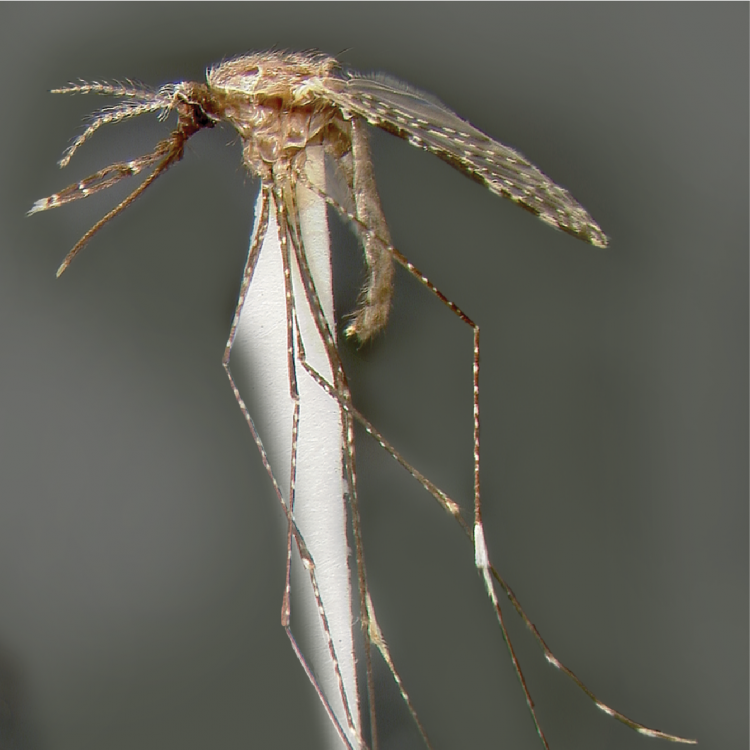
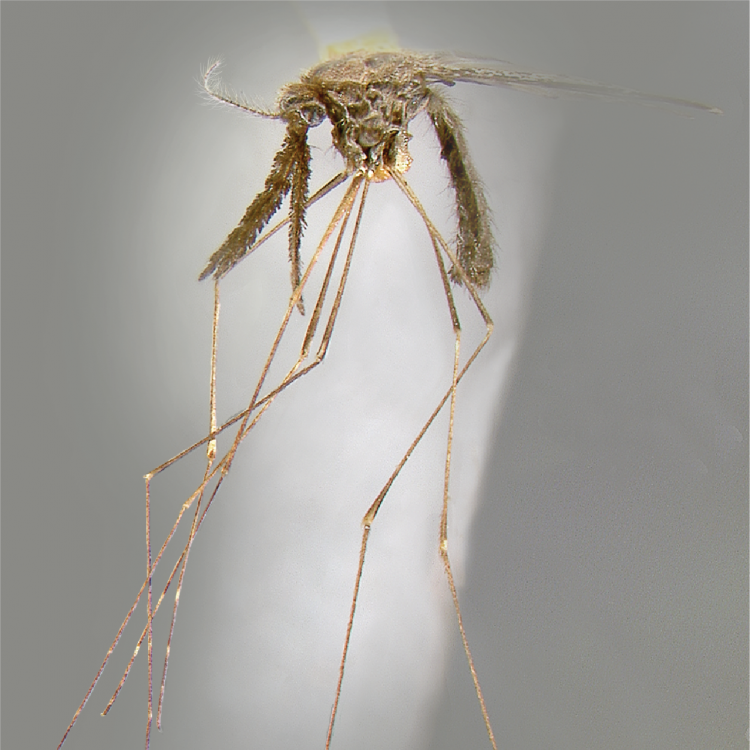
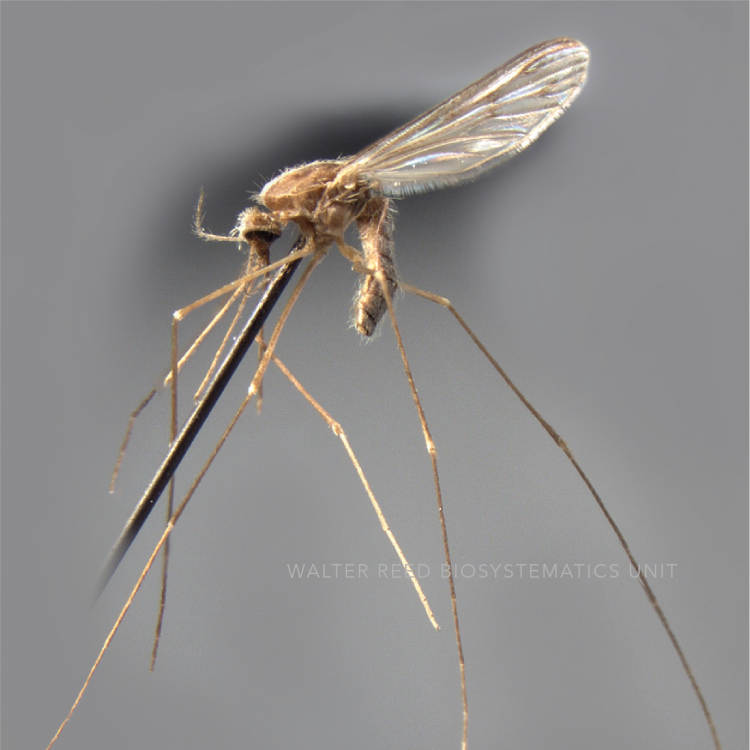
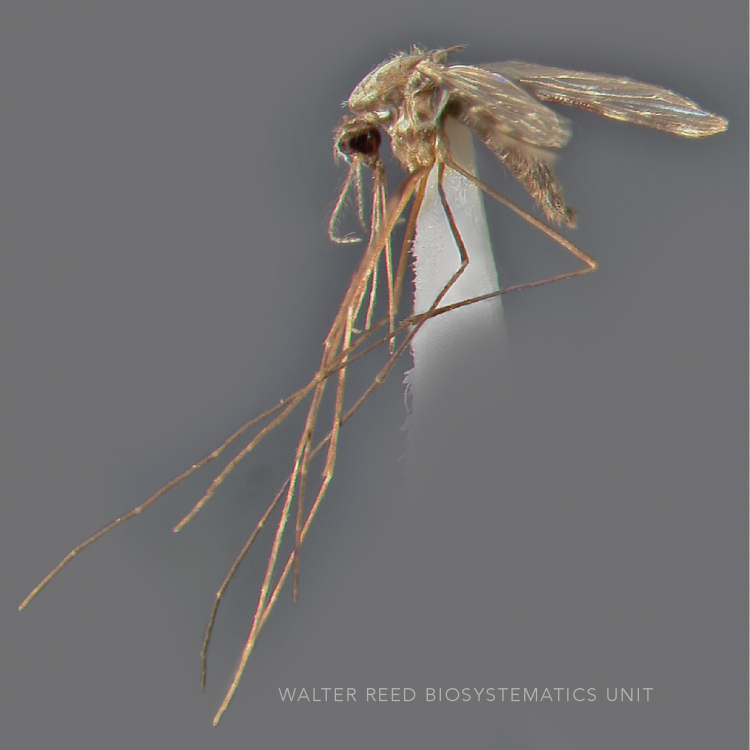
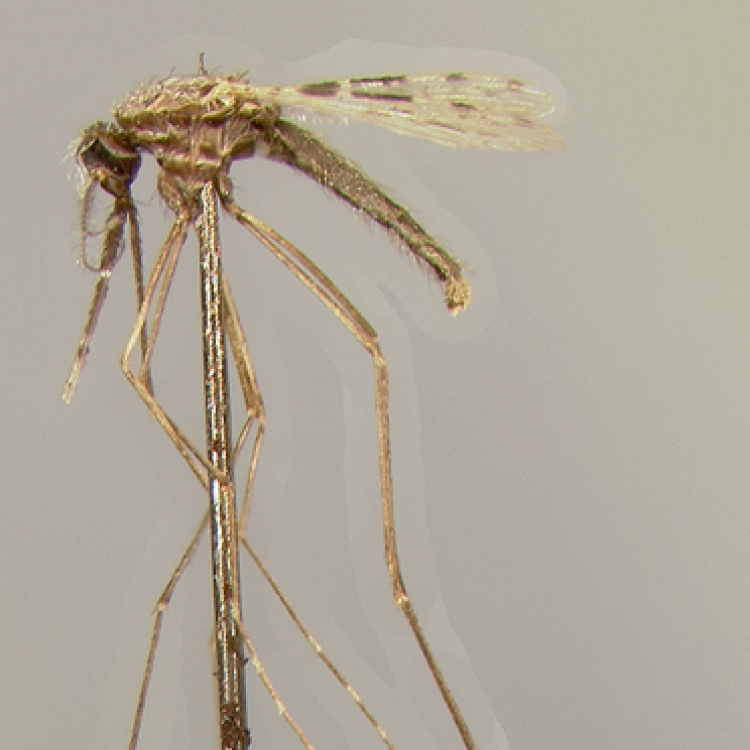
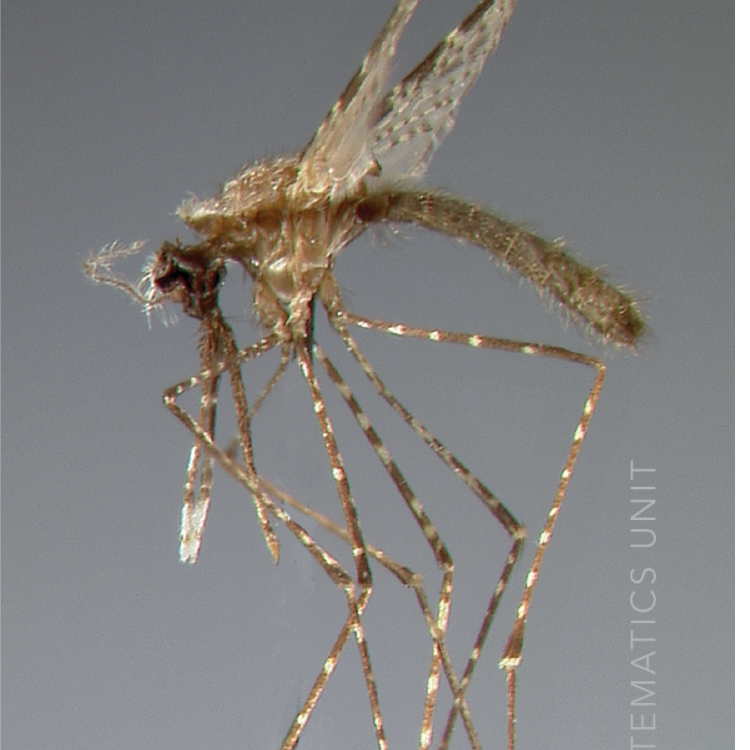
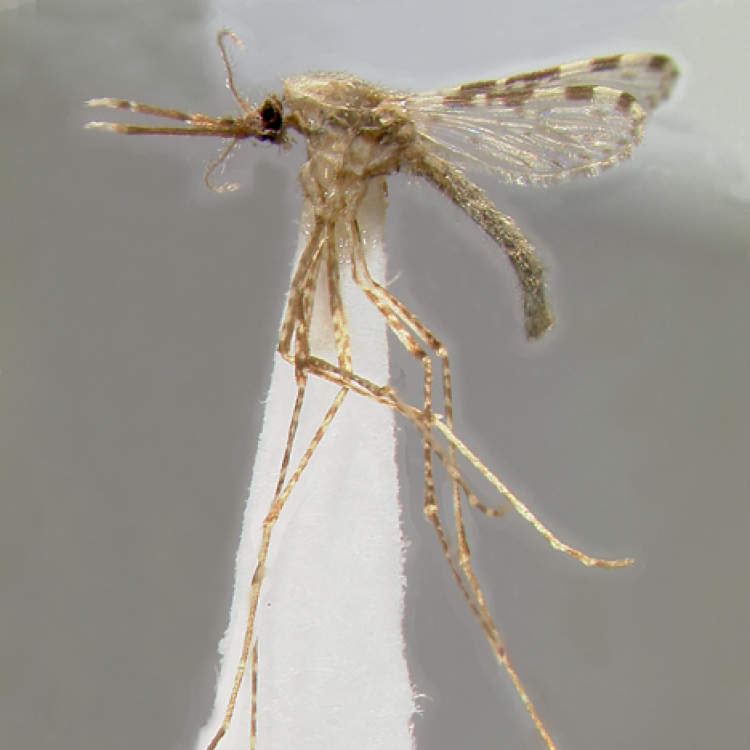
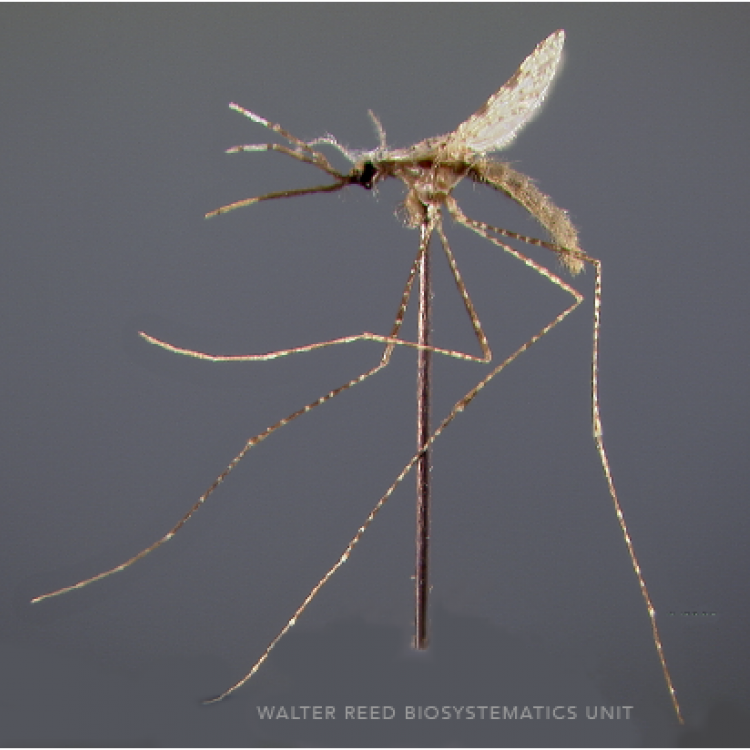
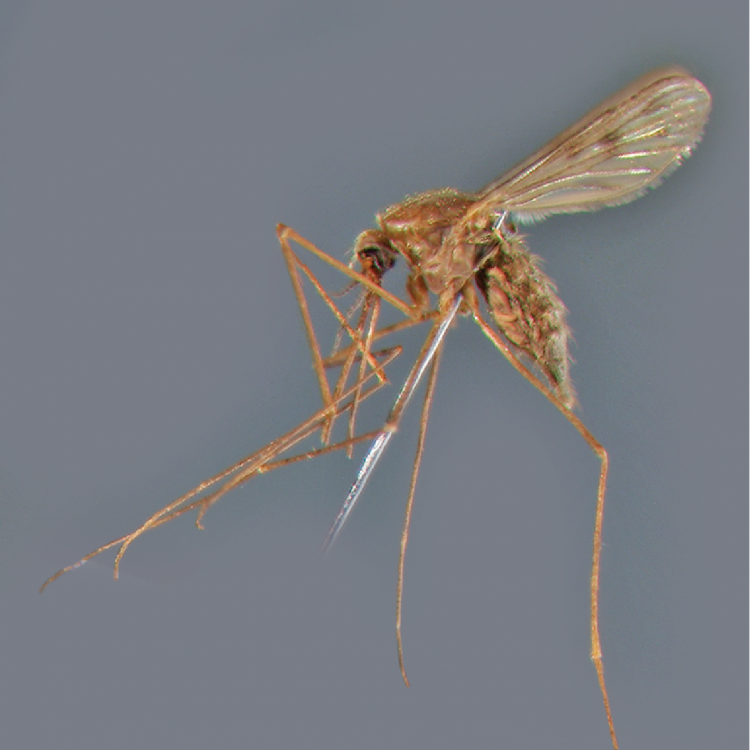
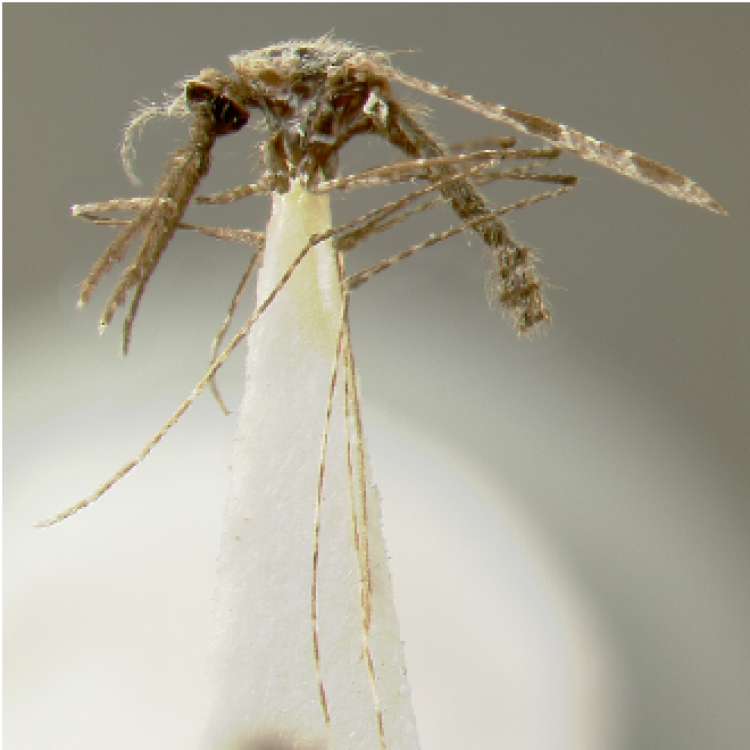
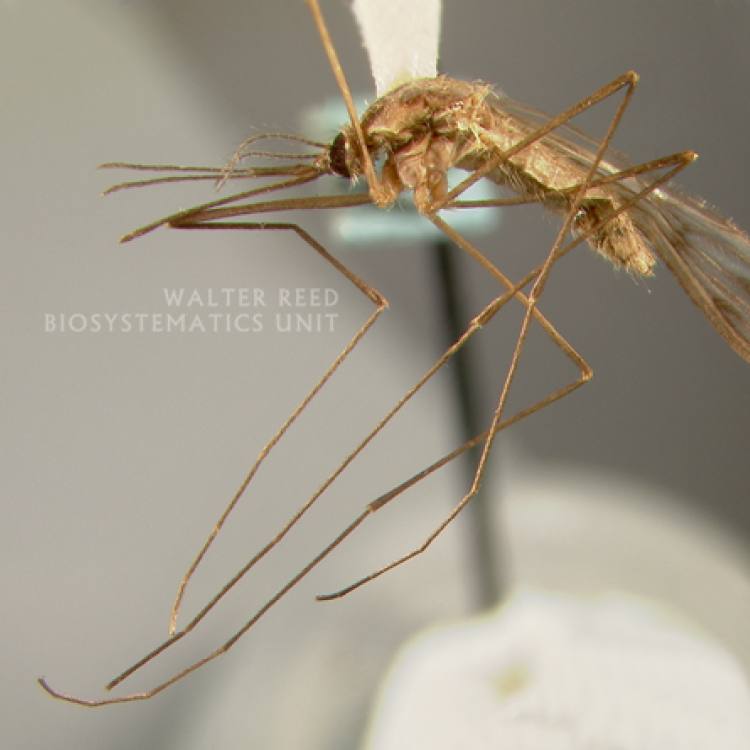
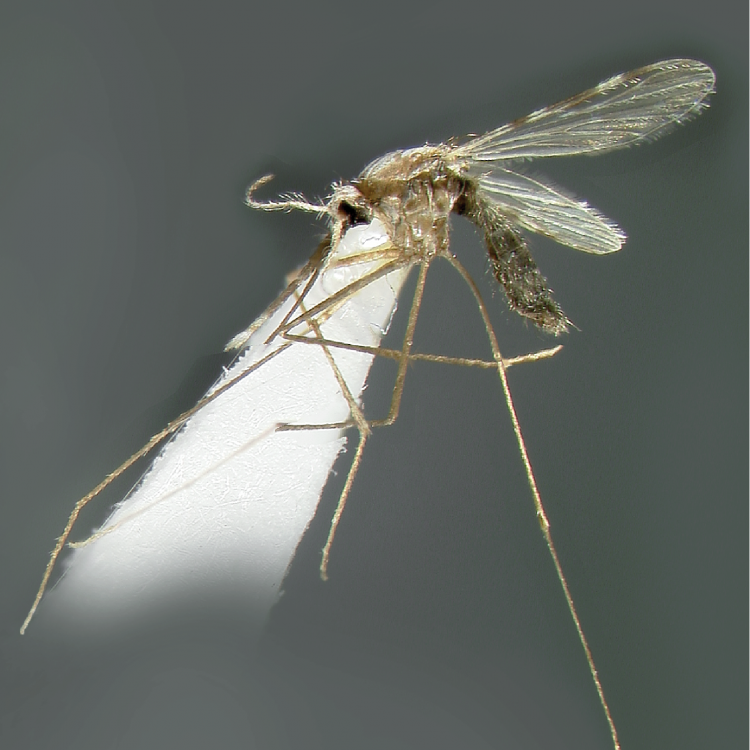
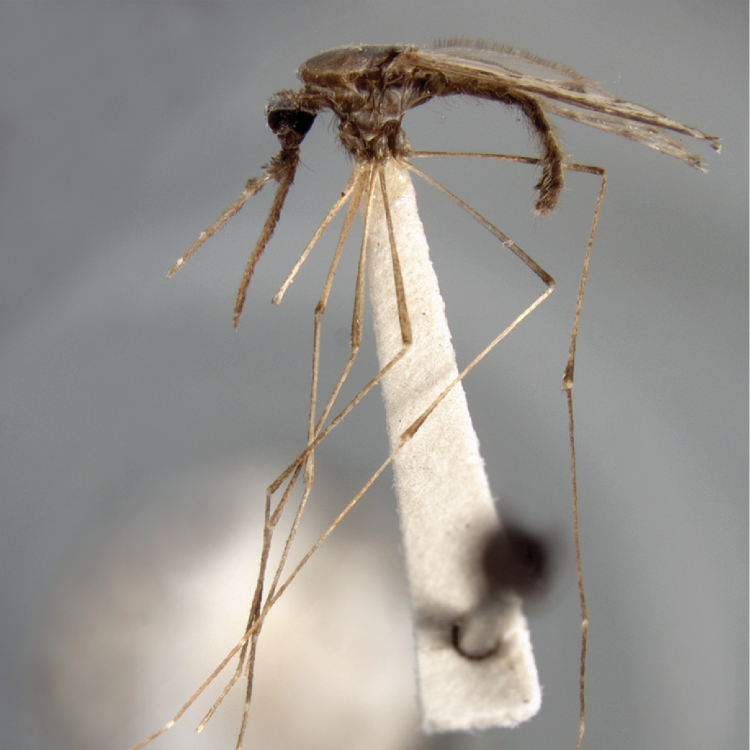
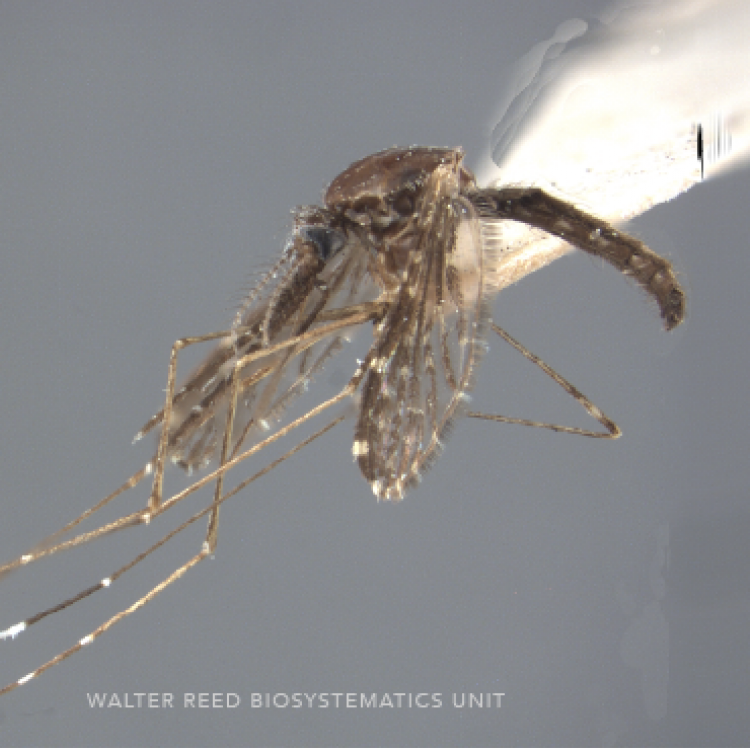
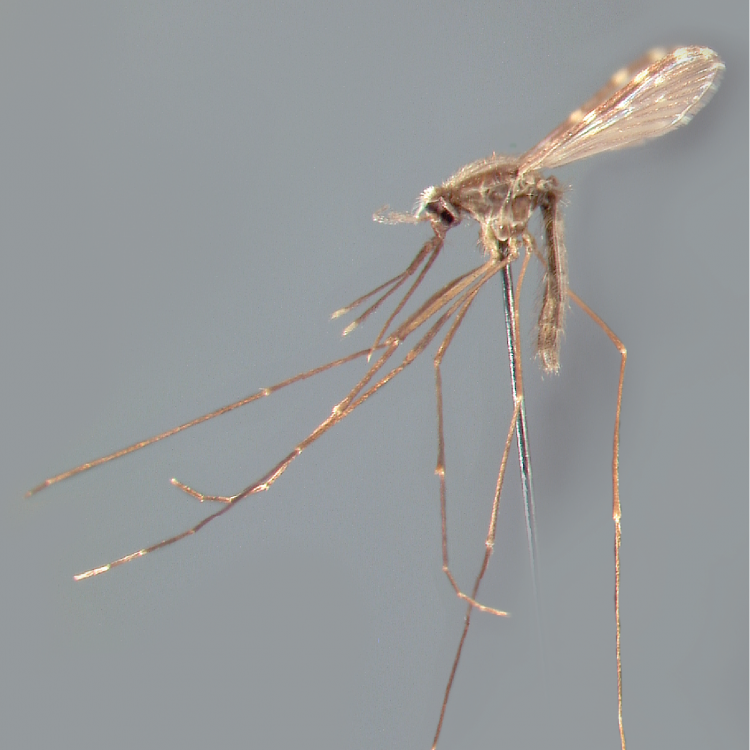
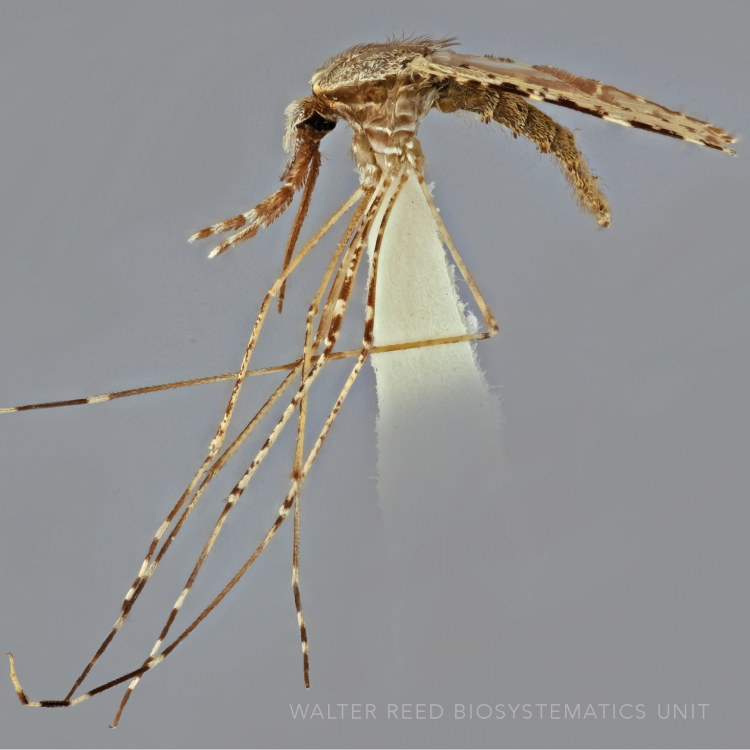
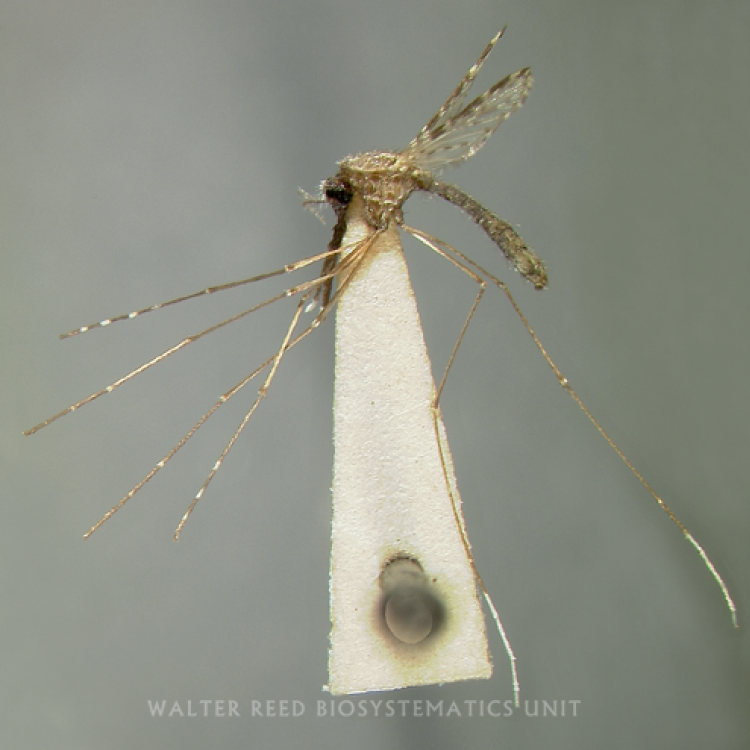
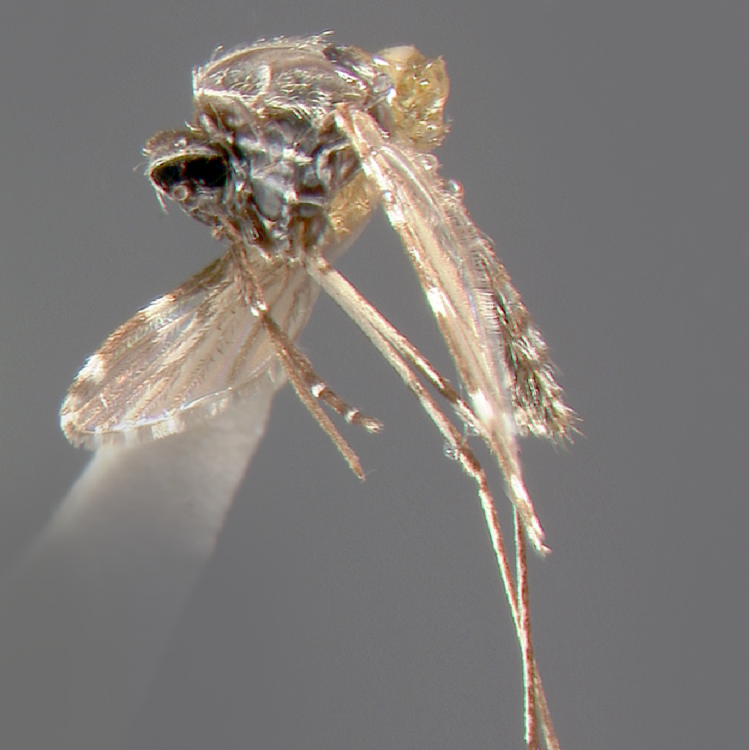
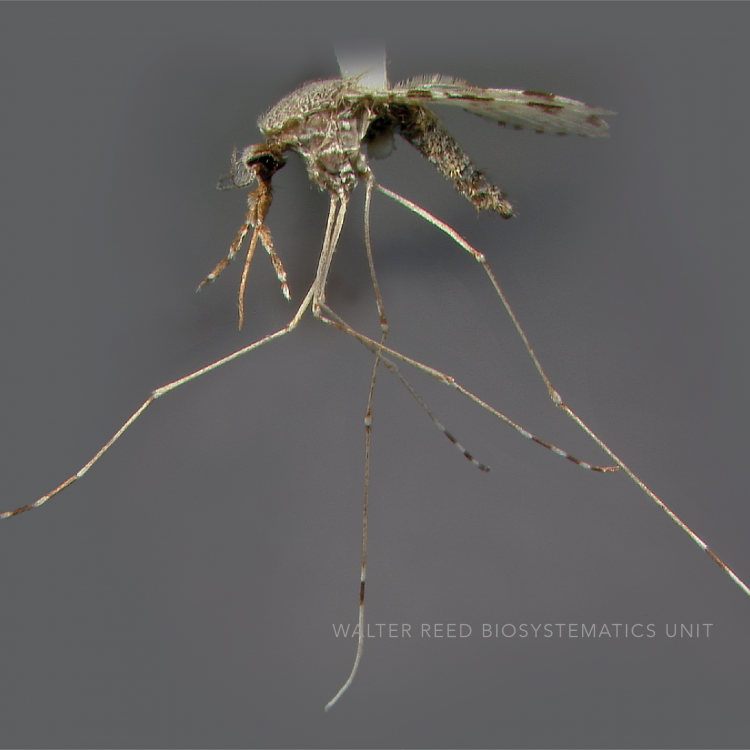
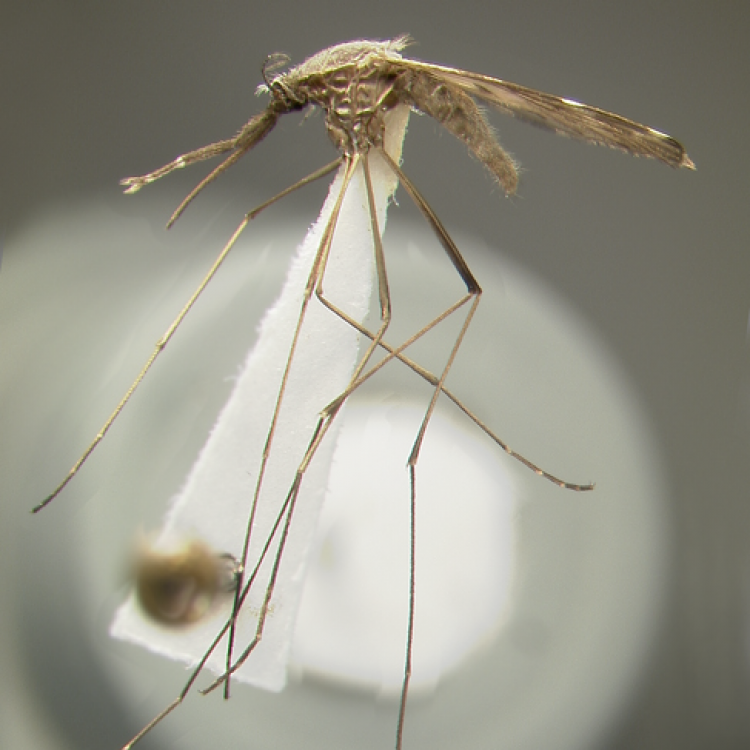
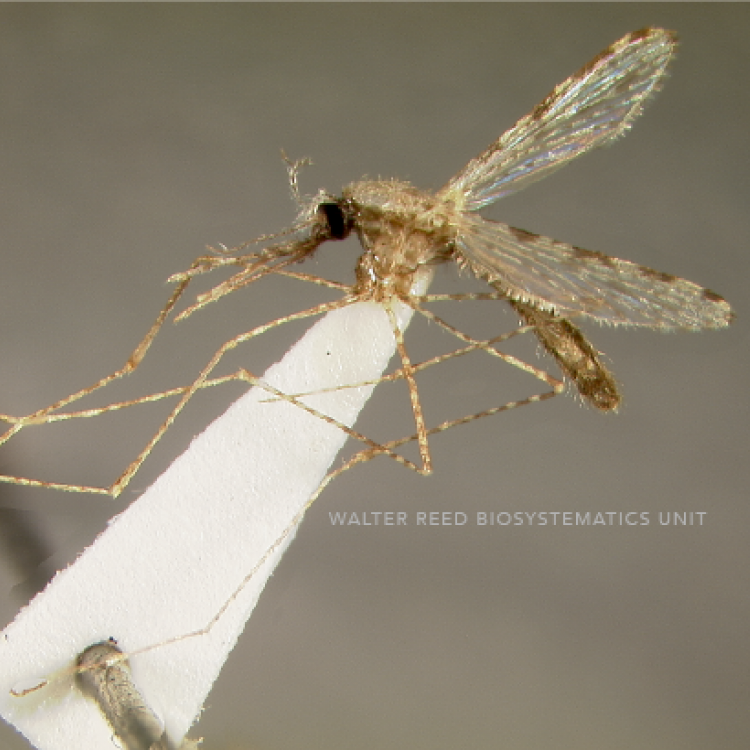
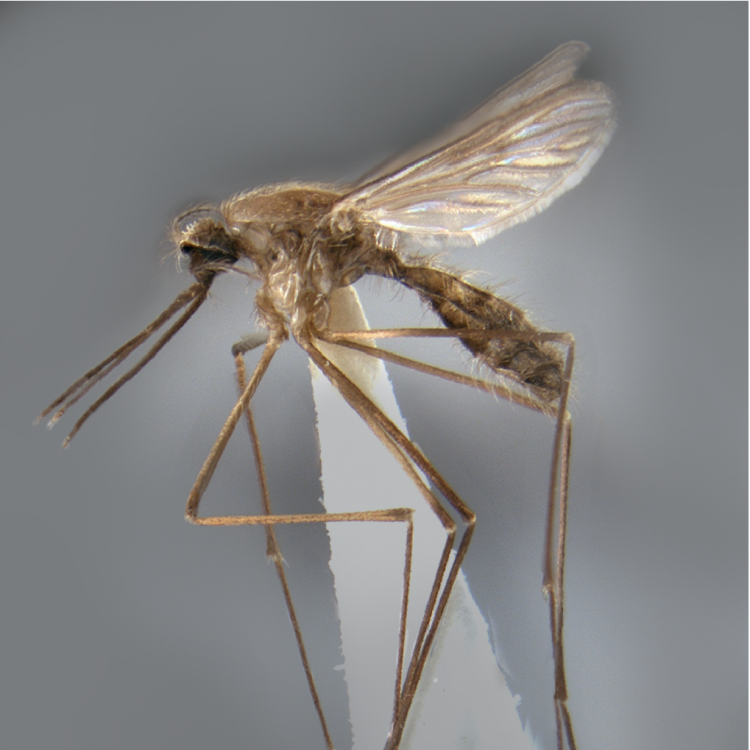
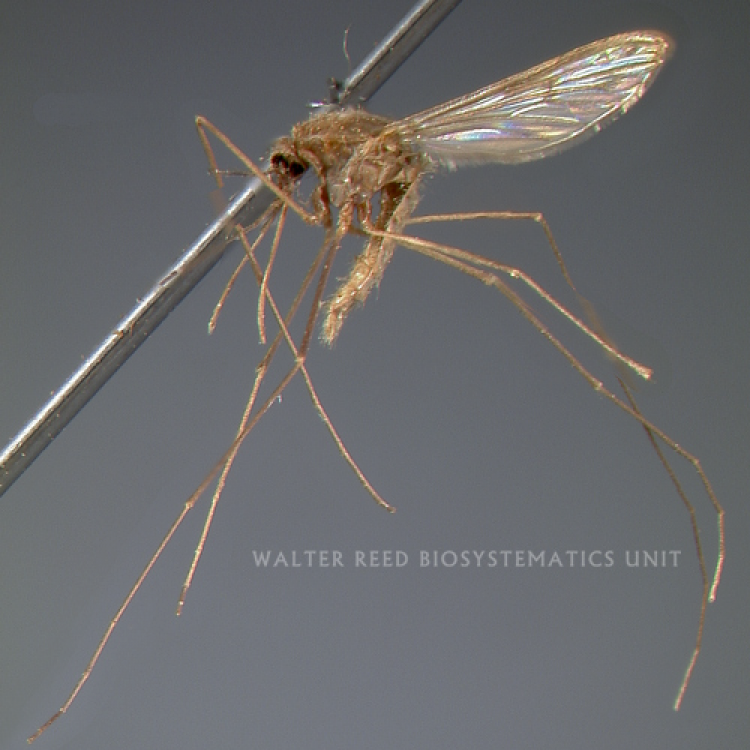
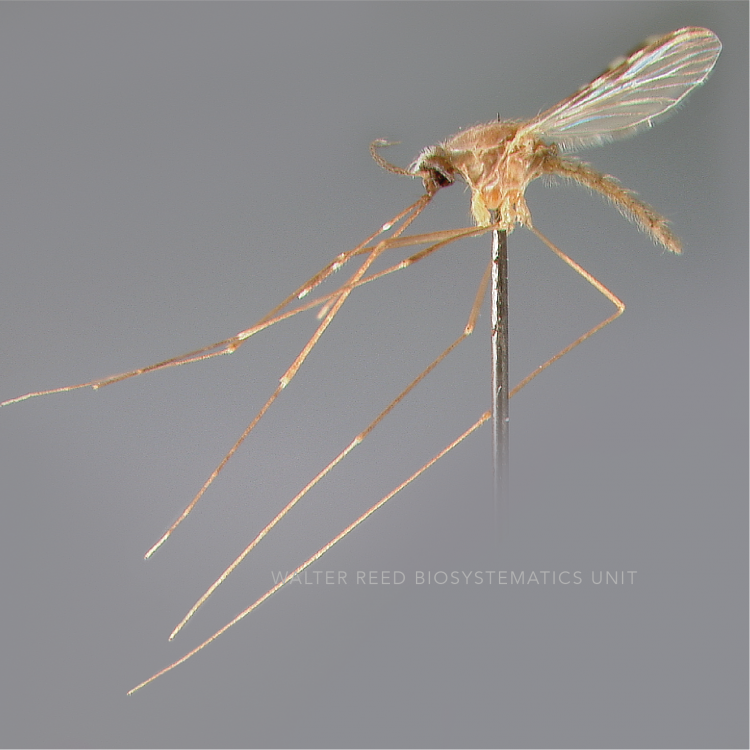
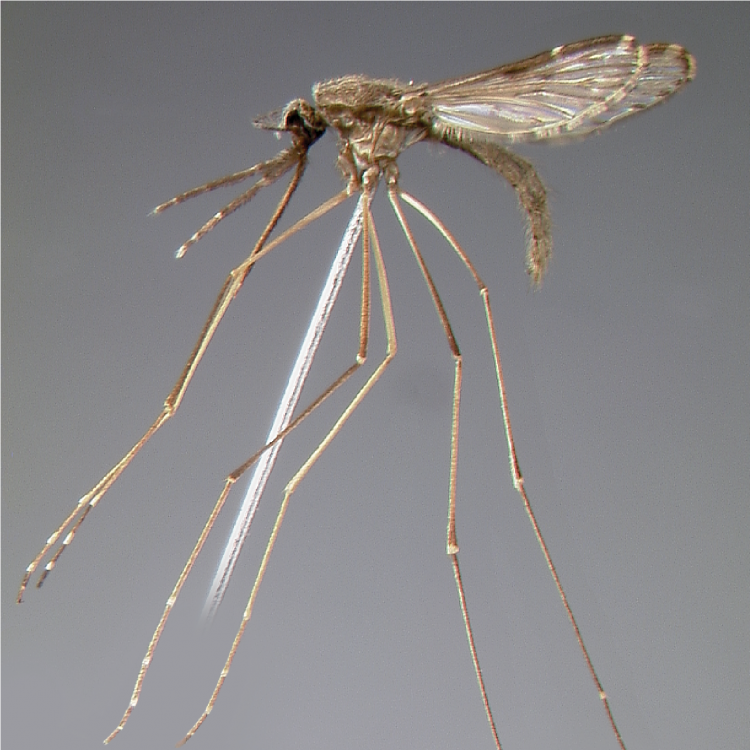
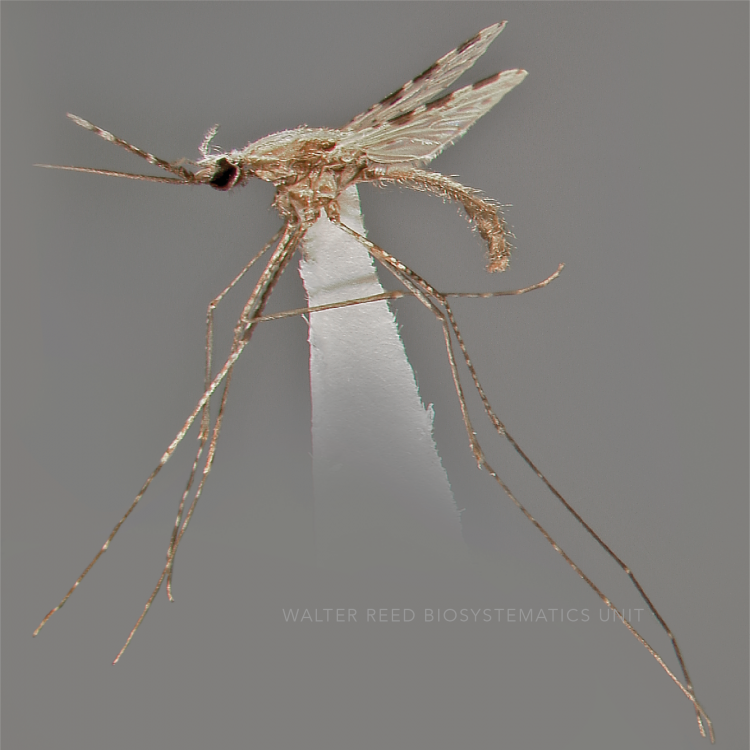
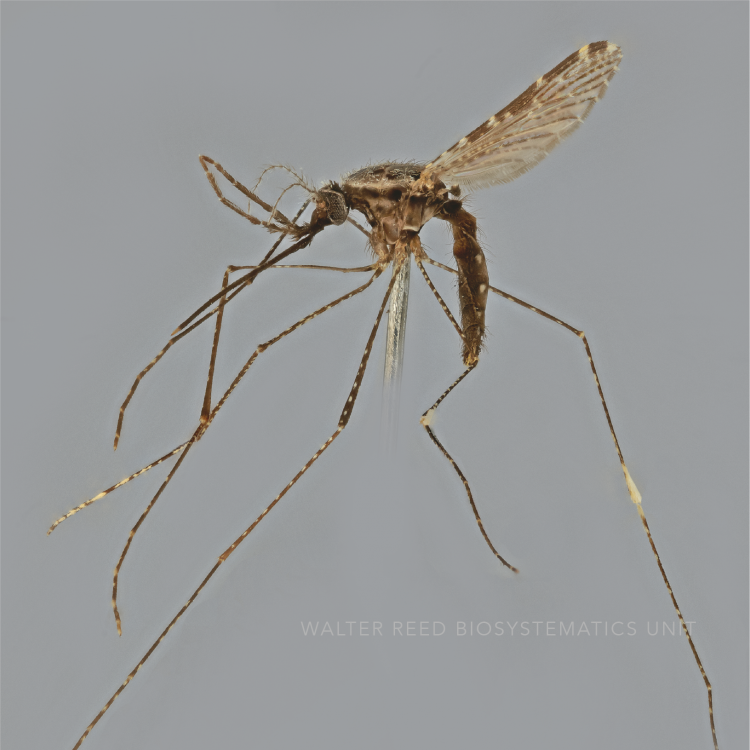
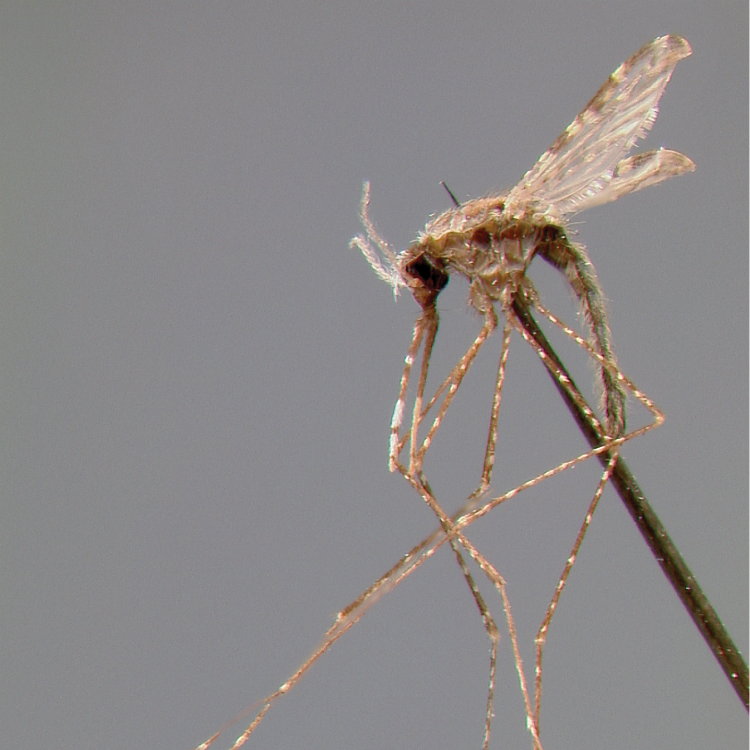
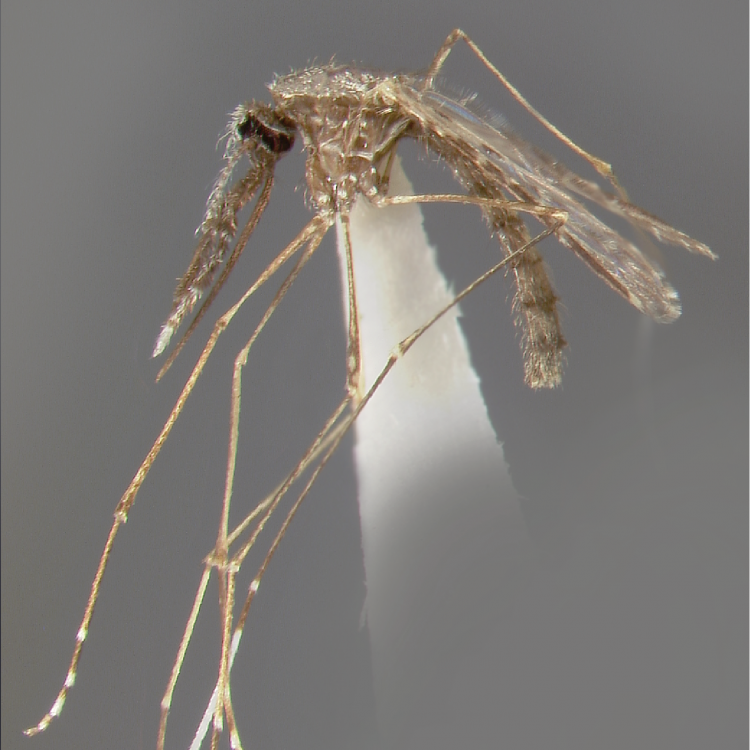
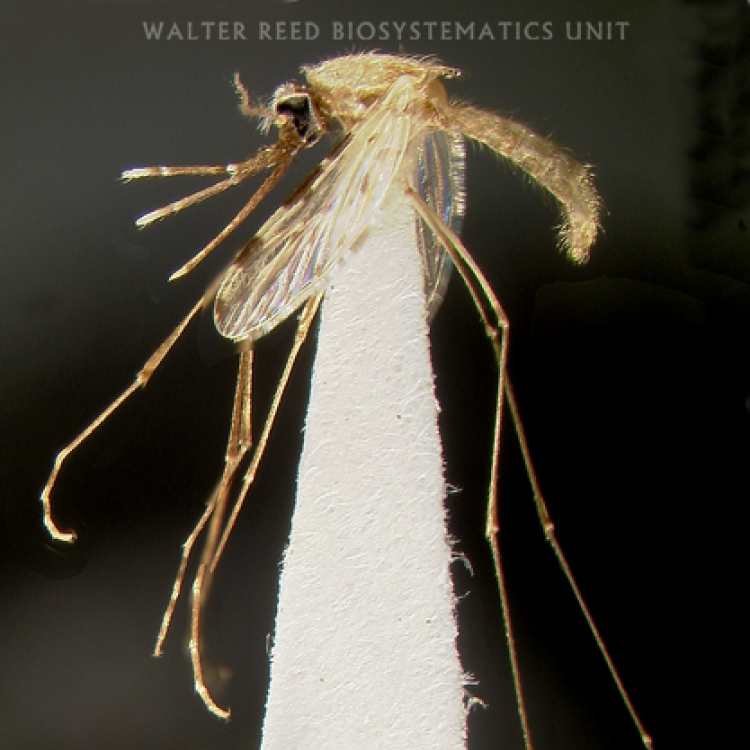
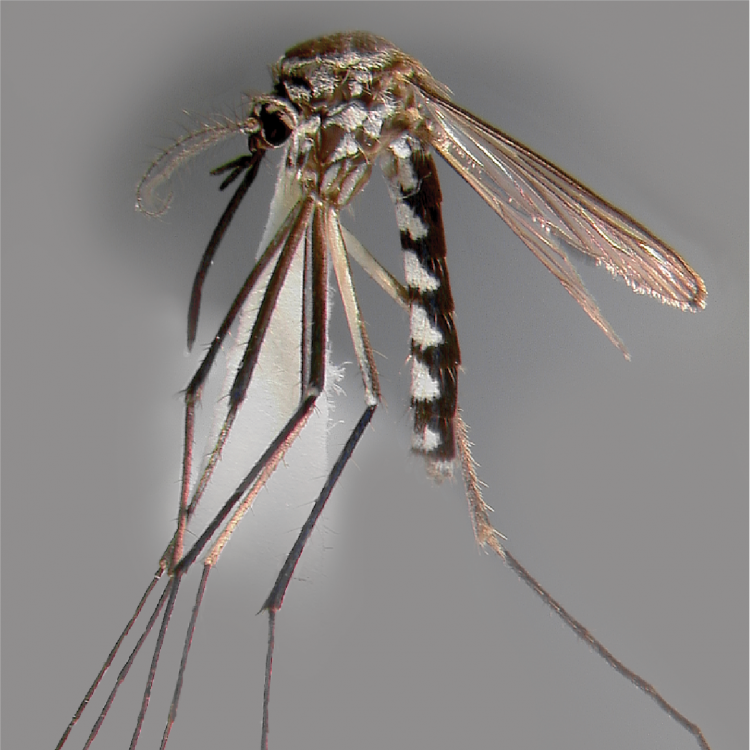
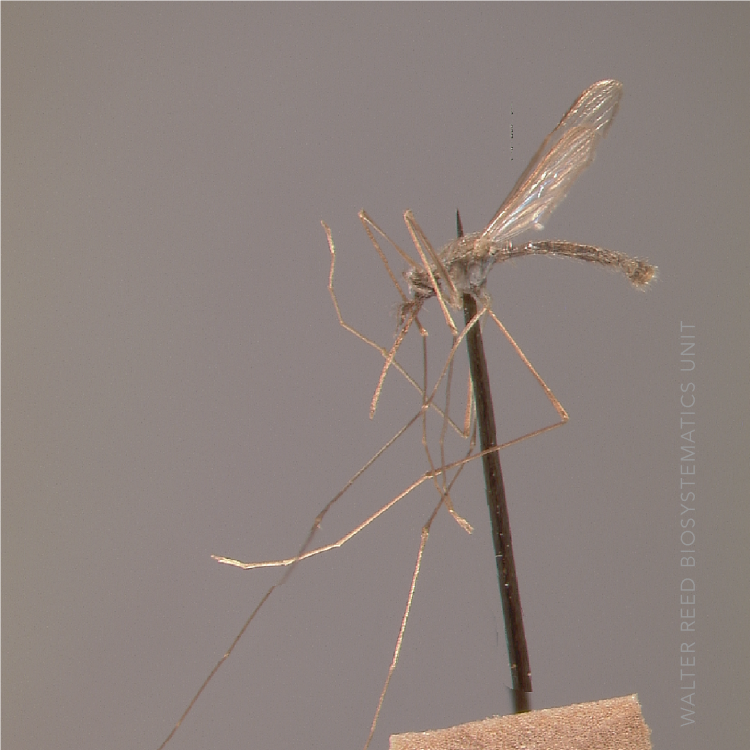
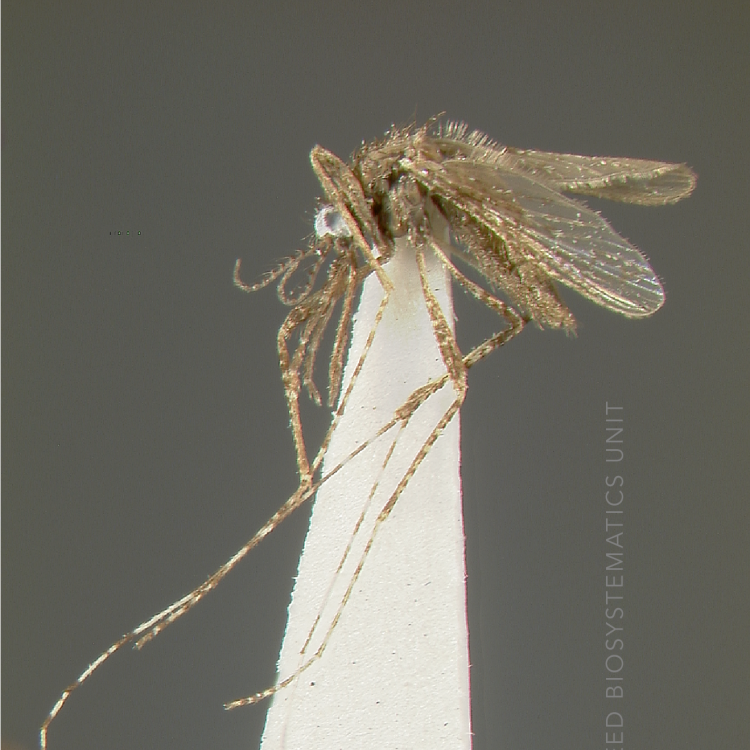
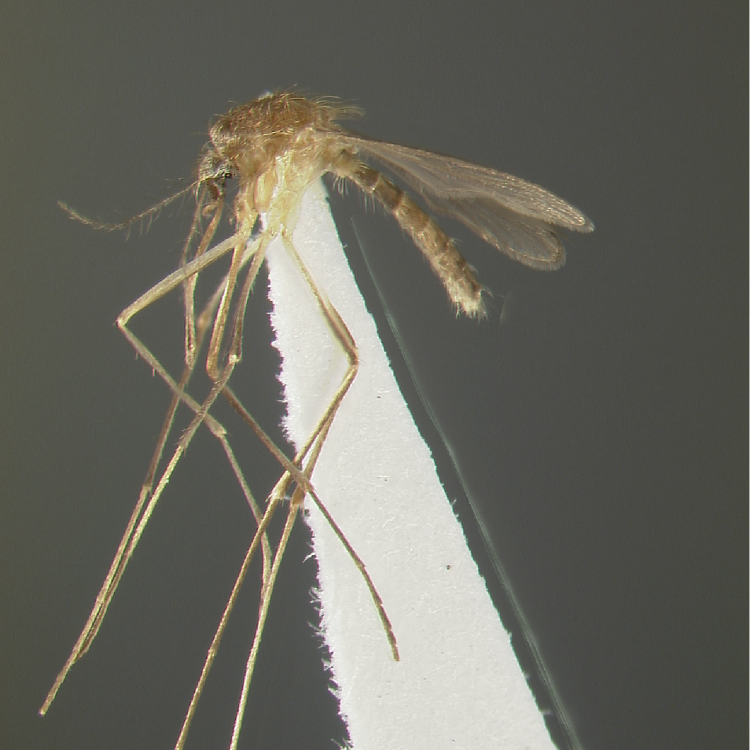
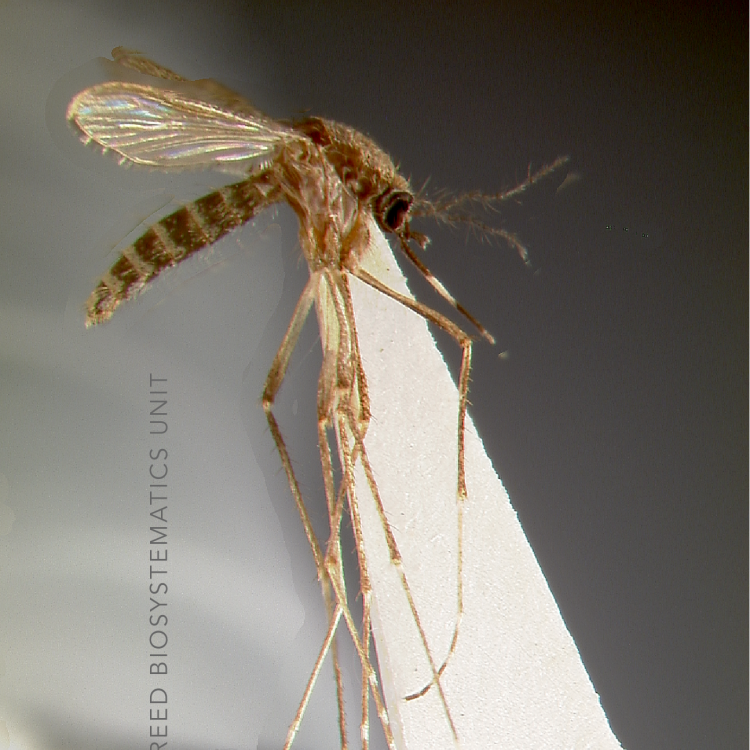
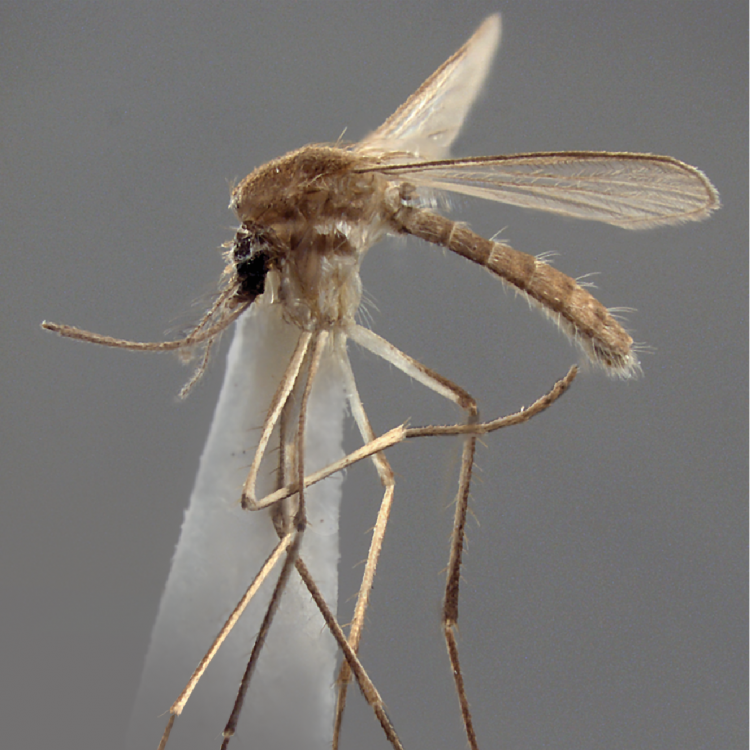
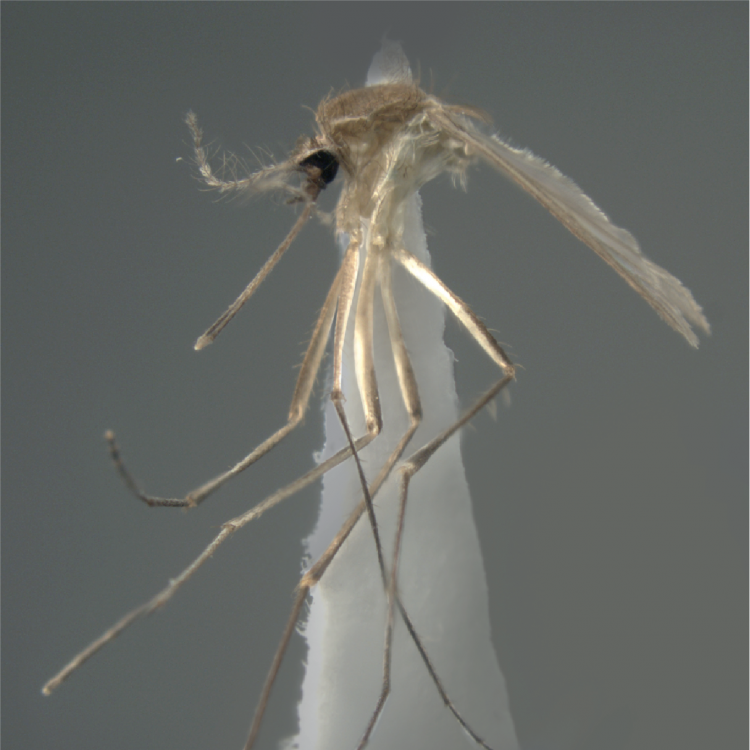
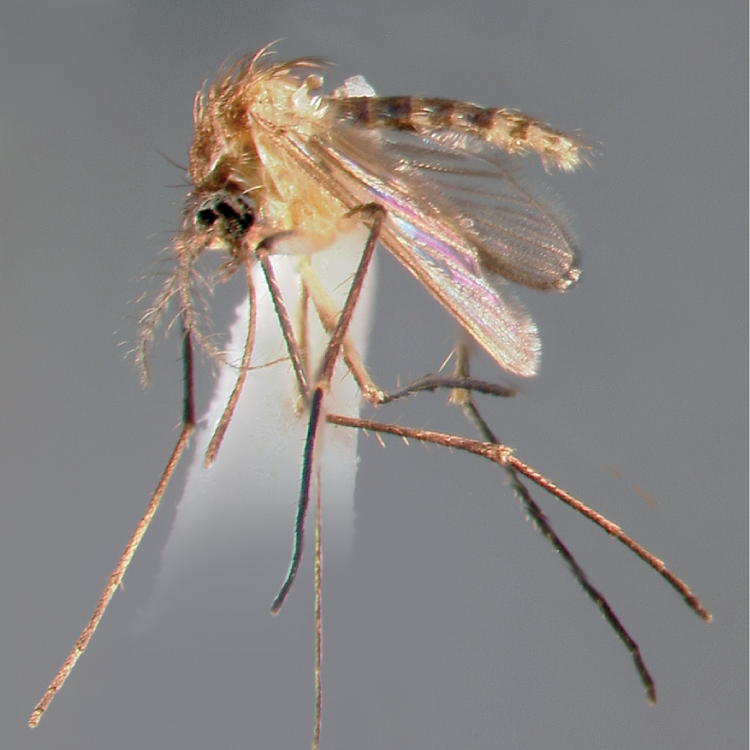
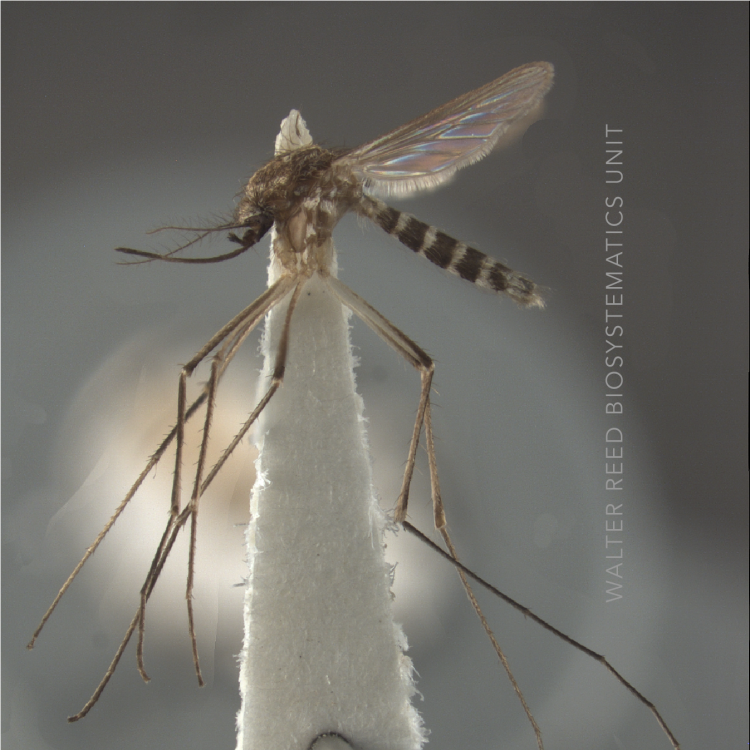
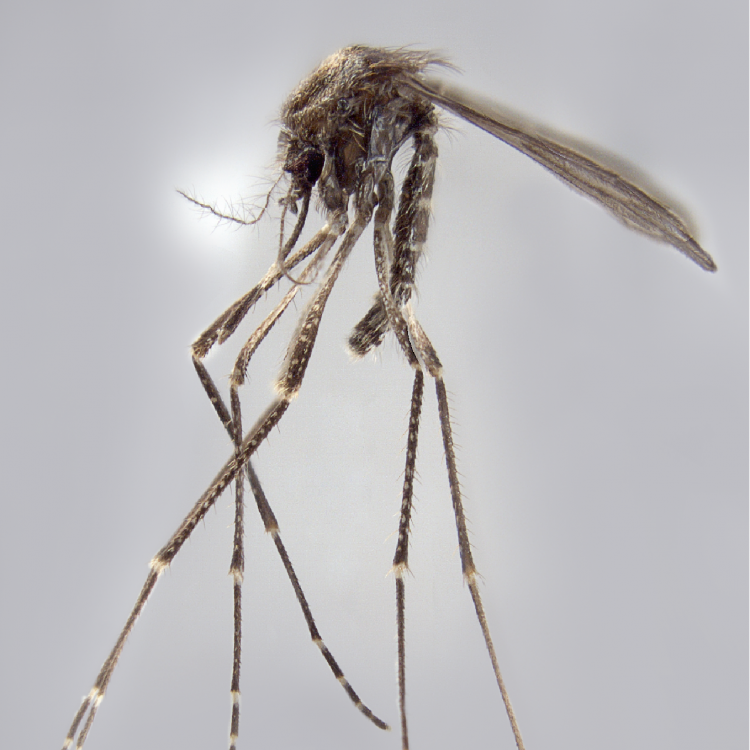
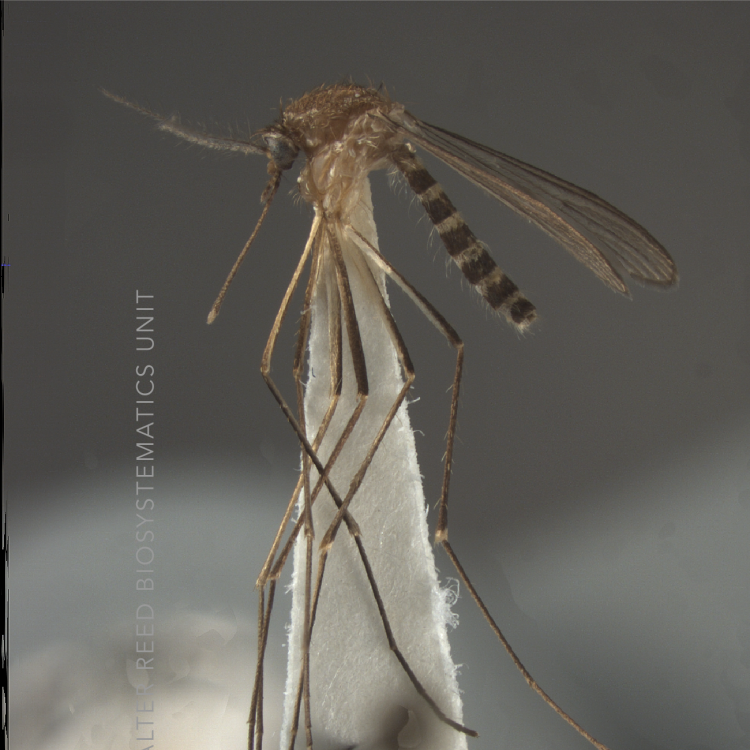
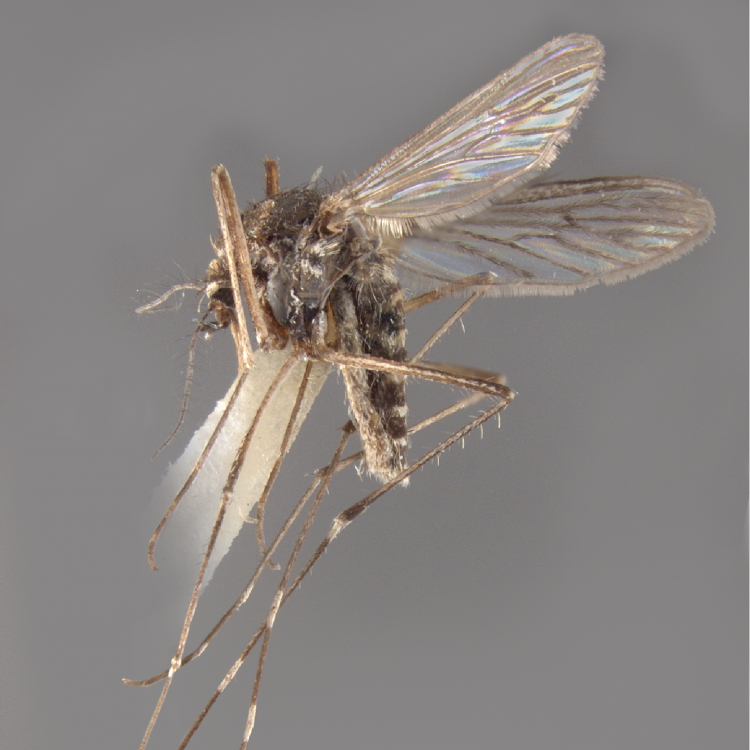
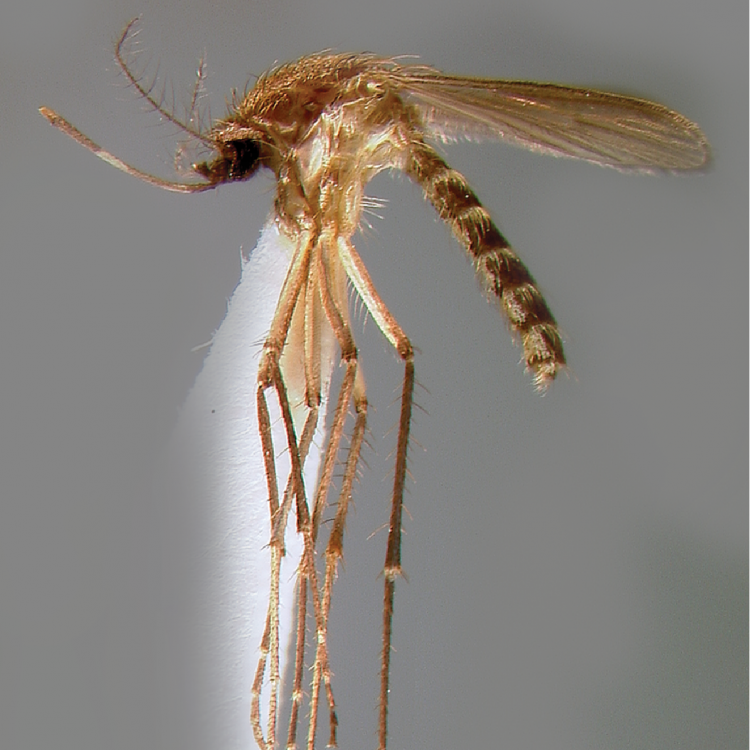
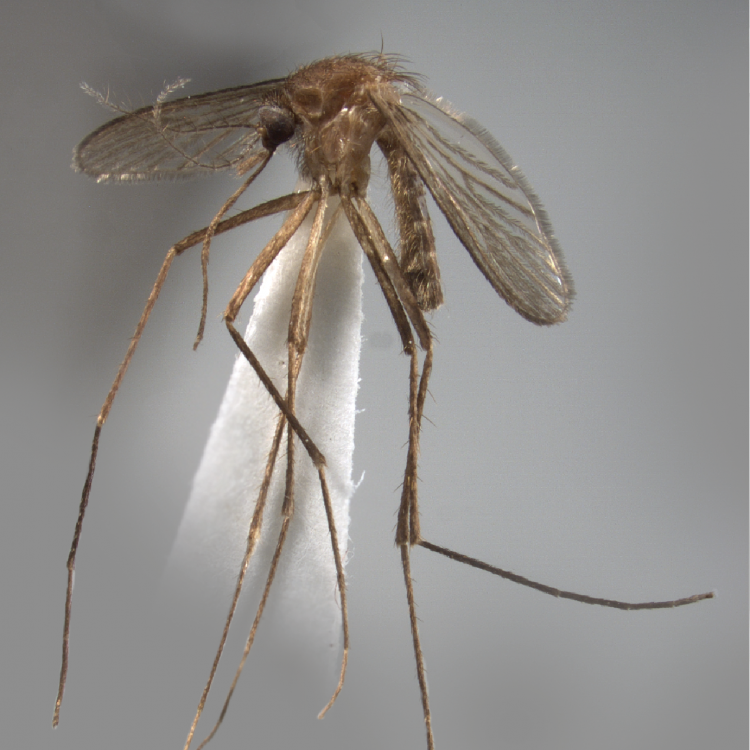
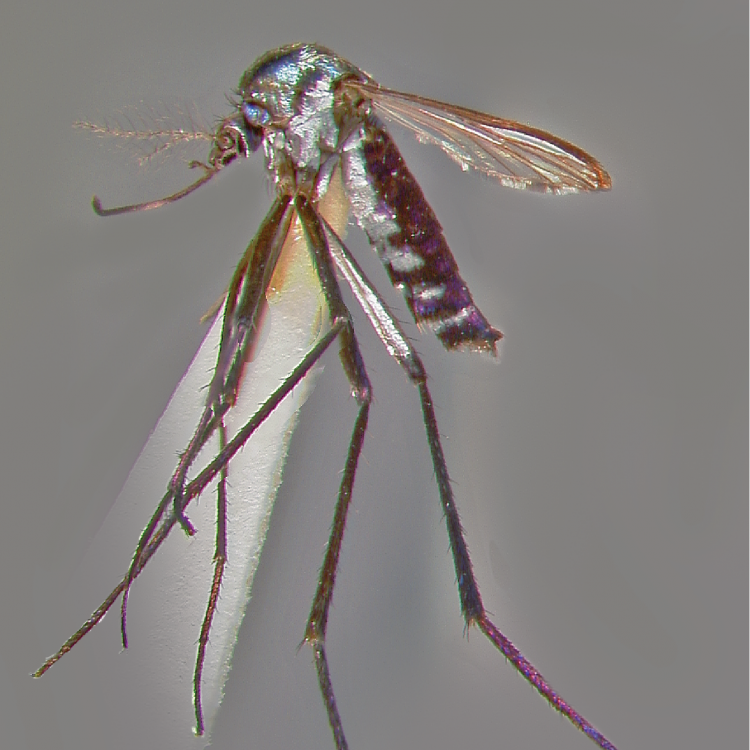
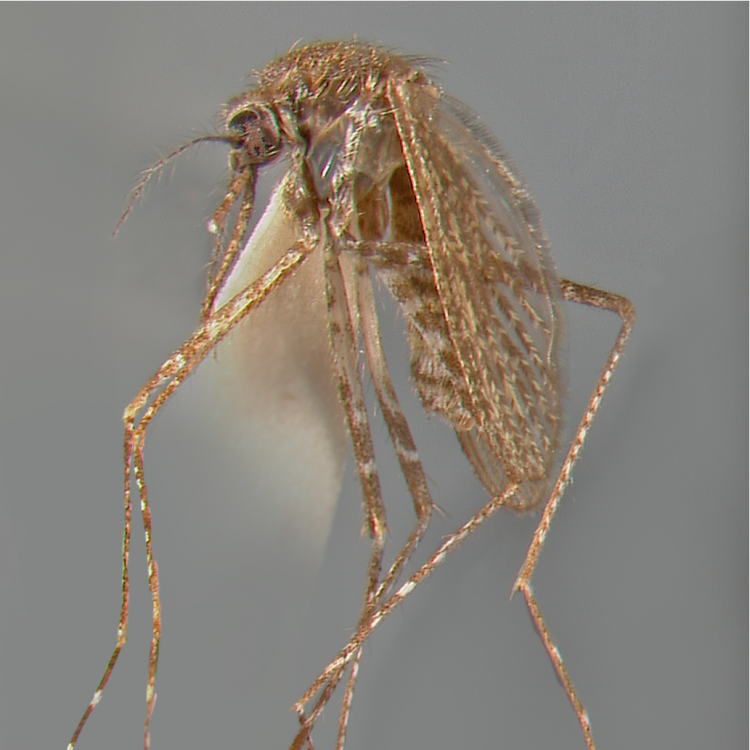
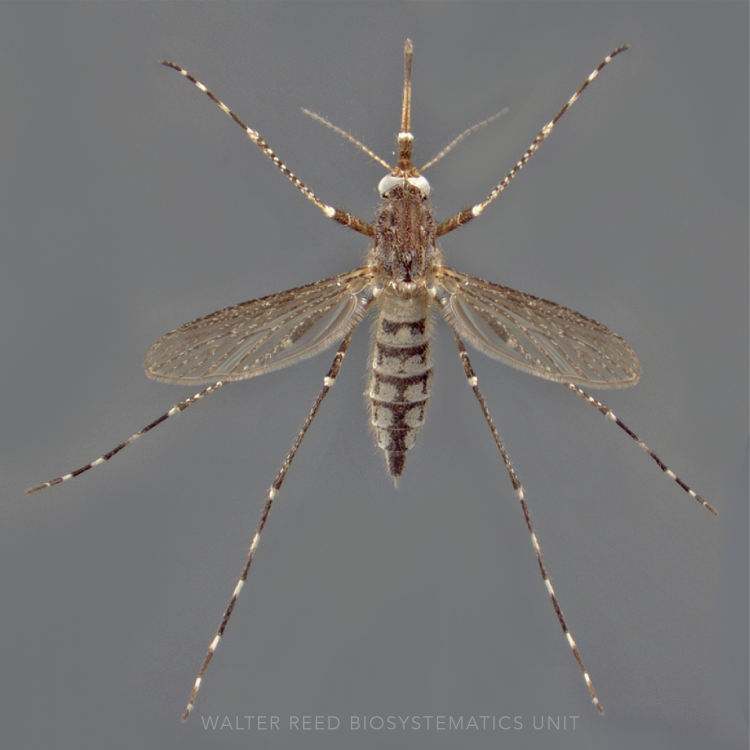
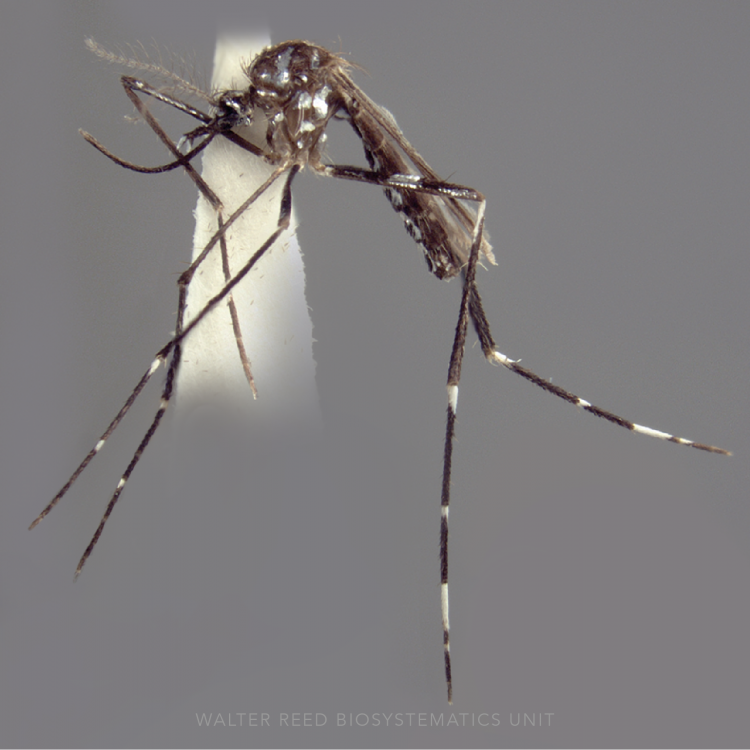
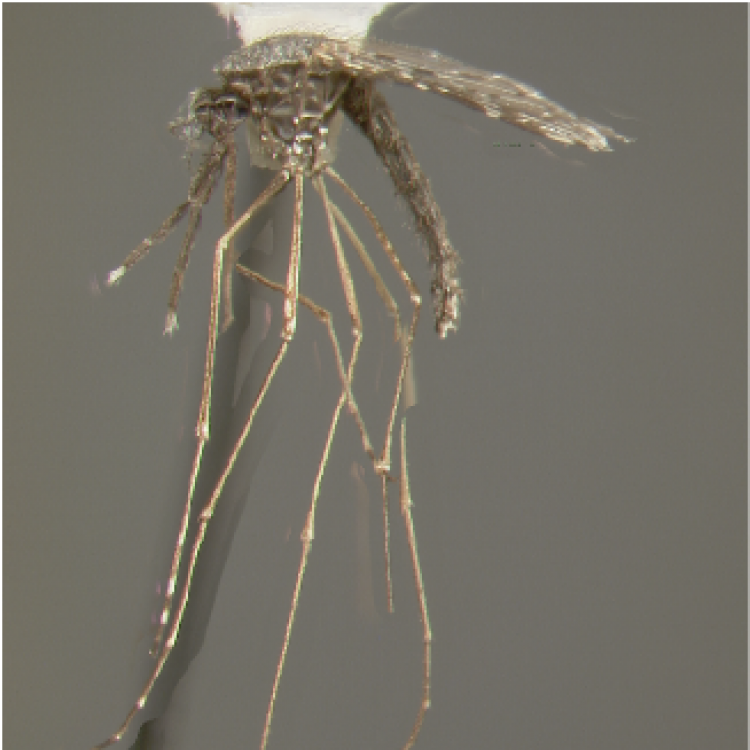
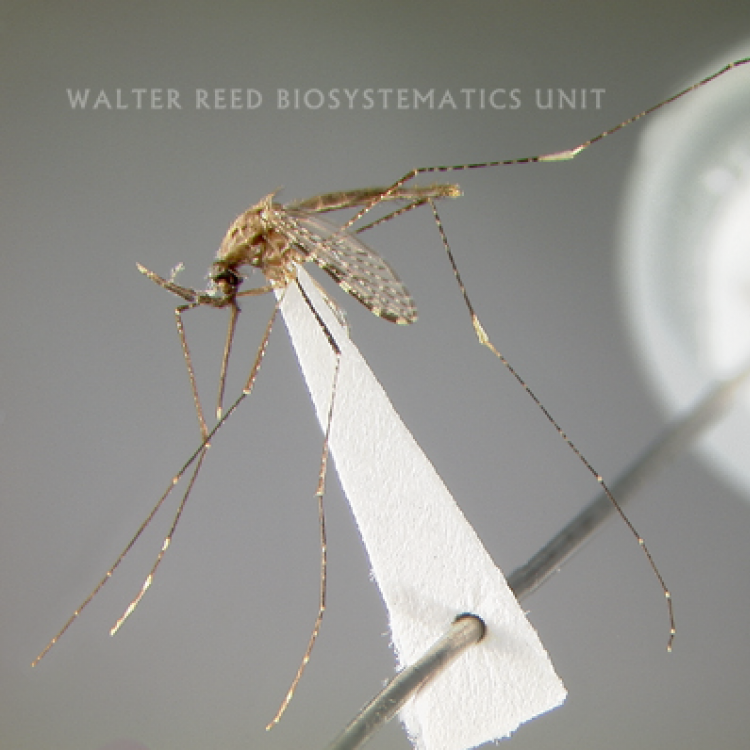
AFROTROPICAL & PALEARCTIC REGIONS
Etymology: n.s. [ash colored (L); poss. ref. to color].
Type locality: Salisbury, Mashonaland [Zimbabwe]
Type depository: Natural History Museum, London, England, United Kingdom (NHMUK)
TAXONOMIC KEYS
None
![]()
WRBU - Genera - Global - Larva
![]()
WRBU - Genera - Afrotropical - Adult
![]()
WRBU - Genera - Afrotropical - Larva
Exemplar DNA sequences
DISTRIBUTION NOTES
Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Eritrea, Eswatini, Ethiopia, FYRO Macedonia, Georgia, Greece, Guinea-Bissau, Israel (and Gaza Strip and West Bank), Italy (includes Sardinia and Sicily), Jordan, Libya, Lithuania, Kenya, Madeira, Malawi, Morocco, Mozambique, Nambia, Niger, Portugal, Republic of the Congo, Republic of South Africa, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Spain, Sudan, Tanzania, Tunisia, Uganda, Ukraine, Yemen, Zimbabwe.
IMPORTANT REFERENCES
Theobald 1901a: 161 (F*)
Evans 1938: 329 (M*, F*, P*, L*, E*)
De Meillon 1947b: 209 (M*, F*, L*, E*)
Mattingly & Knight 1956 (taxonomy)
Gillies & De Meillon 1968: 316 (distribution)
Ramsdale & Snow 2000: 9 (distribution)
Trari et al. 2002: 331 (distribution; Morocco)
Ahmed et al. 2011 (distribution; Saudi Arabia)
Kyalo et al. 2017 (distribution; sub-Saharan Africa)
Robert et al. 2019 (distribution; western Palearctic)
CURRENT SYNONYMS
None
CURRENT SUBSPECIES
None
CITED REFERENCES
Ahmed, A.M., Shaalan, E.A., Aboul-Soud, M.A.M., Tripet, F., & Al-Khedhairy, A.A. (2011). Mosquito vectors survey in the Al-Ahsaa district of eastern Saudi Arabia. Journal of Insect Science, 11, 176.
Aitken, T.H.G. (1953). The anopheline fauna of Sardinia. American Journal of Hygiene Monograph Series, 20, 303–352.
Baeza Cuéllar, M. (1933). Estudio médico de los Culicidos hematófagos. Madrid: Talleres Gráficos Herrera.
Becker, N., Petrić, D., Zgomba, M., Boase, C., Madon, M., Dahl, C., & Kaiser, A. (2010). Mosquitoes and their control (2nd ed.). Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag.
Dahl, C., & White, G.B. (1978). Culicidae. In J. Illies (Ed.), Limnofauna Europaea: A checklist of the animals inhabiting european inland waters, with accounts of their distribution and ecology (except Protozoa) (pp. 390–395). Stuttgart, German: Fischer Verlag.
De Meillon, B. (1947b). The Anophelini of the Ethiopian geographical region. Publications of the South African Institute for Medical Research, 10(49), 1–272.
Evans, A.M. (1938). Mosquitoes of the Ethiopian Region. II. Anophelini adults and early stages. London, England: British Museum (Natural History).
Gillies, M.T., & De Meillon, B. (1968). The Anophelinae of Africa, south of the Sahara (Ethiopian Zoogeographical Region). Publications of the South African Institute for Medical Research, 54, 1–343.
Horsfall, W.R. (1955). Mosquitoes. Their bionomics and relation to disease. New York, NY: Hafner. (Reprinted 1972)
Kyalo, D., Amratia, P., Mundia, C.W., Mbogo, C.M., Coetzee, M., & Snow, R.W. (2017). A geo-coded inventory of anophelines in the Afrotropical Region south of the Sahara: 1898–2016. Wellcome Open Research, 2, 57.
Mattingly, P.F., & Knight, K.L. (1956). The mosquitoes of Arabia. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History, 43(3), 91–141.
Patton, W.S. (1905). The culicid fauna of the Aden Hinterland, their haunts and habits. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society, 16(4), 623–637.
Ramsdale, C.D., & Snow, K. (2000). Distribution of the genus Anopheles in Europe. European Mosquito Bulletin, 7, 1–26.
Ribeiro, H., da Cunha Ramos, H., Pires, C.A., & Capela, R.A. (1980b). Research on the mosquitos of Portugal (Diptera, Culicidae). 4. Two new anopheline records. García de Orta: Série de zoologia, 9(1–2), 129–137.
Robert, V., Günay, F., Le Goff, G., Boussès, P., Sulesco, T., Khalin, A., Medlock, J.M., Kampen, H., Petrić, D., & Schaffner, F. (2019). Distribution chart for Euro-Mediterranean mosquitoes (western Palaearctic region). Journal of the European Mosquito Control Association, 37, 1–28.
Romeo Viamonte, J.M. (1950). Los anofelinos de España y de la zona Española del Protectorado de Marruecos. Su relacioncon la difusion del paludismo. Revista de sanidad e higiene pública (Madrid), 24, 213–295.
Séguy, E. (1924). Les moustiques de l’Afrique Mineure, de l’Égypte et de la Syrie. Encyclopédie Entomologique A, 1, 1–257.
Senevet, G. (1930). Contribution à l’étude des nymphes de culicides. Description de celles de certain anophelines et plus spécialement des espèces européennes et meditérranéennes. Archives de l’Institut Pasteur d’Algérie, 8(3–4), 297–382.
Senevet, G., & Rioux, J. (1960). Anopheles (Myzomyia) hispaniola Theobald 1903 simple sous-espèce de Anopheles (Myzomyia) cinereus Theobald, 1901. Archives de l’Institut Pasteur d’Algérie, 38(4), 530–535.
Sergent, E. (1937). Les oeufs d’Anopheles hispaniola Theo. Archives de l’Institut Pasteur d’Algérie, 15(1), 102–103.
Theobald, F.V. (1901a). A monograph of the Culicidae or mosquitoes (Vol. 1). London, England: British Museum (Natural History).
Theobald, F.V. (1903a). A monograph of the Culicidae of the World (Vol. 3). London, England: British Museum (Natural History).
Theobald, F.V. (1907). A monograph of the Culicidae of the World (Vol. 5). London, England: British Museum (Natural History).
Trari, B., Dakki, M., Himmi, O., & El Agbani, M.A. (2002). Le moustiques (Diptera: Culicidae) du Maroc: Revue bibliographique (1916–2001) et inventaire des espèces. Bulletin de la Société de Pathologie Exotique, 96(4), 329–334.
CITE THIS PAGE
Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit (Year). Anopheles cinereus species page. Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit Website, http://wrbu.si.edu/vectorspecies/mosquitoes/cinereus, accessed on [date (e.g. 03 February 2020) when you last viewed the site].